Inductive Rotor Position Sensor
Inductive rotor position sensor with four inductance coils.
blockType: AcausalElectricPowerSystems.Sensors.InductiveRotorPosition
Path in the library: |
Description
The Inductive Rotor Position Sensor unit uses eddy current loss theory to obtain rotor position data. The sensor consists of four planar coils and a conductive disc that detect the rotor position. The sensor disc has a sinusoidal shape and is made of conductive material. The distance between the four flat coils is equivalent to 90 degrees of one cycle.

Equations
The voltages between the sensor elements are described by the equations:
Where:
-
- cosine voltage,
-
- sinusoidal voltage,
-
and are voltage amplitudes for axes and , reflecting the sensitivity mismatch,
-
and - voltage offsets for axes and ,
-
- number of pole pairs,
-
- rotor angle,
-
- quadrature error,
-
- instability coefficient.
The angle decoding is calculated by the formula:
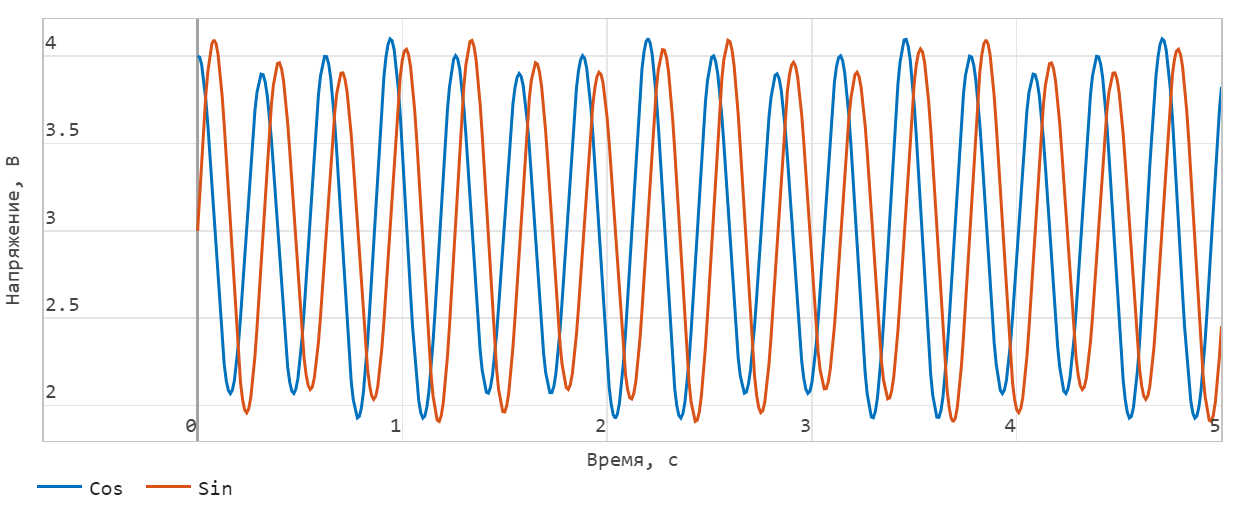
This figure shows the effect of the volatility factor:
Ports
Non-directional
R - encoder shaft
`rotational mechanics
Mechanical rotation port corresponding to the positive connection of the sensor.
C - sensor housing
`rotational mechanics
Rotational mechanical port corresponding to the negative (reference) connection of the sensor.
yp is the positive terminal of the y-axis
electricity
The electrical port associated with the positive terminal of the y-axis.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Output interface to Electrical connections.
yn is the negative terminal of the y-axis
electrical
The electrical port associated with the negative terminal of the y-axis.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Output interface to Electrical connections.
xp is the positive terminal of the x-axis
electrical
The electrical port associated with the positive terminal of the x-axis.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Output interface to Electrical connections.
xn is the negative terminal of the x-axis
electrical
The electrical port associated with the negative terminal of the x-axis.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Output interface to Electrical connections.
Parameters
Number of pole pairs - number of pole pairs
2 (by default) | `scalar `
Number of pole pairs.
X-axis voltage amplitude - x-axis voltage amplitude
2.5 V (by default) | scalar
x-axis voltage amplitude.
Y-axis voltage amplitude - y-axis voltage
2.5 V (by default) | scalar
Y-axis voltage amplitude.
X-axis voltage offset - x-axis voltage offset
0 (By default) | scalar
The potential difference when an electric current flows through a conductor in the absence of an external magnetic field along the x-axis.
Y-axis voltage offset - y-axis voltage offset
0 (by default) | scalar
The potential difference when an electric current flows through a conductor in the absence of an external magnetic field along the y-axis.
Quadrature error - quadrature error
0 (By default) | scalar
The magnitude of the quadrature error. Quadrature switching can reduce offset errors.
Tumbling coefficient - instability coefficient
0 (By default) | scalar
Instability coefficient.
Output interface - interface for decoded information
Electrical connections (by default) | Decoded angular position.
Interface for decoded information, available values:
-
Electrical connections (by default). -
Decoded angular position.
