Морфологические операции
Морфологическая обработка изображений — это область компьютерного зрения, которая занимается устранением недостатков на двоичных изображениях и изображениях в оттенках серого.
В ImageMorphology.jl включен набор нелинейных операций, связанных с формой или морфологией объектов на изображении.
В этой демонстрации мы рассмотрим восемь наиболее распространенных морфологических операций:
-
эрозия;
-
расширение;
-
открытие;
-
закрытие;
-
«верх шляпы»;
-
«дно шляпы»;
-
морфологический градиент;
-
морфологический лапласиан.
Импортируем изображение:
using Images
using ImageMorphology, TestImages
img = Gray.(testimage("morphology_test_512"))
Эрозия
В ходе эрозии к смежным элементам применяется фильтр минимума. По умолчанию используется связность 8 в двухмерном случае, связность 27 в трехмерном случае и т. д. Вы можете указать список измерений, которые нужно включить в связность, например, при region = [1,2] из фильтрации исключается третье измерение.
В приведенном ниже примере показано, как эрозия работает на двоичном изображении с использованием структурирующего элемента 3x3. Структурирующий элемент размера 3x3 проверяет соседние элементы каждого пикселя на исходном изображении и на итоговом изображении изменяет значение этого пикселя на минимальное (minimum) из значений соседних элементов.
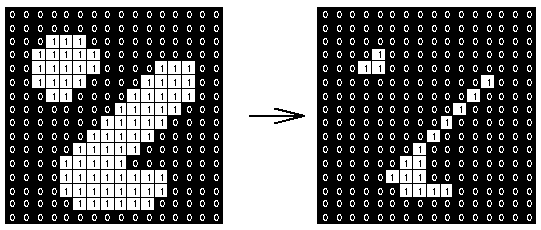
img_erode = @. Gray(img < 0.8); # белые объекты остаются белыми
img_erosion1 = erode(img_erode)
img_erosion2 = erode(erode(img_erode))
mosaicview(img_erode, img_erosion1, img_erosion2; nrow = 1)
Расширение
В ходе расширения к смежным элементам применяется фильтр максимума. По умолчанию используется связность 8 в двухмерном случае, связность 27 в трехмерном случае и т. д. Вы можете указать список измерений, которые нужно включить в связность, например, при region = [1,2] из фильтрации исключается третье измерение.
В приведенном ниже примере показано, как расширение работает на двоичном изображении с использованием структурирующего элемента 3x3. Структурирующий элемент размера 3x3 проверяет соседние элементы каждого пикселя на исходном изображении и на итоговом изображении изменяет значение этого пикселя на минимальное (maximum) из значений соседних элементов.
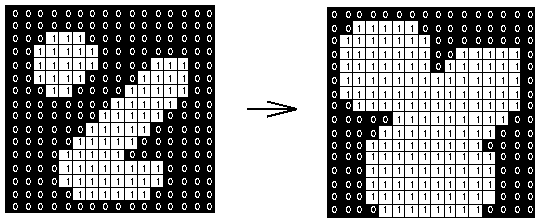
img_dilate = @. Gray(img > 0.9);
img_dilate1 = dilate(img_dilate)
img_dilate2 = dilate(dilate(img_dilate))
mosaicview(img_dilate, img_dilate1, img_dilate2; nrow = 1)
Открытие
Морфологическая операция открытия эквивалентна dilate(erode(img)). В opening(img, [region]) параметр region позволяет указывать измерения, по которым выполняется операция. Открытие позволяет удалять небольшие яркие пятна (то есть «соль») и соединять небольшие темные разрывы.
img_opening = @. Gray(1 * img > 0.5);
img_opening1 = opening(img_opening)
img_opening2 = opening(opening(img_opening))
mosaicview(img_opening, img_opening1, img_opening2; nrow = 1)
Закрытие
Морфологическая операция закрытия эквивалентна erode(dilate(img)). В closing(img, [region]) параметр region позволяет указывать измерения, по которым выполняется операция. Закрытие позволяет удалять небольшие темные пятна (то есть «перец») и соединять небольшие яркие разрывы.
img_closing = @. Gray(1 * img > 0.5);
img_closing1 = closing(img_closing)
img_closing2 = closing(closing(img_closing))
mosaicview(img_closing1, img_closing1, img_closing2; nrow = 1)
«Верх шляпы»
Операция «верх шляпы» определяется как вычитание из изображения его морфологического открытия. В tophat(img, [region]) параметр region позволяет указывать измерения, по которым выполняется операция. Эта операция возвращает яркие пятна изображения, которые меньше структурирующего элемента.
img_tophat = @. Gray(1 * img > 0.2);
img_tophat1 = tophat(img_tophat)
img_tophat2 = tophat(tophat(img_tophat))
mosaicview(img_tophat, img_tophat1, img_tophat2; nrow = 1)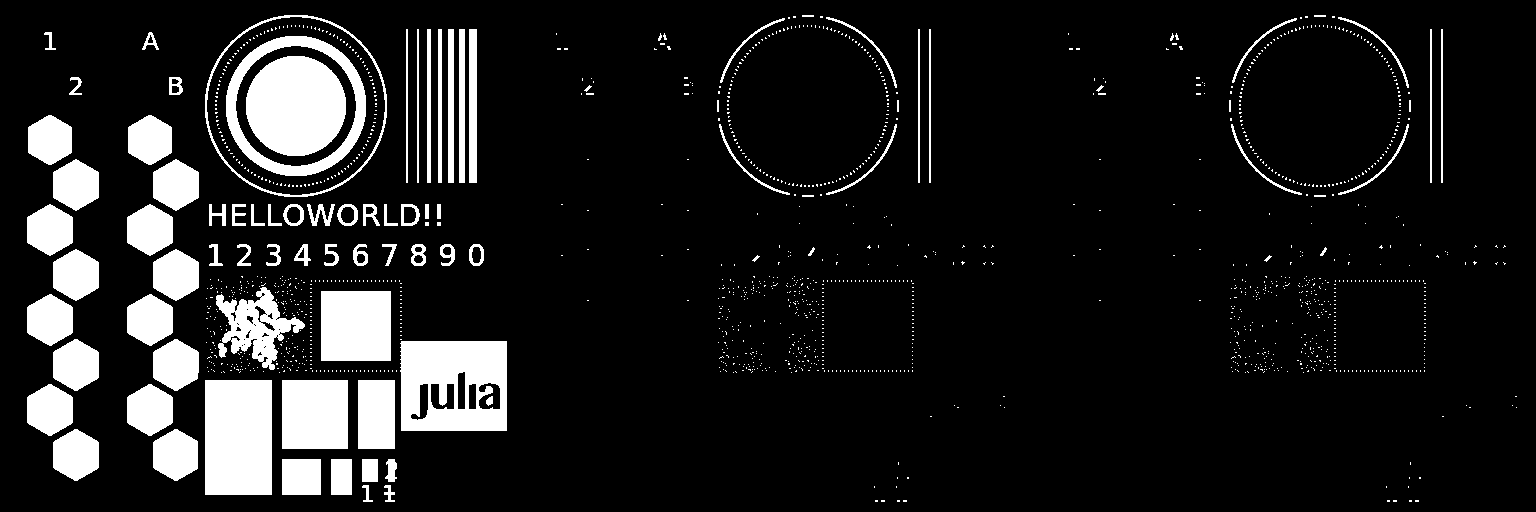
«Дно шляпы»
Морфологическая операция «дно шляпы» определяется как вычитание из морфологического закрытия изображения исходного изображения. В bothat(img, [region]) параметр region позволяет указывать измерения, по которым выполняется операция. Эта операция возвращает темные пятна изображения, которые меньше структурирующего элемента.
img_bothat = @. Gray(1 * img > 0.5);
img_bothat1 = bothat(img_tophat)
img_bothat2 = bothat(bothat(img_tophat))
img_bothat3 = bothat(bothat(bothat(img_tophat)))
mosaicview(img_bothat, img_bothat1, img_bothat2; nrow = 1)
Морфологический градиент
Эта операция возвращает морфологический градиент изображения, то есть разницу его расширения и эрозии. В morphogradient(img, [region]) параметр region позволяет указывать измерения, по которым выполняется операция.
img_gray = @. Gray(0.8 * img > 0.7);
img_morphograd = morphogradient(@. Gray(0.8 * img > 0.4))
mosaicview(img_gray, img_morphograd; nrow = 1)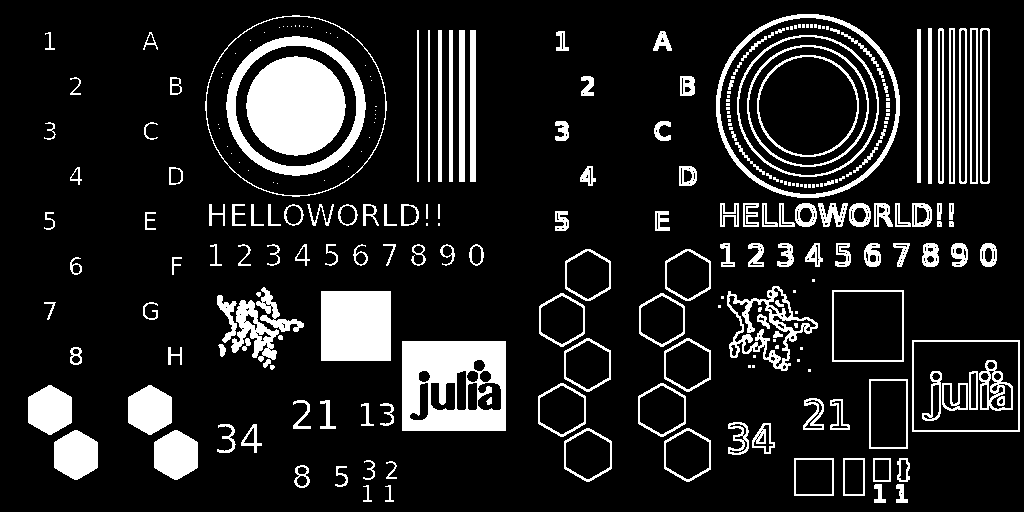
Морфологический лапласиан
Эта операция находит морфологический лапласиан (Morphological Laplacian) изображения, который определяется как арифметическая разность внутреннего и внешнего градиентов. В morpholaplace(img, [region]) параметр region позволяет указывать измерения, по которым выполняется операция.
img_gray = @. Gray(0.8 * Gray.(img) > 0.7);
img_morpholap = morpholaplace(img_gray)
mosaicview(img_gray, img_morpholap; nrow = 1)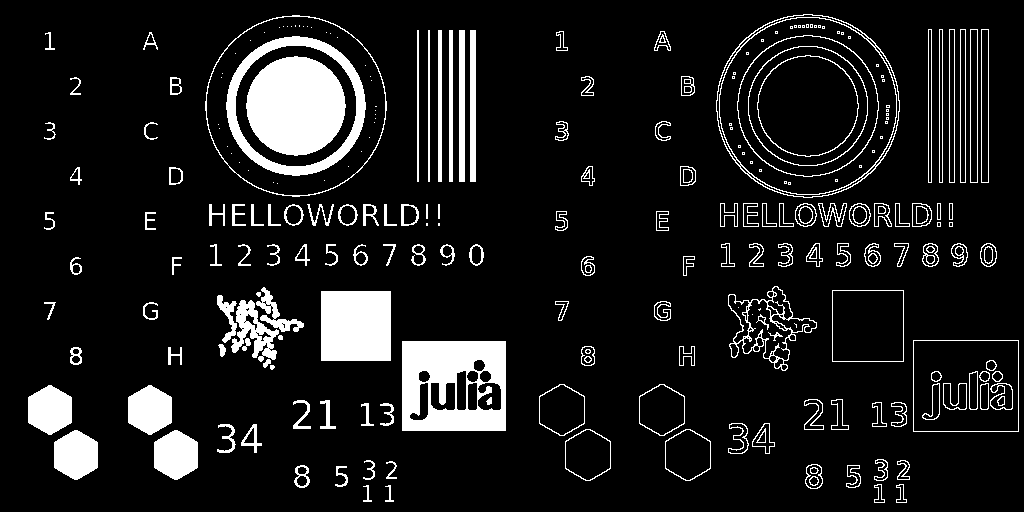
Справочные материалы
-
Основные морфологические операции, разработанные в HIPR доктором Р. Фишером (R. Fisher) с соавторами: ссылка
Эта страница была создана с помощью DemoCards.jl и Literate.jl.