Cumulative Product
Partial product of channel, column, or row elements.
blockType: CumulativeProduct
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Cumulative Product calculates a partial (intermediate) product based on a given input dimension or time (current product).
The input signal can be a vector or a matrix.
Characteristics of input and output signals
Correct input signal
Block Cumulative Product accepts vector or matrix input signals containing real or complex values.
Correct reset signal
The optional reset port Rst accepts scalar values, which can be any data type supported by Engee, including Bool. The quantization frequency of the signal on the Rst port must be the same or less than the quantization frequency of the input signal. The step of calculating the input to the Rst port must be a positive integer multiple of the step of calculating the input signal.
Calculating the product by channels
If the Multiply input along parameter is set to Channels (running product), the block calculates the partial product of the elements in each input channel. The partial product of each input takes into account the partial (intermediate) product of all previous values. In this mode, you must also specify a value for the Input processing parameter. If it is set to Columns as channels (frame based), the block calculates the partial product along each column of the input signal. If the Input processing parameter is set to Elements as channels (sample based), the block calculates the partial product for each entry element in time.
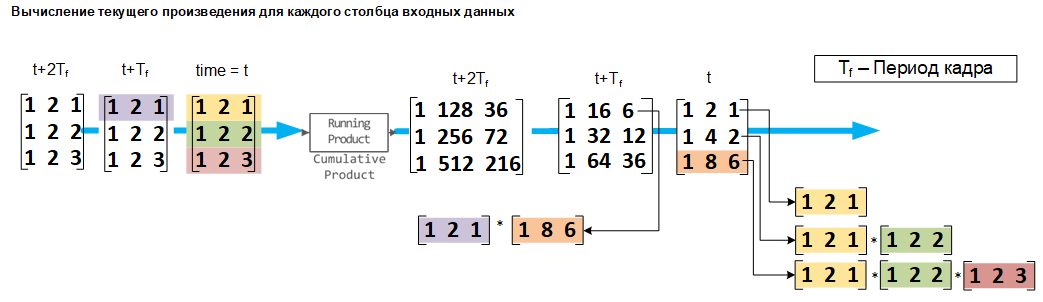
Calculating the current product for each column of the input signal
If the Input processing parameter is set to Columns as channels (frame based) the block processes each input column as an independent channel. As shown in the following figure and in the equation, the output signals have the following characteristics:
-
The first line of the first output is the same as the first line of the first input.
-
The first line of each subsequent output represents the element-wise product of the first line of the current input signal (time ) and the last line of the previous output (time , where — frame period).
-
The output signals have the same size, dimension, and data type as the input signals.
If at the entrance The matrix block on , then the output is is a matrix on , the first line of which consists of the elements
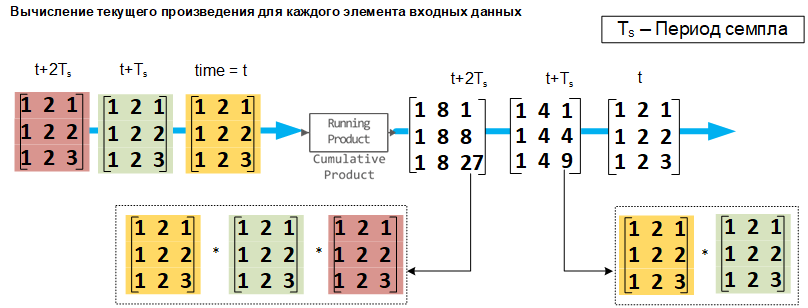
Calculating the partial product for each element of the input signal
If the Input processing parameter is set to Elements as channels (sample based) The block processes each element of the input matrix as an independent channel. As shown in the following figure and in the equation, the output signals have the following characteristics:
-
The first exit is the same as the first entrance.
-
Each subsequent output is a piece-by-piece product of the current input (time ) and the previous output (time , where — calculation step).
-
The output data has the same size, dimension, and data type as the input data.
If at the entrance The matrix block on , then the output is is a matrix on
For convenience, when multiplying by channels, the block processes the input undirected length vector. as a column vector of size on 1. In such cases, the output is an undirected length vector. .
Resetting a partial work
When you calculate the partial product, you can configure the block to reset whenever it detects a reset event on the additional Rst port. The quantization frequency of the signal on the Rst port must be the same or less than the quantization frequency of the input signal. The step of calculating the input to the Rst port must be a positive integer multiple of the step of calculating the input signal. The signal on the Rst port can be any type of data supported by Engee, including Bool.
If a reset event occurs while the block is performing sampling-based processing, the block initializes the current output with the values of the current input. If a reset event occurs when the block performs frame-based processing, the block initializes the first row of the current output with the values in the first row of the current input.
The Reset port parameter specifies a reset event, which can be one of:
-
None— disables the Rst port. -
Rising edge— starts the reset operation when the input signal is Rst:-
Increases from a negative value to a positive or zero value.
-
It increases from zero to a positive value (it is not a continuation of the growth from a negative value to zero).
-
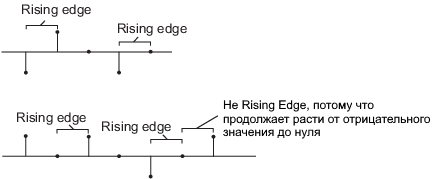
-
Falling edge— starts the reset operation when the input signal is Rst:-
Decreases from a positive value to negative or zero.
-
It decreases from zero to a negative value (it is not a continuation of the decrease from a positive value to zero).
-
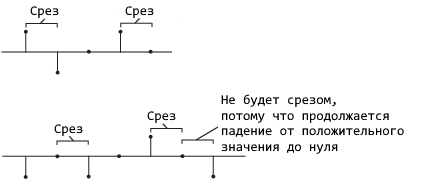
-
Either edge— starts the reset operation if any of the conditions are metRising edgeorFalling edge(as described above). -
Non-zero sample— initiates a reset operation if the input value Rst is not zero.
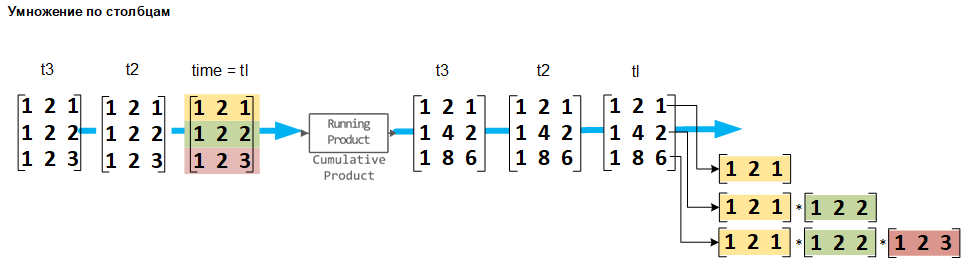
Multiplication by columns
If the Multiply input along parameter is set to Columns, the block calculates the partial product of each input column. In this mode, the current partial product does not depend on the partial products of the previous values.
The output signals have the same size, dimension, and data type as the input signals. The mth output string is the piecemeal product of the first m input strings.
If at the entrance The matrix block on , then the output is is a matrix on , the -th column of which consists of the elements
When multiplying by columns, the block processes the input undirected length vector. as a column vector of size on 1.
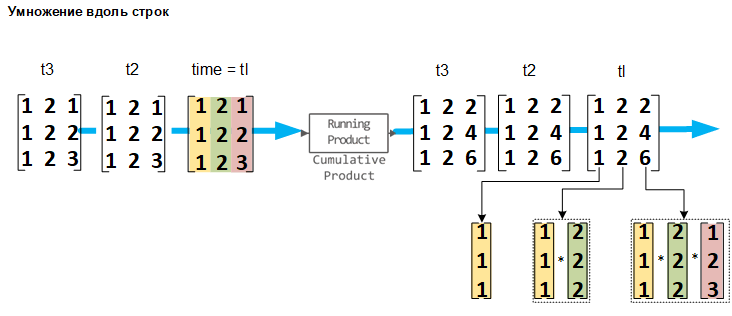
Multiplication along the lines
If the Multiply input along parameter is set to Rows, the block calculates the partial product of the row elements. In this mode, the current partial product does not depend on the partial products of the previous values.
The output signals have the same size, dimension, and data type as the input signals. The th output column is the element-wise product of the first input columns.
If at the entrance The matrix block on , then the output is is a matrix on , -I am a string that consists of the elements
When multiplying by lines, the block processes the input undirected length vector. as a vector-string size 1 on .
Parameters
Multiply input along — dimension of the pass multiplication:q[<br>] Channels (running product) (default) | Columns | Rows
The dimension by which the cumulative product is calculated.
Input processing — input processing method
Columns as channels (frame based) (default) | Elements as channels (sample based)
Defines how the block should process the input when calculating the current product through the input channels.
You can set this parameter to one of the following options:
Columns as channels (frame based) — When you select this option, the block treats each input column as a separate channel.
Elements as channels (sample based) — When you select this option, the block treats each entry element as a separate channel.
For more information, see Signal processing by frames and counts.
Dependencies
This parameter is used if the Multiply input along parameter is set to Channels (running product).
Reset port — pass reset event:q[<br>] None (by default) | Rising edge | Falling edge | Either edge | Non-zero sample
Defines a reset event that causes the block to reset the product across channels. The quantization frequency of the signal on the Rst port must be the same or less than the quantization frequency of the input signal. The step of calculating the input to the Rst port must be a positive integer multiple of the step of calculating the input signal.
Dependencies
This parameter is only available if the Multiply input along parameter is set to Channels (running product).
