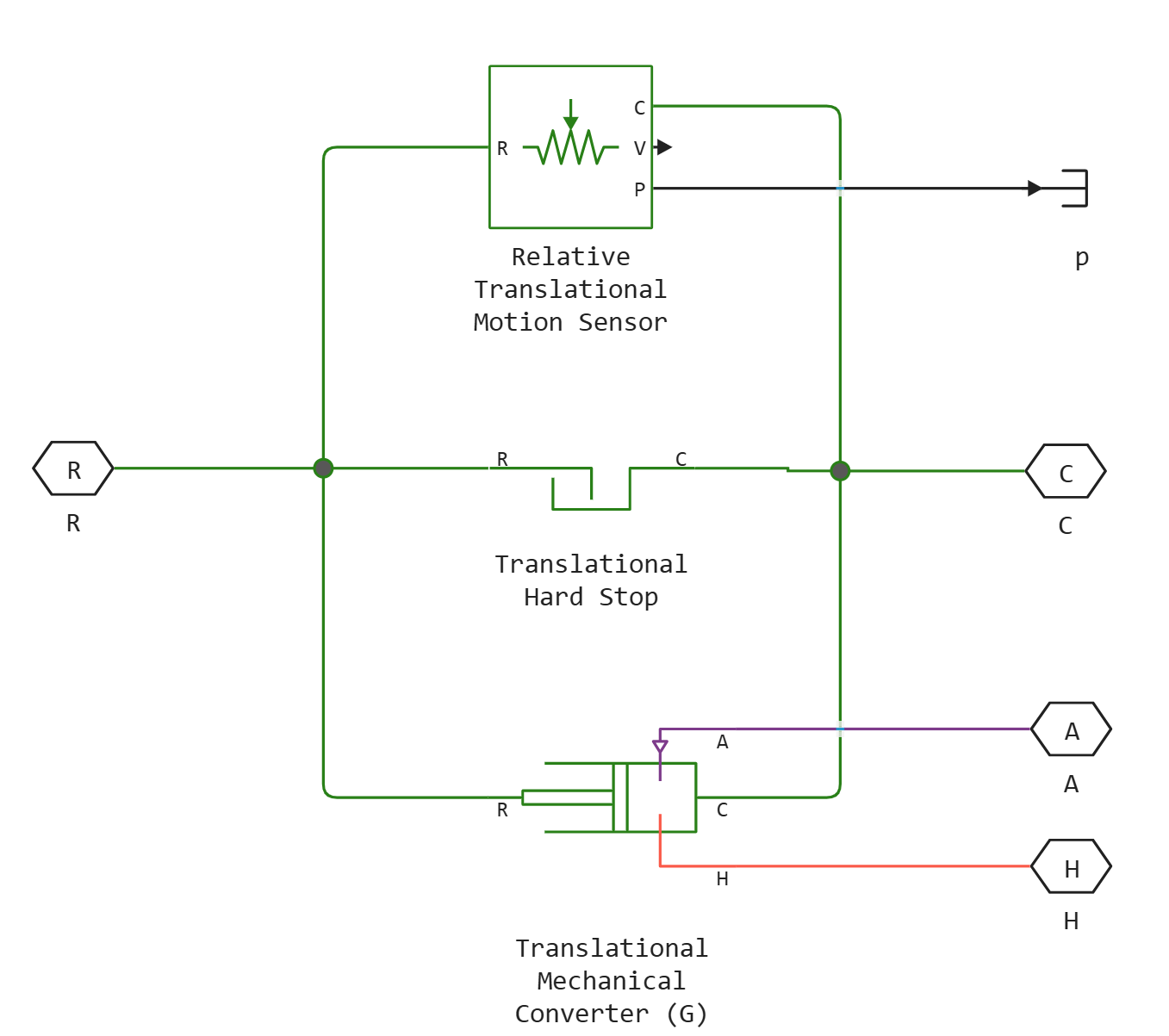
Single-Acting Actuator (G)
One-way linear actuator in the gas network.
blockType: EngeeFluids.Gas.Actuators.SingleActing
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Single-Acting Actuator (G) simulates a linear actuator, the piston of which is controlled by a gas chamber. The drive creates a reciprocating motion of the piston, the force of which is determined by the overpressure of the gas chamber.
The figure shows the main drive components for different parameter values. Mechanical orientation. Port A is the entrance to the gas chamber. Port R is associated with the piston, and port C is associated with the drive housing. The H port provides thermal interaction between the gas chamber and the environment.
Moving
The movement of the piston is determined by the displacement of port R relative to port C. The direction of movement of the piston is set by the parameter Mechanical orientation. The movement of the piston is neutral (equal to 0), when the volume of the camera is Dead volume.
The rigid stop model
The movement of the piston is limited by a pair of rigid stops located within the stroke of the piston. The block uses the same model of rigid stops as the block Translational Hard Stop, and takes into account the damping and stiffness coefficients at both ends of the piston stroke.
If the movement of the piston is positive, then the lower rigid stop is on , and the upper hard focus is on . If the movement of the piston is negative, then the lower rigid stop is at the point , and the top one is at the point .
Ports
Conserving
#
A
—
gas inlet or outlet
gas
Details
The port corresponding to the gas inlet or outlet of the gas chamber.
| Program usage name |
|
#
R
—
actuator piston
translational mechanics
Details
A mechanical progressive port corresponding to the actuator piston.
| Program usage name |
|
#
H
—
heat port
heat
Details
A port related to the thermal conductivity of a gas.
| Program usage name |
|
#
C
—
drive housing
translational mechanics
Details
Mechanical progressive port corresponding to the actuator housing.
| Program usage name |
|
Output
#
p
—
piston position
scalar
Details
Piston position in m.
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
No |
Parameters
Actuator
#
Mechanical orientation —
the direction of movement of the piston
Pressure at A causes positive displacement of R relative to C | Pressure at A causes negative displacement of R relative to C
Details
Determines the direction of displacement of the piston. Options to choose from:
-
Pressure at A causes positive displacement of R relative to C— the movement of the piston is positive if the volume of gas in port A increases. This corresponds to the movement of the rod out of the cylinder. -
Pressure at A causes negative displacement of R relative to C— piston displacement is negative if the volume of gas in port A increases. This corresponds to the movement of the rod inside the cylinder.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Piston cross-sectional area —
the cross-sectional area of the piston rod
m^2 | um^2 | mm^2 | cm^2 | km^2 | in^2 | ft^2 | yd^2 | mi^2 | ha | ac
Details
The cross-sectional area of the piston rod.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Piston stroke —
stroke of the piston
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The maximum possible displacement of the piston.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Dead volume —
the volume of gas in the chamber at which the piston movement is 0
m^3 | um^3 | mm^3 | cm^3 | km^3 | ml | l | gal | igal | in^3 | ft^3 | yd^3 | mi^3
Details
The volume of gas at the value of the piston displacement 0. This volume of gas corresponds to the position of the piston, at which it is located at the top in relation to the end cap of the actuator.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Cross-sectional area at port A —
port cross-sectional area A
m^2 | um^2 | mm^2 | cm^2 | km^2 | in^2 | ft^2 | yd^2 | mi^2 | ha | ac
Details
The cross-sectional area of the hole is A.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Environment pressure specification —
the method of setting the ambient pressure
Atmospheric pressure | Specified pressure
Details
The method of setting the ambient pressure. Option Atmospheric pressure sets the ambient pressure equal to 0.101325 MPa.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Environment pressure —
ambient pressure
Pa | uPa | hPa | kPa | MPa | GPa | kgf/m^2 | kgf/cm^2 | kgf/mm^2 | mbar | bar | kbar | atm | ksi | psi | mmHg | inHg
Details
User-defined ambient pressure.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Environment pressure specification meaning Specified pressure.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Hard Stop
#
Hard stop model —
choosing a rigid stop model
Stiffness and damping applied smoothly through transition region, damped rebound | Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, undamped rebound | Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, damped rebound | Based on coefficient of restitution
Details
Selecting a model for the force acting on the piston when it is in extreme positions. For more information, see the section Translational Hard Stop.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Hard stop stiffness coefficient —
stiffness coefficient
N/m | mN/m | kN/m | MN/m | GN/m | kgf/m | lbf/ft | lbf/in
Details
The coefficient of piston stiffness.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Hard stop damping coefficient —
damping coefficient
N*s/m | kgf*s/m | lbf*s/ft | lbf*s/in
Details
Piston damping coefficient.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Transition region —
the range of action of the rigid stop model
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The area of operation of the rigid stop. Outside of this range for the extreme positions of the piston Hard stop model it is not applied, and the additional force from the stop side does not act on the piston.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model meaning Stiffness and damping applied smoothly through transition region, damped rebound.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Coefficient of restitution — the ratio of the final and initial relative velocity between the rod and the stop after a collision
Details
The ratio of the final and initial relative velocity between the rod and the stop after the rod rebounds.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model meaning Based on coefficient of restitution.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Static contact speed threshold —
threshold value of the relative velocity between the rod and the stop before the collision
m/s | mm/s | cm/s | km/s | m/hr | km/hr | in/s | ft/s | mi/s | ft/min | mi/hr | kn
Details
The threshold value of the relative velocity between the rod and the stop before the collision. If the rod hits the housing at a speed lower than the value of this parameter, they remain in contact. Otherwise, the rod bounces off. To avoid simulating static contact between the rod and the housing, set this parameter to 0.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model meaning Based on coefficient of restitution.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Static contact release force threshold —
the threshold value of the force required to transition from the contact state to the free state
N | nN | uN | mN | kN | MN | GN | dyn | lbf | kgf
Details
The minimum force required to remove the rod from the static contact state.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model meaning Based on coefficient of restitution.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Initial Conditions
#
Initial piston displacement —
the initial position of the piston
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The position of the piston at the beginning of the simulation.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial gas pressure —
initial gas pressure
Pa | uPa | hPa | kPa | MPa | GPa | kgf/m^2 | kgf/cm^2 | kgf/mm^2 | mbar | bar | kbar | atm | ksi | psi | mmHg | inHg
Details
The initial gas pressure in the drive.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial gas temperature —
initial gas temperature
K | degC | degF | degR | deltaK | deltadegC | deltadegF | deltadegR
Details
The initial temperature of the gas in the drive.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |