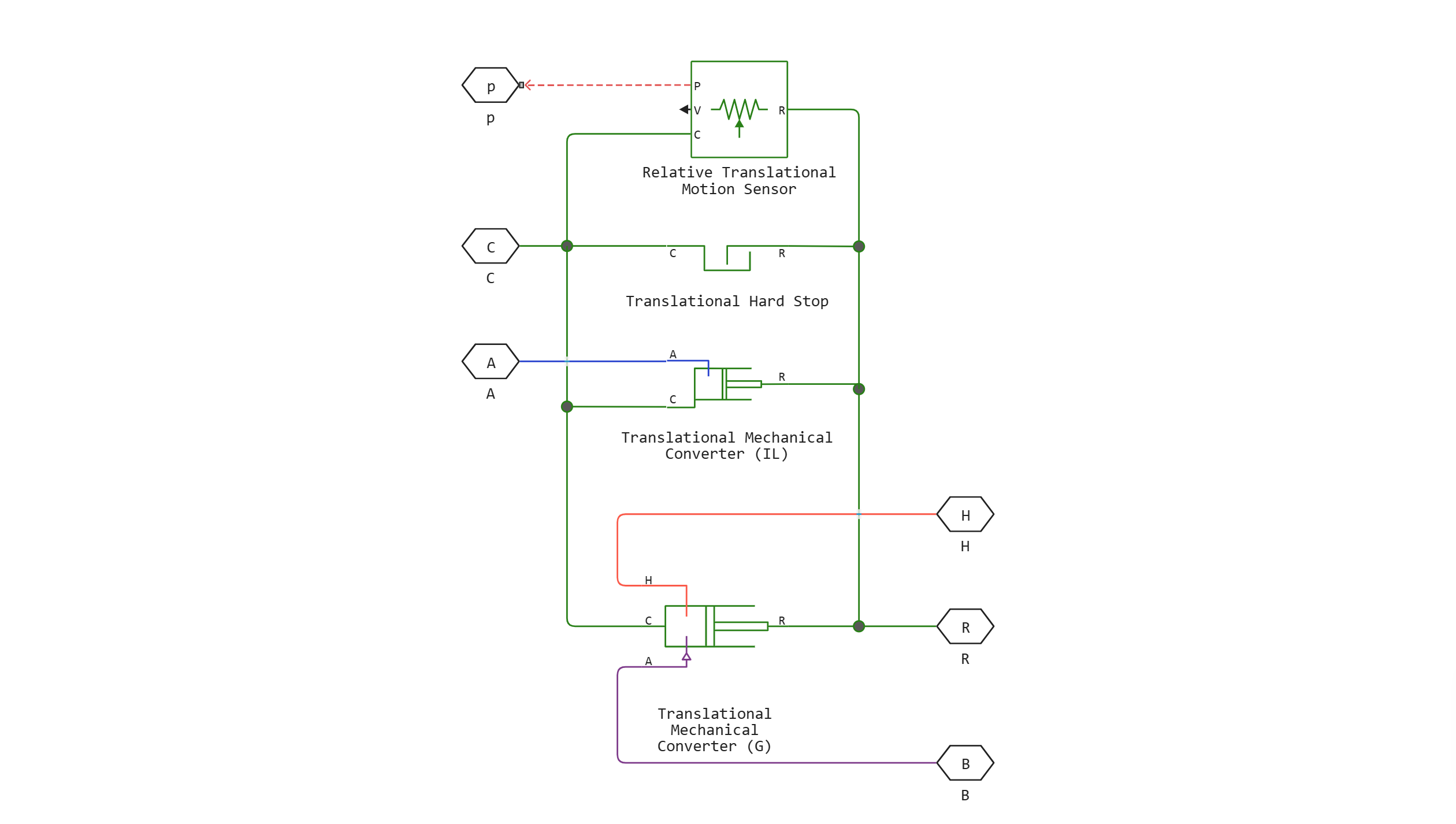
Double-Acting Actuator (G-IL)
Linear actuator with chambers for isothermal liquid and gas.
blockType: EngeeFluids.IsothermalLiquid.Actuators.TranslationalDoubleActingWithGasChamber
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Double-Acting Actuator (G-IL) It consists of a chamber for an isothermal liquid and a chamber for a gas, separated by a piston plate. The piston is actuated by the pressure difference between the chambers. The movement of the piston in a position close to full extension or full retraction is limited to one of the four stop patterns.
Port A is designed for isothermal liquid intake, and port B is designed for gas intake. The heat transfer elements between the gas chamber and the environment are connected to the H port. Port C is used for mechanical translational movement of the drive housing. The R port is connected to the drive piston. The position of the piston is determined by the port p.
Offset
The displacement of the piston is measured as the position in port R relative to port C. Parameter Mechanical orientation determines the direction of displacement of the piston. The displacement of the piston is zero when the volume of the chamber is equal to the dead volume of the chamber. When you receive an offset as an input signal, make sure that the derivative of the position is equal to the piston velocity.
The stop model
To avoid mechanical damage to the piston when it is fully extended or retracted, the actuator usually exhibits non-linear behavior when the piston approaches these limits. Block Double-Acting Actuator (G-IL) simulates this behavior using four stop models that simulate the ductility of the material through a spring-damping system. Stop models:
-
Stiffness and damping applied smoothly through transition region, damped rebound; -
Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, undamped rebound; -
Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, damped rebound; -
Based on coefficient of restitution.
The thrust force is modeled when the piston is at the upper or lower limit. The boundary region is located in the transition region (parameter Transition region) stroke of the piston (parameter Piston stroke) or the initial displacement of the piston. Outside of this area .
For more information about these settings, see the block page. Translational Hard Stop.
Ports
Output
#
interface_displacement_out
—
description missing
Details
Description missing
| Data types |
Description missing |
| Complex numbers support |
Description missing |
Conserving
#
H
—
heat flow
heat
Details
A non-directional port associated with the transfer of heat to or from the gas chamber.
| Program usage name |
|
#
C
—
drive housing
translational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the case.
| Program usage name |
|
#
A
—
Entrance to chamber A
Isothermal liquid
Details
A non-directional port for isothermal liquid connected to the entrance to chamber A.
| Program usage name |
|
#
R
—
drive piston rod
translational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the piston rod.
| Program usage name |
|
#
B
—
Entrance to chamber B
gas
Details
A non-directional gas port connected to the entrance to chamber B.
| Program usage name |
|
Parameters
Configuration
#
Mechanical orientation —
the direction of displacement of the piston
Pressure at A causes positive displacement of R relative to C | Pressure at A causes negative displacement of R relative to C
Details
The direction of displacement of the piston. Pressure at A causes positive displacement of R relative to C corresponds to the piston extension when the pressure difference between chambers A and B is positive. Pressure at A causes negative displacement of R relative to C corresponds to the retraction of the piston when the pressure difference between chambers A and B is positive.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Piston stroke —
maximum stroke of the piston
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The maximum stroke of the piston.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial piston displacement from chamber A cap —
the position of the piston at the beginning of the simulation
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The position of the piston at the beginning of the simulation.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Hard stop model —
choosing a stop model
Stiffness and damping applied smoothly through transition region, damped rebound | Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, undamped rebound | Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, damped rebound | Based on coefficient of restitution
Details
Selecting the model of the force acting on the piston when fully extended or fully retracted. For more information, see the block page Translational Hard Stop.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Hard-stop stiffness coefficient —
stiffness coefficient
N/m | mN/m | kN/m | MN/m | GN/m | kgf/m | lbf/ft | lbf/in
Details
The coefficient of piston stiffness.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model one of the following values:
-
Stiffness and damping applied smoothly through transition region, damped rebound; -
Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, undamped rebound; -
Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, damped rebound.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Hard-stop damping coefficient —
damping coefficient
N*s/m | kgf*s/m | lbf*s/ft | lbf*s/in
Details
Piston damping coefficient.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model one of the following values:
-
Stiffness and damping applied smoothly through transition region, damped rebound; -
Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, undamped rebound; -
Full stiffness and damping applied at bounds, damped rebound.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Transition region —
the field of application of the thrust force model
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The range of application of the force model in the stop. Outside of this range of maximum extension and maximum retraction of the piston, the parameter Hard stop model it is not applied, and the piston is not affected by additional force.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model meaning Stiffness and damping applied smoothly through transition region, damped rebound.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Coefficient of restitution — the ratio of the final and initial relative velocity between the slider and the stop after the collision
Details
The ratio of the final and initial relative velocity between the slider and the stop after the slider rebounds.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model meaning Based on coefficient of restitution.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Static contact speed threshold —
the threshold value of the relative velocity between the slider and the stop before the collision
m/s | mm/s | cm/s | km/s | m/hr | km/hr | in/s | ft/s | mi/s | ft/min | mi/hr | kn
Details
The threshold value of the relative velocity between the slider and the stop before the collision. When the slider hits the housing at a speed lower than the parameter value Static contact speed threshold they stay in contact. Otherwise, the slider will bounce. To avoid simulating static contact between the slider and the housing, set this parameter to 0.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model meaning Based on coefficient of restitution.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Static contact release force threshold —
the threshold value of the force required to switch from contact mode to free mode
N | nN | uN | mN | kN | MN | GN | dyn | lbf | kgf
Details
The minimum force required to exit the slider from static contact mode.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Hard stop model meaning Based on coefficient of restitution.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Isothermal Liquid Side
#
Piston cross-sectional area in chamber A —
the cross-sectional area of the piston rod
m^2 | um^2 | mm^2 | cm^2 | km^2 | in^2 | ft^2 | yd^2 | mi^2 | ha | ac
Details
The cross-sectional area of the piston rod in chamber A.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Dead volume in chamber A —
the volume of the chamber when the piston is fully retracted
m^3 | um^3 | mm^3 | cm^3 | km^3 | ml | l | gal | igal | in^3 | ft^3 | yd^3 | mi^3
Details
An open volume in the liquid chamber when the piston is fully retracted.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Fluid dynamic compressibility — should I simulate the compressibility of a liquid
Details
Whether to simulate a change in the density of a liquid due to the compressibility of a liquid. If next to the parameter Fluid dynamic compressibility If the box is checked, then the changes caused by the mass flow in the unit are calculated in addition to the density changes caused by the pressure change. In the library Isothermal Liquid all blocks calculate density as a function of pressure.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Initial liquid pressure in chamber A —
initial fluid pressure for compressible fluids
Pa | uPa | hPa | kPa | MPa | GPa | kgf/m^2 | kgf/cm^2 | kgf/mm^2 | mbar | bar | kbar | atm | ksi | psi | mmHg | inHg
Details
The initial fluid pressure for compressible fluids.
Dependencies
To use this option, check the box next to the option Fluid dynamic compressibility.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Environment pressure specification —
reference ambient pressure
Atmospheric pressure | Specified pressure
Details
Reference ambient pressure. Meaning Atmospheric pressure sets the ambient pressure equal to 0.101325 MPa.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Environment pressure —
user-defined ambient pressure
Pa | uPa | hPa | kPa | MPa | GPa | kgf/m^2 | kgf/cm^2 | kgf/mm^2 | mbar | bar | kbar | atm | ksi | psi | mmHg | inHg
Details
User-defined ambient pressure.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Environment pressure specification meaning Specified pressure.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Gas Side
#
Piston cross-sectional area in chamber B —
the cross-sectional area of the piston rod
m^2 | um^2 | mm^2 | cm^2 | km^2 | in^2 | ft^2 | yd^2 | mi^2 | ha | ac
Details
The cross-sectional area of the piston rod in chamber B.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Cross-sectional area at port B —
port cross-sectional area
m^2 | um^2 | mm^2 | cm^2 | km^2 | in^2 | ft^2 | yd^2 | mi^2 | ha | ac
Details
The cross-sectional area of the port B.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Dead volume in chamber B —
the volume of the chamber when the piston is fully retracted
m^3 | um^3 | mm^3 | cm^3 | km^3 | ml | l | gal | igal | in^3 | ft^3 | yd^3 | mi^3
Details
An open volume in the gas chamber when the piston is fully retracted.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial gas pressure in chamber B —
initial gas pressure in the chamber
Pa | uPa | hPa | kPa | MPa | GPa | kgf/m^2 | kgf/cm^2 | kgf/mm^2 | mbar | bar | kbar | atm | ksi | psi | mmHg | inHg
Details
The initial pressure of the gas in the chamber.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial gas temperature in chamber B —
initial temperature in the gas chamber
K | degC | degF | degR | deltaK | deltadegC | deltadegF | deltadegR
Details
The initial temperature in the gas chamber.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Environment pressure specification —
reference ambient pressure
Atmospheric pressure | Specified pressure
Details
Reference ambient pressure. Meaning Atmospheric pressure sets the ambient pressure equal to 0.101325 MPa.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Environment pressure —
user-defined ambient pressure
Pa | uPa | hPa | kPa | MPa | GPa | kgf/m^2 | kgf/cm^2 | kgf/mm^2 | mbar | bar | kbar | atm | ksi | psi | mmHg | inHg
Details
User-defined ambient pressure.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Environment pressure specification meaning Specified pressure.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |