Code generation based on custom templates
Engee allows you to generate code using Templates.
Templates are text files with the extension .cgt (Codegen Template), which uses a special syntax for automatically adding data and creating code. Code generation using templates is supported for C and Chisel languages.
There are two types of user templates — for blocks and for functions. main:
-
Templates for blocks allow you to generate code for individual components of the model (functions or modules) that implement specific logic. They ensure the use of code at the level of individual operations, which is preferable in the development of complex models with a large number of blocks.
-
Templates for the function
mainThey focus on the overall execution structure of the model, including initialization, step-by-step processing, and shutdown. This approach is preferable for the sequence of operations in multitasking models.
The choice between these approaches depends on the level of detail and scale: block templates are used to fine—tune the logic, and a template is used to control the entire model. main.
Generating code for blocks
Custom templates can be used to generate code for Engee model blocks. After adding the template to the path, click the Generate Code button ![]() /
/![]() . In the results folder you will find the generated file in the selected language.
. In the results folder you will find the generated file in the selected language.
If the template is located in a folder (any directory except /user), then it should be added to path. To do this, select the folder with the template, right-click on it and add it to the path. After adding, the folder will be displayed with a blue icon. |
| The code generator analyzes all the templates added to the path. If multiple templates are found, the code generator will use the last added template. |
For the generation to work, the template file for the blocks must have the extension .cgt.
|
Syntax of block templates
The syntax of the templates is based on comments. They can be single-line, starting with //!, or multi-line, enclosed in /*! */. You can write any correct code in Julia language inside the comments. Comments are used so that the template code is executed, but not included in the final generated file.
The uncommented parts of the template are written directly to the file. There should be a language code in these areas. Si or Chisel. Inside such a code, you can insert a small Julia code using the syntax $(). Inside the brackets, you can specify any working code for Julia that will be executed, and its result will replace this construction in the final file. If the expression is clear and unambiguous, then you can use $ without brackets, but the option with brackets is always recommended.
Syntax $() It uses special functions only for working with inputs, outputs, and states, but not for block parameters (except for the function state_addr).
|
Special functions supported for code generation inside $() presented below:
list of supported functions
Category |
Function |
Description |
Functions for inputs |
|
Returns the input port of the block |
|
Returns the data type of the input port |
|
|
Returns the dimension of the input port |
|
|
Returns the number of dimensions of the input port |
|
|
Returns the length ( |
|
|
Returns the complexity of the input port |
|
|
Returns the step of calculating the input port |
|
|
Returns the number of input ports in the block |
|
Functions for outputs |
|
Returns the output port of the block |
|
Returns the data type of the output port |
|
|
Returns the dimension of the output port |
|
|
Returns the number of dimensions of the output port |
|
|
Returns the length ( |
|
|
Returns the complexity of the output port |
|
|
Returns the step of calculating the output port |
|
|
Returns the number of output ports of the block |
|
Functions for states |
|
Returns the block status |
|
Returns the state data type |
|
|
Returns the dimension of the state |
|
|
Returns the number of dimensions of the state |
|
|
Returns the length ( |
|
|
Returns the complexity of the state |
|
|
Returns the number of block states |
|
Functions for working with block paths |
|
Returns the block name |
Functions for working with Chisel templates |
|
Returns a string with the Chisel signal type. For example, if |
Functions for working with the scheduler |
|
Returns the block calculation step (you can use |
|
Returns the number of sampling frequencies in the model |
|
|
Returns the base sampling rate of the model |
|
|
Returns an array of ratios of the base and other sampling frequencies, for example, |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns |
Code generation in templates is carried out using special meta-code macros that determine which parts of the final code the necessary fragments will be added (switch the output of the code generator to the appropriate buffer). These macros are used to structure the code and control its placement. The list of supported macros includes:
list of metacode macros
| Category | The macro | Description |
|---|---|---|
Template Buffers |
|
Used to declare local variables of a function |
|
Adds the code to the end of the generated file. It is usually used to complete work or add comments. |
|
|
Contains the code that is executed during initialization of the model. The buffer is emitted in the function |
|
|
It is used to generate a description of the block’s input ports. The buffer is included in the corresponding section of the model code. |
|
|
Contains the code for describing the block’s output ports. Generated in the section related to output processing. |
|
|
Adds the code to the beginning of the file, before the section |
|
|
It is used to describe block states, including their sizes, data types, and initialization. Generated in the model status section. |
|
|
The main buffer to which the code is written by default, unless another macro is specified. This code is executed at each step of the simulation. |
|
|
Contains the code executed when the model is shut down. The buffer is emitted in the function |
|
|
It is used to declare global variables and data types. The code will be inserted in model.h after the directives |
A global data structure is used in templates to work with block parameters. param. This is a named Julia tuple that contains a description of all block parameters, including signal-like parameters (for example, the value of the Gain parameter in the Gain block) and all other block characteristics.
To examine the contents of the structure param in the template , you can add a comment with the expression $param. During code generation, this expression will be replaced with a full description of the block’s parameters and characteristics. After that, you can refer to the individual fields of the structure. param.
Example:
/* !
* BlockType = :SomeBlockINeedToExplore
* TargetLang = :C
*/
/* Let's see the block description:
$param
*/After code generation, comment with $param It will be replaced by a description of the block parameters, which allows you to study its structure and properties.
Sample template for C
Let’s look at an example template for the following model:
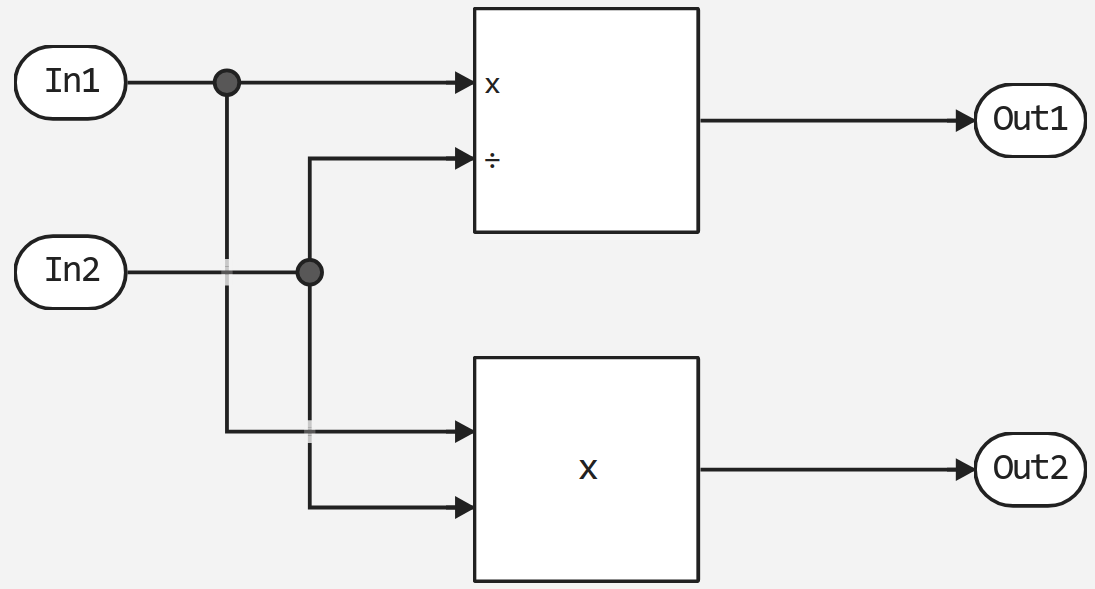
// ! BlockType = :Product
// ! TargetLang = :C
// ! @Step
// ! if contains(param.Inputs,"/")
/* Division is performed if the symbol "/" is specified in the block parameters. */
/* To avoid a division by zero error, input value verification has been added. */
$(output_datatype_name(1)) $(output(1)) = $(input(2)) == 0 ? $(input(1)) : $(input(1)) / $(input(2));
// ! else
/* Multiplication is performed if division is not specified in the parameters. */
$(output_datatype_name(1)) $(output(1)) = $(input(1)) * $(input(2));
// ! endThe above example shows an updated template for generating the block code. Divide in C language. In this code:
-
BlockType = :Product: Specifies the type of block for which the code is generated; -
TargetLang = :C: Specifies the target language for generation, in this case, C; -
The template code uses a section
@Step, which defines the calculations performed at each calculation step; -
Condition
if contains(param.Inputs,"/")checks whether the parameter containsInputsa string"/". If this is the case, then a division operation is performed.:-
$(input(2)) == 0— check the division by zero. If the denominator is zero, then the result is taken to be$(input(1)); -
Otherwise, division is performed
$(input(1)) / $(input(2)).
-
-
If division is not used, multiplication is performed.
$(input(1)) * $(input(2)).
The principle of operation:
-
Section code
@Stepit is executed at each step of the calculation, determining the behavior of the block depending on the configuration of the parameters. -
Using
$(input(n))and$(output(n))allows dynamic access to the input and output ports of the block. -
The output port data type variables are defined via
$(output_datatype_name(1)), which makes the code universal for different types of data.
The template syntax is different for the C Function and Engee Function blocks. Instead of specifying the standard block type via BlockType, the format is used //!BlockType = :EngeeFunction!EngeeFunction, Where after ! the block name from the model is specified, converted for the target language. If the specified BlockType If it is incorrect, the system will generate a generation error.
|
As a result of using the template for the newmodel_1 model with the block Divide a newmodel_1.c file will be generated with the following contents:
#include "newmodel_1.h"
/* External inputs */
Ext_newmodel_1_U newmodel_1_U;
/* External outputs */
Ext_newmodel_1_Y newmodel_1_Y;
/* Model initialize function */
void newmodel_1_init() {
/* (no initialize code required) */
}
/* Model terminate function */
void newmodel_1_term() {
/* (no terminate code required) */
}
/* Model step function */
void newmodel_1_step() {
/* Product: /Product incorporates:
* Inport: /In2
* Inport: /In1
*/
const double Product = newmodel_1_U.In2 * newmodel_1_U.In1;
/* Product: /Divide incorporates:
* Inport: /In1
* Inport: /In1
*/
const double Divide = newmodel_1_U.In1 / newmodel_1_U.In1;
/* Outport: /Out1 incorporates:
* Product: /Divide
*/
newmodel_1_Y.Out1 = Divide;
/* Outport: /Out2 incorporates:
* Product: /Product
*/
newmodel_1_Y.Out2 = Product;
}The generated code implements the main functions for the operation of the model: initialization (newmodel_1_init), performing the calculation step (newmodel_1_step) and shutdown (newmodel_1_term).
Function newmodel_1_step performs key operations of the model. In this example, two calculations are implemented: multiplication (Product) and division (Divide). The results of these operations are recorded in the corresponding output parameters of the Out1 and Out2 models. To calculate the values, the data coming through the inputs In1 and In2 defined in the structure is used. Ext_newmodel_1_U.
In the initialization functions (newmodel_1_init) and completion of work (newmodel_1_term) specified /* (no initialize code required) / and / (no terminate code required) */. This means that for this model, at the code generation stage, it was not necessary to add additional user code to perform initialization or shutdown operations. These functions remain empty, but are still included in the code to support the template syntax.
|
In the generated function code For example, in the given template for the Product block there is only a section Functions Thus, a place is always reserved for each section in the generated code, but their use depends entirely on the content of the template. |
Sample template for Verilog
For a detailed example of a template for Verilog, see the article Working with signal parameters for custom templates.
Generating the main function
Function main It represents the entry point for program execution and serves as a binding for managing the lifecycle of the model. In Julia, the function main It is often used to organize the launch of a program, where key stages are set: initialization of the model, completion of modeling steps, and shutdown.
To create a function main a template in the Julia language is used, in which the structure of the generated code is formed using C-style comments (/* … */ as specified in the syntax section above), and the function engee.generate_code on the command line or in the script editor. Function signature generate_code it looks like this:
@with_exception_handling function generate_code(
model_path::String,
output_path::String;
subsystem_id::Maybe{String} = nothing,
subsystem_name::Maybe{String} = nothing,
target::Maybe{String} = nothing,
template_path::Maybe{String} = nothing
)To generate the function code main in the function engee.generate_code you need to specify the path to the template using a named parameter. template_path.
Example of a function call:
engee.generate_code(
"/user/codegen_model.engee", # the path to the model from which the code is generated
"/user/codegen_dir"; # the path where the code will be generated
template_path = "/user/main_template.jl" # the path to the template of the main function
)Sample template
Let’s look at an example of a template for generating a function main:
_ Template for generating_
function main_template() :: String
#=%
# include "$model_name.h"
void do_step(void){
%=#
if !is_singlerate_model && !is_singletask_model
zeroes = "0"
for ji = 2:rates_num zeroes *= ", 0" end
#=%
static bool OverrunFlags[$rates_num] = {$zeroes};
static bool eventFlags[$rates_num] = {$zeroes};
static int taskCounter[$rates_num] = {$zeroes};
if (OverrunFlags[0]) return;
%=#
for ji = 2:rates_num
i = ji - 1
rate_ratio = Int(rates[ji] / get_baserate())
#=%
if (taskCounter[$i] == 0) {
if (eventFlags[$i]) {
OverrunFlags[0] = false;
OverrunFlags[$i] = true;
/* Sampling too fast */
return;
}
eventFlags[$i] = true;
}
taskCounter[$i]++;
if (taskCounter[$i] == $rate_ratio) {
taskCounter[$i] = 0;
}
/* Step the model for base rate */
$(model_substep(0))
/* Indicate task for base rate complete */
OverrunFlags[0] = false;
%=#
end
for ji = 2:rates_num
i = ji - 1
#=%
/* If task {0} is running, do not run any lower priority task */
if (OverrunFlags[$i]) return;
/* Step the model for subrate */
if (eventFlags[$i]) {
OverrunFlags[$i] = true;
/* Step the model for subrate $i */
$(model_substep(i))
/* Indicate task complete for subrate */
OverrunFlags[$i] = false;
eventFlags[$i] = false;
}
%=#
end
else
#=%
static bool OverrunFlag = false;
/* Check for overrun */
if (OverrunFlag) {
return;
}
OverrunFlag = true;
/* Step the model */
$model_step
/* Indicate task complete */
OverrunFlag = false;
%=#
end
print_sig(s) = "$(s.ty) $(s.full_qual_name)$(dims(s))"
#=%
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
(void) argc;
(void) argv;
/* Initialize model */
$model_init
while (1) {
/* Perform application tasks here */
// Signals available:
// INS
// $(print_sig.(ins))
// OUTS
// $(print_sig.(outs))
}
/* Terminate model */
$model_term
return 0;
}
%=#
endhere:
-
At the beginning of the template, the model header file is connected via
#include "$model_name.h"to access the model’s functions. -
The basic modeling step is performed by calling
$(model_substep(0))and reset status flags. For sub-frequency tasks, execution is monitored, and steps are processed using$(model_substep(i))and the completion flags are updated. -
For single-task models, overload control is implemented via the OverrunFlag flag, and model execution is called via
$model_step. -
In the function
maincalled$model_initto prepare the model for execution. -
The tasks of the model and the signals available for interaction are processed inside the infinite loop.
-
Before work is completed, it is called
$model_termfor the correct completion of the model and the release of resources.