Divide
Performs multiplication and division of scalars and non-scalars.
blockType: Product
Divide Path in the library: |
|
Product Path in the library: |
|
Product of Elements Path in the library: |
Description
Block Divide outputs the result of multiplication or division of input signals.
The block icon, the operation performed, and the number of ports vary depending on the parameter values. Multiplication and Number of inputs.
This table shows the output data of the block. Divide for approximate input data using block parameter values:
-
Multiplication:
Element-wise(.*) -
Number of inputs:
*/
| Input data | Block behavior |
|---|---|
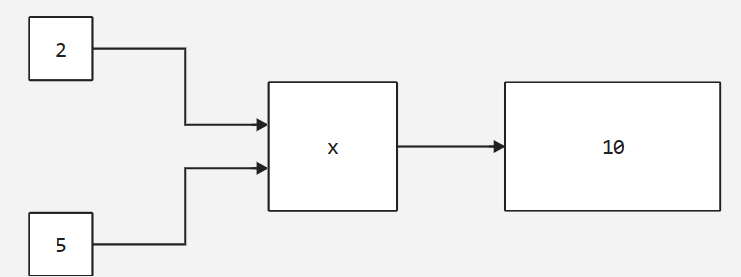
scalar ÷ scalar |
Outputs the result of dividing the first input scalar by the second one. |
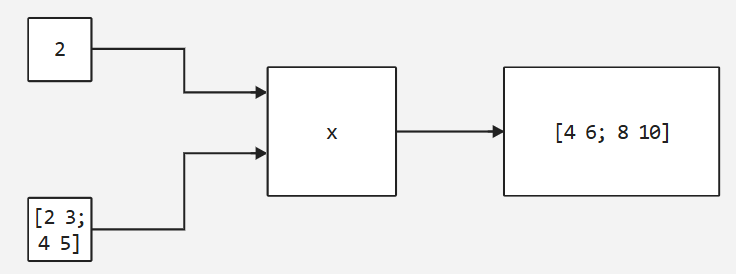
scalar ÷ non-scalar |
Outputs a nonscalar having the same dimensions as the input nonscalar. Each element of the output non-scalar is the result of dividing the input scalar by the corresponding element of the input non-scalar. |
non-scalar ÷ non-scalar |
Outputs a nonscalar having the same dimensions as the input data. Each element of the output data is the result of dividing an element of the first input non-scalar by the corresponding element of the second input non-scalar. |
Block Divide can:
-
Numerically multiply and divide any number of scalar, vector or matrix inputs.
-
Perform matrix multiplication and division on any number of matrix inputs.
Block Divide performs element-wise or matrix multiplication or division, depending on the parameter value Multiplication. The block accepts one or more input data streams, depending on the parameter Number of inputs. Parameter Number of inputs it also defines the operation to be performed for each input.
Input data for the block Divide there can be any combination of scalars, vectors, and matrices for which the operation performed has a mathematically defined result. The block performs the specified operations on the input data, then outputs the result.
Block Divide It has two modes:
-
Element-wise(.*)— processes non-scalar input data piecemeal. -
Matrix(*)— processes non-scalar input data in the form of matrices.
Piecemeal mode
When you install Multiplication on Element-wise(.*), block Divide It works with individual numeric elements of any non-scalar input data. In the mode Element-wise(.*) block Divide It can perform various operations of multiplication, division and arithmetic inversion.
Parameter value Number of inputs determines both the number of input data and whether each of them will be multiplied or divided to form the output data.
When the block Divide It is in the mode of Element-wise(.*) and it has only one input, it works as described in the Algorithms section.
To calculate the output data, the block first expands all inputs to a single size (using a standard broadcast), and then performs piecemeal actions.
This table shows the output data of the block. Divide for approximate input data using the specified values for the parameter Number of inputs.
| Parameter values | Example |
|---|---|
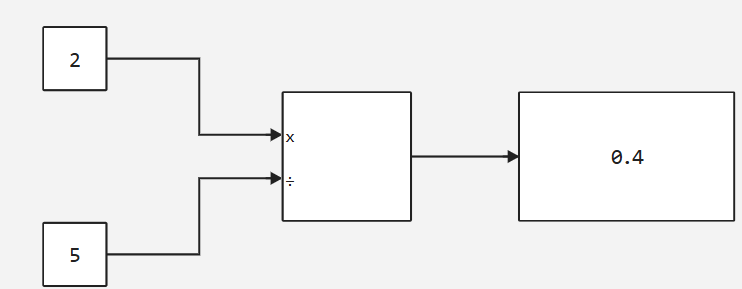
Number of inputs: |
|
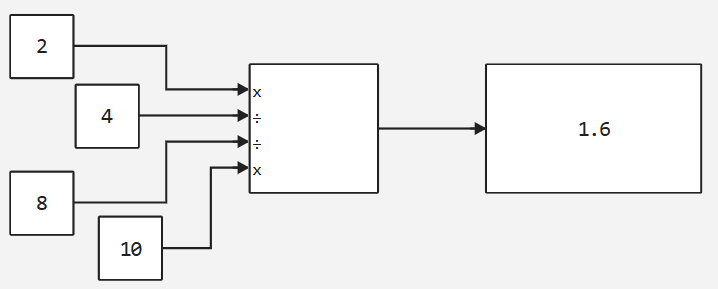
Number of inputs: |
|
Number of inputs: |
|
Number of inputs: |
|
Number of inputs: |
|
Matrix mode
When the parameter value is Multiplication equally Matrix(*), block Divide processes non-scalar input data in the form of matrices. In this mode, the block Divide It can invert a single square matrix or multiply and divide any number of matrices whose dimensions are mathematically determined.
Parameter value Number of inputs determines both the amount of existing input data and whether each input matrix will be multiplied or divided to form the output data. Syntax Number of inputs the same as for the mode Element-wise(.*). The difference between the modes is the type of multiplication and division.
Interactions between block inputs and modes
Interactions between the block input data Divide and its modes Multiplication:
-
In the parameter Number of inputs The values are set to
1,*or/.The unit has one input port. In the mode
Element-wise(.*)The block processes the input data as described in the Algorithms section. In the modeMatrix(*)if the parameter value is1or*, the block outputs the input value. If the value is/, the input data must be a square matrix (including a scalar as a degenerate case), and the block outputs the inverse matrix. For more information, see Piecemeal mode and Matrix mode. -
In the parameter Number of inputs an integer value strictly greater than
1is setThe block has the number of input data specified by an integer value. The input data is multiplied together in the mode
Element-wise(.*)or in the modeMatrix(*)as specified by the parameter Multiplication. For more information, see Piecemeal mode and Matrix mode. -
In the parameter Number of inputs an unquoted string consisting of two or more characters
*and/is specifiedThe block has the amount of input data specified by the length of the character vector. Each input signal corresponding to the character
' is multiplied by the output signal. Each output signal corresponding to the symbol `/is divided into an input signal. Operations are performed in the modeElement-wise(.*)or in the modeMatrix(*)as specified by the parameter *Multiplication. For more information, see Piecemeal mode and Matrix mode.
Ports
Output
#
OUT_1
—
Output signal
scalar | vector | the matrix
Details
An output signal calculated by multiplying or dividing the input signals.
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
Input
#
x
—
input signal for multiplication
scalar | vector | the matrix
Details
An input signal to multiply by other input signals.
Dependencies
To use one or more x ports, specify one or more characters for the parameter *Number of inputs and set for the parameter Multiplication value Element-wise(.*).
To use one or more ports *, specify one or more characters for the parameter *Number of inputs and set for the parameter Multiplication value Matrix(*).
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
#
/
—
input signal for division or inversion
scalar | vector | the matrix
Details
An input signal for division or inversion operations.
Dependencies
To use one or more ports -, specify one or more characters / for the parameter Number of inputs and set for the parameter Multiplication value Element-wise(.*).
To use one or more Inv ports, specify one or more characters / for the parameter Number of inputs and set for the parameter Multiplication value Matrix(*).
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
Parameters
Main
# Number of inputs — the number and names of the input ports and the type of operation
Details
Operations performed by the block: multiplication or division.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Multiplication —
type of multiplication
Element-wise(.) | Matrix()
Details
Specify the mode in which the block performs multiplication or division. Element-wise(.*) or Matrix(*).
For more information, see the sections Piecemeal mode and Matrix mode.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
Output settings
#
Output data type —
type of output data
Inherit: auto | Same as first input | Float64 | Float32 | Float16 | Int8 | UInt8 | Int16 | UInt16 | Int32 | UInt32 | Int64 | UInt64 | Int128 | UInt128 | Fixed-point
Details
Specify the type of output data. The type can be inherited or specified directly.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Output fixed-point type —
the type of fixed-point output
Data type
Details
Specify the type of fixed-point output.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Output data type meaning Fixed-point.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Main
#
Integer rounding mode —
rounding mode for fixed point operations
Ceiling | Convergent | Floor | Nearest | Round | Zero
Details
Select the rounding mode for fixed-point operations. You can choose:
-
Floor— rounds down both positive and negative numbers (towards negative infinity). -
Ceiling— rounds up both positive and negative numbers (towards positive infinity). -
Convergent— rounds the number to the nearest representable value. If the fractional part of the number ends in 5, the number is rounded to the nearest even integer. -
Nearest— rounds the number to the nearest representable value. If the fractional part of the number ends in 5, the number is rounded up (towards positive infinity). -
Round— rounds the number to the nearest integer.
-
Zero— rounds the number towards zero.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Saturate on integer overflow —
method of action in case of overflow
Logical
Details
When this option is selected, saturation is applied to all internal block operations, not just the output or result.
| Action | Reasons for making this decision | What happens when there is an overflow | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Check this box. |
Overflow is possible in your model, and you need explicit protection against saturation in the generated code. |
Overflows are saturated to the minimum or maximum value that a given data type can represent. |
Overflow associated with a signed 8-bit integer can saturate to |
Do not check this box. |
You want to optimize the efficiency of the generated code. |
Overflows are wrapped into an appropriate value, which can be represented by a data type. |
The number |
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Require all inputs to have the same data type —
the same data type mode for all inputs
Logical
Details
Select this option to set the same data type for all input ports.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
Algorithms
Block Divide with one input in the mode Element-wise(.*) uses the algorithms presented below to perform piecemeal operations on input data:
| Input data | Piecemeal operation | Algorithm |
|---|---|---|
A valid scalar, |
Multiplication |
|
Division |
|
|
A valid vector or matrix with elements, |
Multiplication |
|
Division |
|
|
The complex scalar, |
Multiplication |
|
Division |
|
|
A complex vector or matrix with elements, |
Multiplication |
|
Division |
|