Solenoid modeling using basic blocks and physical modeling blocks
This example shows a solenoid with a return spring. The solenoid is modeled as an inductance, the value of which depends on the position of the piston x. The reverse EMF for a time-varying inductance is defined as:
Because L depends on x:
it can be obtained using data from the manufacturer and using the ratio:
Then it can be integrated to get L as a function of x.
In the model, equation (2) is recalculated to solve for i, and then implemented using physical blocks. The controlled current source then limits the amount of current, equating it to I.
Model diagram:
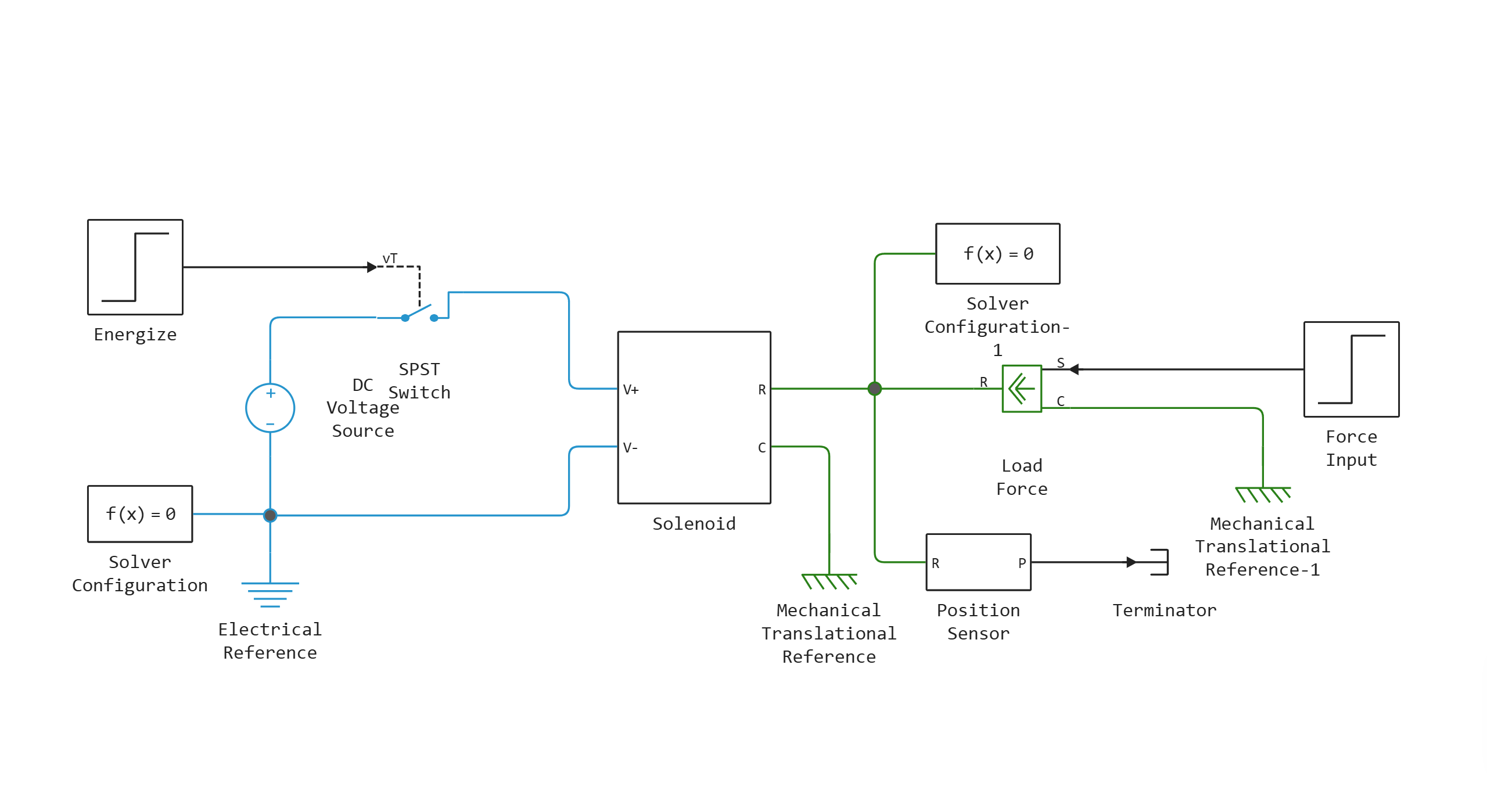
Simulation results:
The values of the solenoid current over time, And:
.png)
The values of the force generated by the solenoid in time, N:
.png)