A model of the interaction of a permanent magnet and an iron surface
This example demonstrates a way to simulate the forces that act between a magnet and an iron plate, such as a wall. The interaction between the magnetic domain and the linear displacement domain is modeled using blocks PermanentMagnet and ReluctanceForceActuator.
Description of the model
Block ReluctanceForceActuator It allows simulating the processes occurring between a permanent magnet and an iron wall due to the fact that its magnetic resistance and the linearly directed force created by it depend on the size of the gap between the poles of the magnet and the wall.
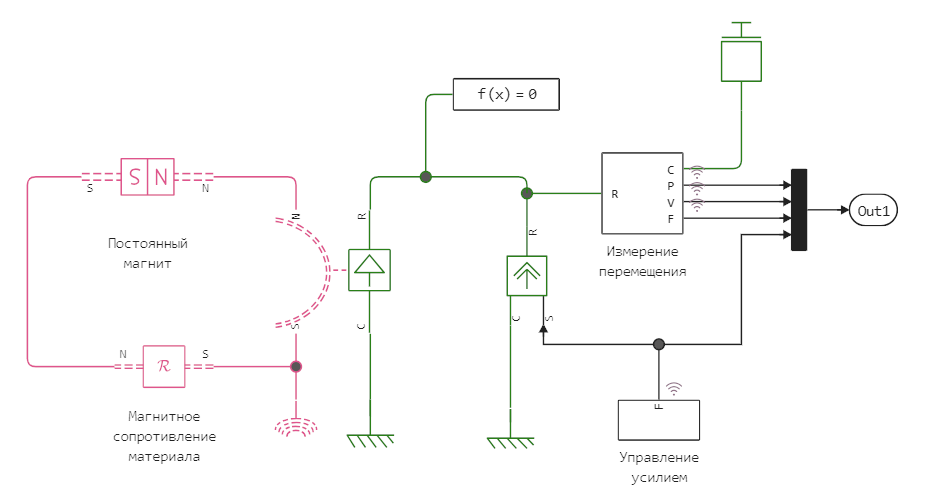
Subsystem Управление усилием sets the profile of the effect of an external force aimed at moving the magnet away from the wall.
Model launch and interpretation
Let's run the model and study the observed phenomena.
modelName = "permanent_magnet_on_wall";
model = modelName in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] ? engee.open( modelName ) : engee.load( "$(@__DIR__)/$(modelName).engee");
data = engee.run( modelName, verbose=false )
At the beginning of the simulation of the model, the magnet comes into contact with the wall. Then the block Управление усилием gradually increases the value of the force aimed at moving the block away from the wall. At the moment when the disconnection force exceeds the critical value, the unit Управление усилием stops applying force so that the magnet does not move too far away from the wall, and then, at the moment t=1.1 the effort stops. The profile of the change in this force is found empirically.
After the termination of the force aimed at separating the magnet and the plate, the magnet is reattached to the iron surface and takes its former place.
plot(
plot( data["Effort management.F"].time, 1e3.*data["Effort management.F"].value,
title="External force\n", ylabel="Power, mN",
titlefont=font(10), guidefont=font(8) ),
plot( data["Measurement of movement.F"].time, 1e3.*data["Measurement of movement.F"].value,
title="The sum of forces\n", ylabel="Power, mN",
titlefont=font(10), guidefont=font(8), lc=2 ),
plot( data["Measurement of movement.V"].time, 1e3.*data["Measurement of movement.V"].value,
title="The speed of movement of the magnet", ylabel="Speed<br>mm/s",
titlefont=font(10), guidefont=font(8), lc=3 ),
plot( data["Measurement of movement.P"].time, 1e3.*data["Measurement of movement.P"].value,
title="Distance from the wall\n", xlabel="Time, from", ylabel="Offset<br>mm",
titlefont=font(10), guidefont=font(8), lc=4 ),
layout=(4,1), legend=:false, size=(400,500)
)
A permanent magnet model implemented using a block PermanentMagnet, allows you to set properties both through the value of permeability (permeability) and through coercivity (coercivity). The choice depends on the magnet parameters specified in the manufacturer's documentation.
Running with other parameters
Once we change the parameters, we will see a different behavior of the model.
engee.get_param( "permanent_magnet_on_wall/Force Control/Saturation" )
We will increase the maximum value of the force that will be directed at separating the magnet from the wall.
engee.set_param!( "permanent_magnet_on_wall/Force Control/Saturation",
"UpperLimit"=>350e-3 )
data = engee.run( modelName, verbose=false )
plot(
plot( data["Effort management.F"].time, 1e3.*data["Effort management.F"].value,
title="External force\n", ylabel="Power, mN",
titlefont=font(10), guidefont=font(8) ),
plot( data["Measurement of movement.F"].time, 1e3.*data["Measurement of movement.F"].value,
title="The sum of forces\n", ylabel="Power, mN",
titlefont=font(10), guidefont=font(8), lc=2),
plot( data["Measurement of movement.V"].time, 1e3.*data["Measurement of movement.V"].value,
title="The speed of movement of the magnet", ylabel="Speed<br>mm/s",
titlefont=font(10), guidefont=font(8), lc=3 ),
plot( data["Measurement of movement.P"].time, 1e3.*data["Measurement of movement.P"].value,
title="Distance from the wall\n", xlabel="Time, from", ylabel="Offset<br>mm",
titlefont=font(10), guidefont=font(8), lc=4 ),
layout=(4,1), legend=:false, size=(400,500)
)
With these settings, the magnet moves too far away from the wall and the field strength is no longer enough to bring it back.
Conclusion
We have built a model that allows us to calculate the force required to remove a magnet from an iron surface, as well as to see the dynamic change in the value of the force of attraction of a permanent magnet to an iron surface.