Modeling of a two-mass oscillatory system
This example shows two models of systems: one using a library of basic blocks and the other using physical models.
The blocks of the basic library use directional connections that determine how data is transferred from one block to another. Physical blocks use non-directional connections that define a bidirectional flow of mass or energy between components. Such blocks allow you to add additional sets of elastic damping elements to the system simply by copying and pasting. Directional models require a revision of the equations and their re-implementation.
The initial deflection for each spring is 1 meter. This is reflected in the block annotations for Spring1 and Spring2. The names of the integration blocks show the initial positions of the masses relative to one fixed point in space.
Model diagram:
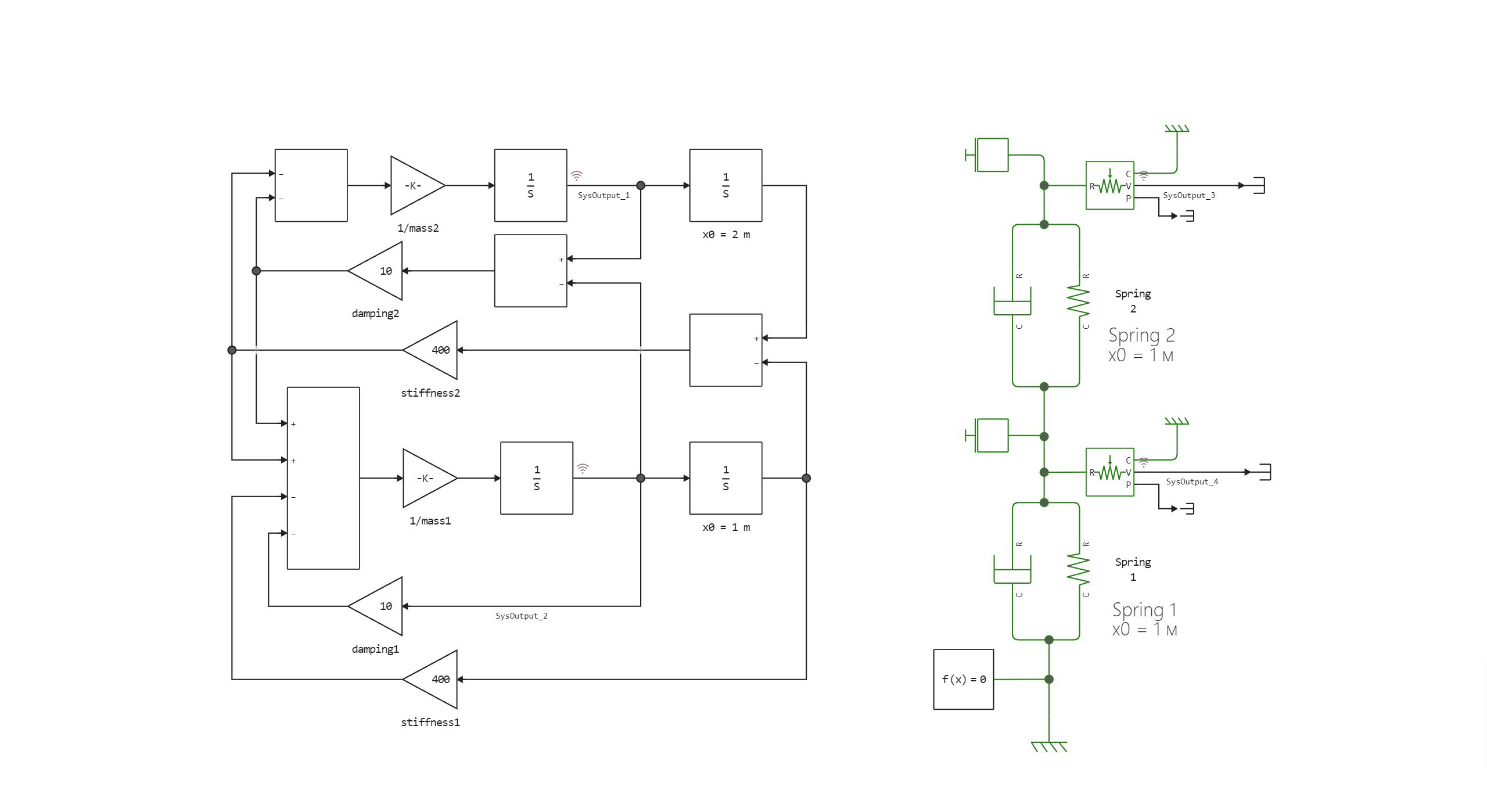
Simulation results:
Mass velocities obtained using a model consisting of basic blocks:
.png)
Mass velocities obtained using a model consisting of blocks of a physical modeling library:
.png)