Simulation of pipeline pressure control
This example demonstrates the simulation of pressure control in a pipeline.
How the model works
The pipeline is described by the blocks of the physical modeling library, in particular, the Volume block is responsible for its volume.
Through Valve 1, liquid flows from the Source unit to the Volume unit. In turn, a pressure sensor ** is connected to it, from which the signal is sent to the control system, represented by an adder, a setpoint sensor and a PID controller.
Model diagram:
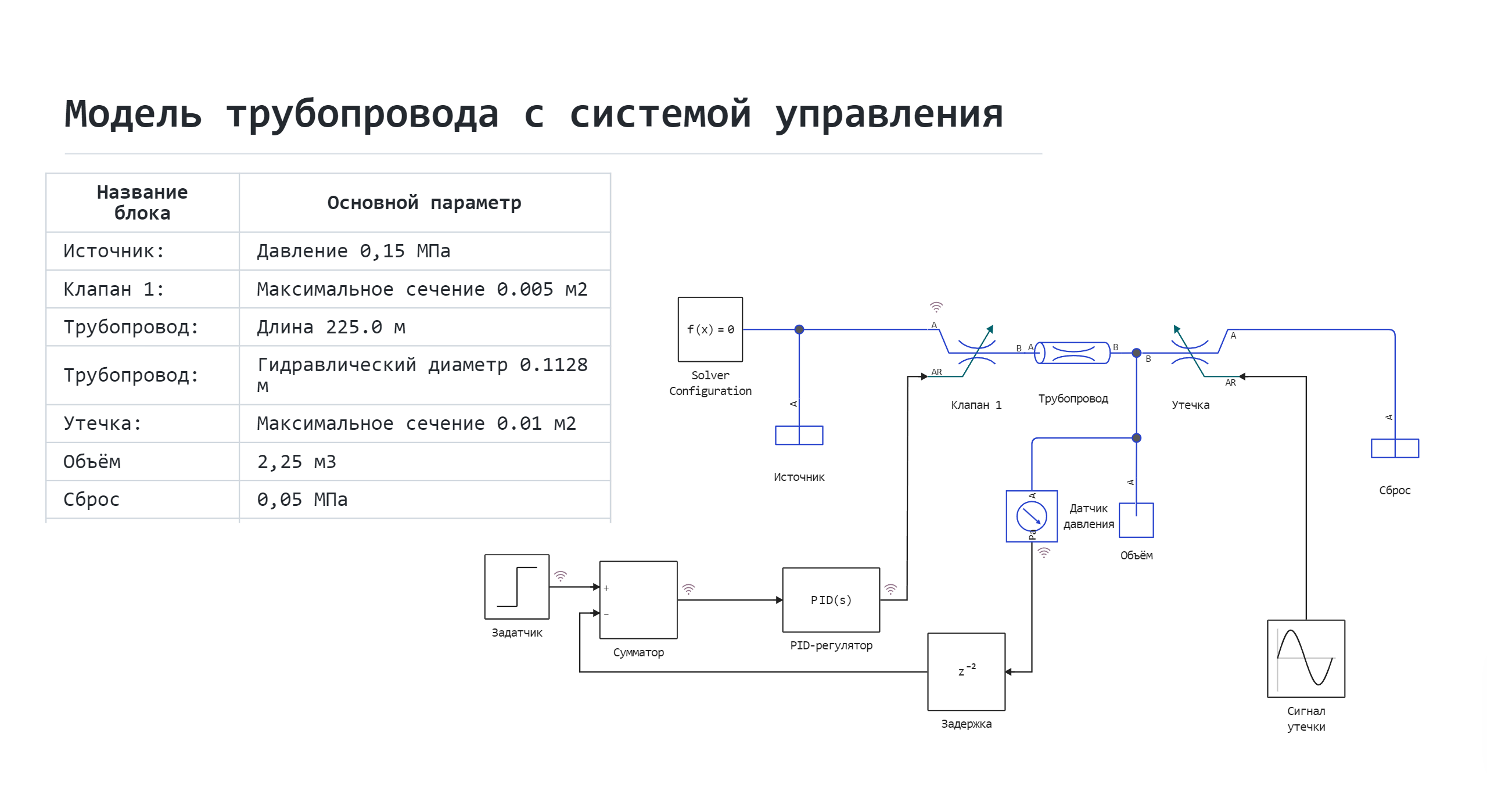
The PID controller sends a control signal to Valve 1 to open or close, providing pressure control.
To the right of the Volume block, along the path of fluid movement, there is a block Leakage, which is, like Valve 1, a controlled throttle.
Block Leakage creates some "accidental" leakage of liquid from the simulated pipeline.
The liquid passing through this unit eventually enters the Discharge, which is described by an infinite reservoir with a set pressure.
Boundary conditions
- The pressure in the source is always maintained at 151.3 kPa.
- In the tank, which characterizes the space where the liquid is discharged through a leak, the pressure is always 50 kPa.
Initial conditions:
- The initial pressure in the pipeline is 100 kPa.
- The setpoint signal is 100000, which in the context of regulation means 100 kPa.
Defining the function to load and run the model:
function start_model_engee()
try
engee.close("liquid_pressure_regulator", force=true) # closing the model
catch err # if there is no model to close and engee.close() is not executed, it will be loaded after catch.
m = engee.load("$(@__DIR__)/liquid_pressure_regulator.engee") # loading the model
end;
try
engee.run(m) # launching the model
catch err # if the model is not loaded and engee.run() is not executed, the bottom two lines after catch will be executed.
m = engee.load("$(@__DIR__)/liquid_pressure_regulator.engee") # loading the model
engee.run(m) # launching the model
end
end
Running the simulation
try
start_model_engee() # running the simulation using the special function implemented above
catch err
end;
Extracting site temperature data from the simout variable and writing it to variables:
result = simout;
res = collect(result)
Recording of setpoint and pressure sensor signals in variables:
control_signal = collect(res[4])
pressure = collect(res[12])
Visualization of simulation results
using Plots
plot(control_signal[:,1], control_signal[:,2], label="The depositor", linewidth=3)
plot!(pressure[:,1], pressure[:,2], label="Pressure sensor", linewidth=3)
Conclusion:
In this example, a simulation of a physical object with an automatic control system was demonstrated. The transition time is about 15 seconds, the pressure stabilizes within acceptable limits, and minor fluctuations are associated with fluid leakage from the pipeline.