Simulation of an artificial lung ventilation system
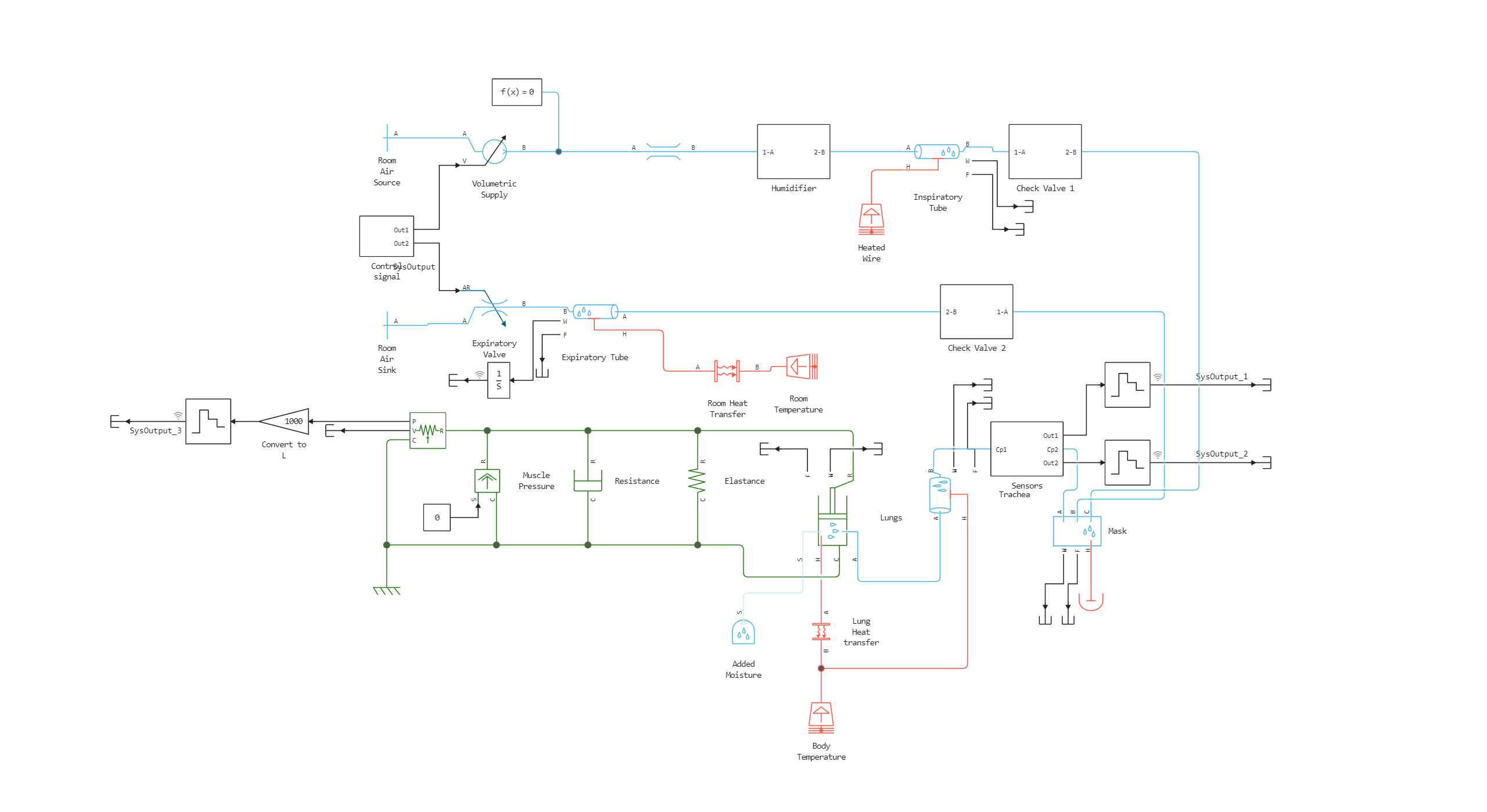
In this example, an artificial lung ventilation system is modeled. The patient is supplied with a preset air flow rate. The lungs are modeled using a translational mechanical transducer that converts the pressure of moist air into translational motion. By setting the area over which moist air exerts pressure equal to one, the displacement in the mechanical transducer becomes an indicator of volume, the source of mechanical energy becomes an indicator of pressure, the elastic element is an indicator of elasticity during breathing, and the damper characterizes breathing resistance.
Oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide emissions are not taken into account in this model.
Model diagram:
Simulation results:
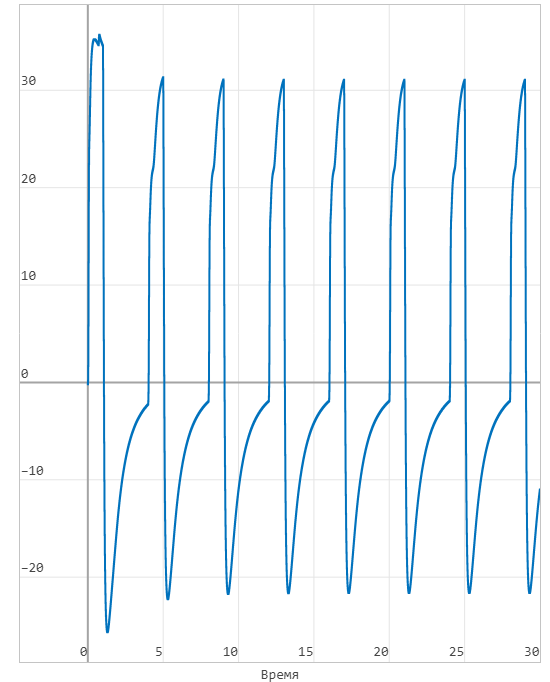
Mass flow rate (l/min):
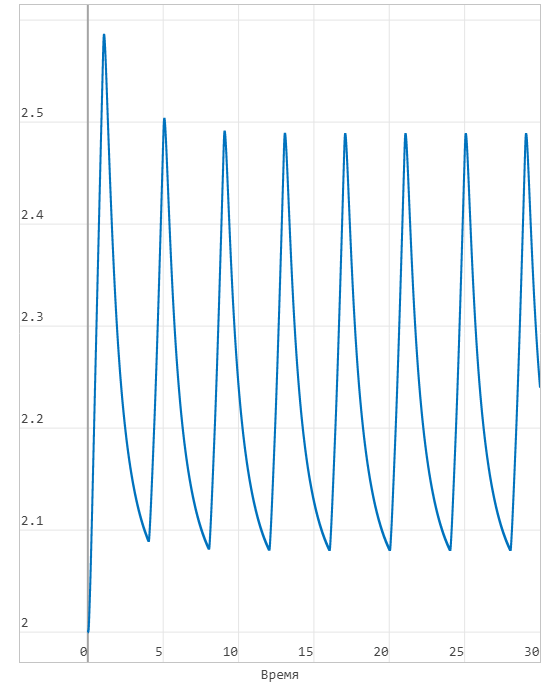
Pressure (see v. art.):
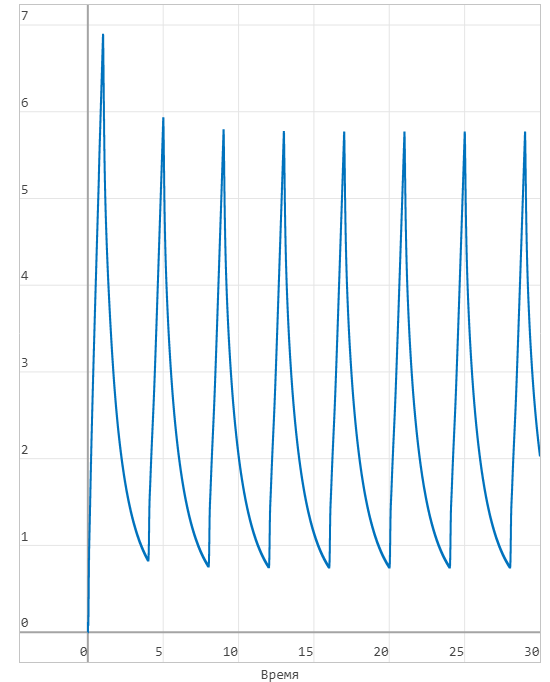
Lung capacity (L):