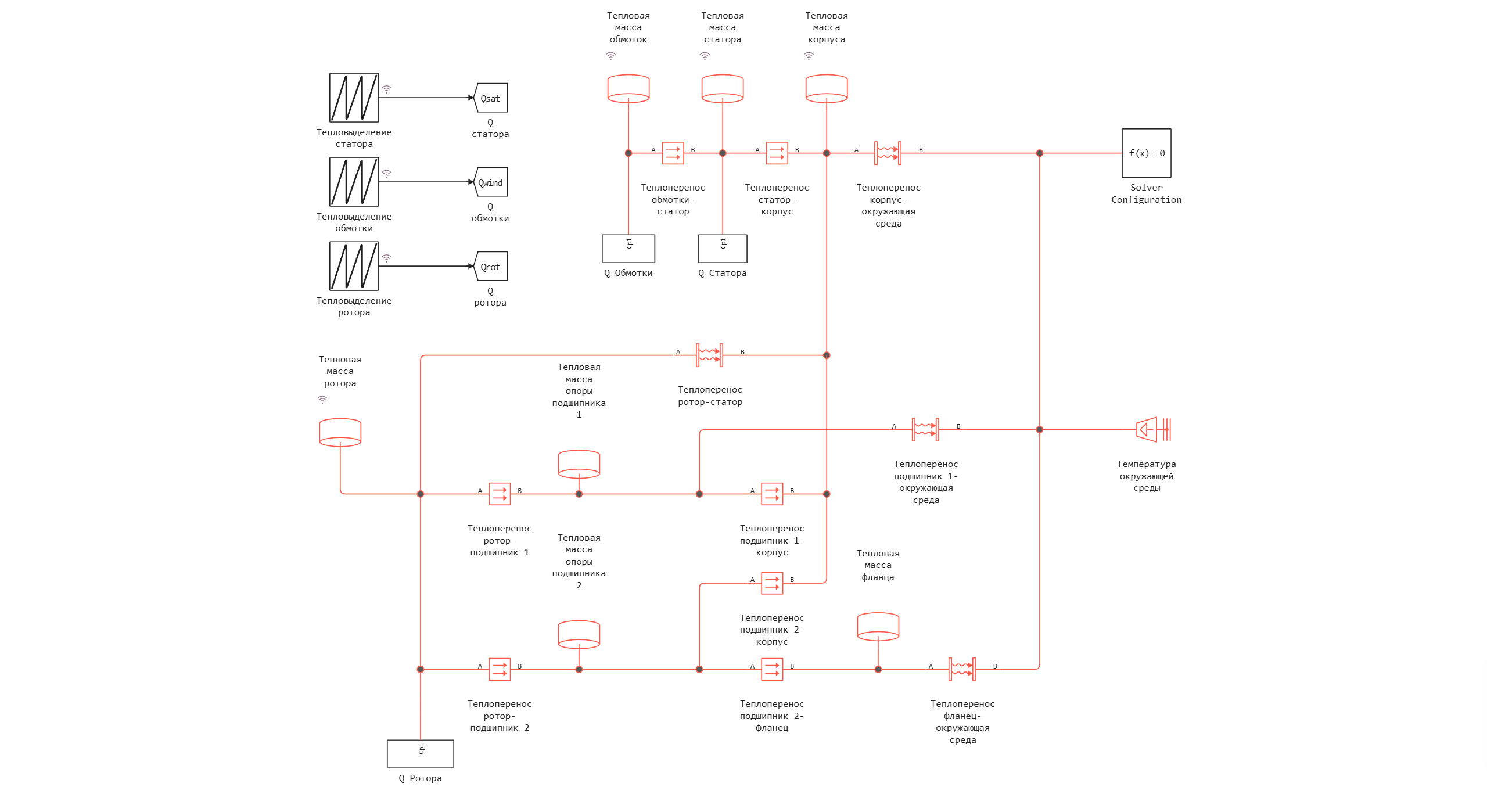
Thermal scheme of the electric motor
This example demonstrates how the thermal state of a brushless motor can be modeled using a lumped-parameter model. The heat generated due to power losses in the stator, winding and rotor is represented by three sources of heat flow: heat generation in the stator (Q of the Stator), heat generation of the winding (Q of the Winding) and heat generation of the rotor due to losses due to magnetization and eddy currents (Q of the Rotor). The losses were recorded during the simulation of a typical electric motor cycle and stored in blocks Repeating table. The thermal circuit of the engine consists of heat-conducting elements, thermal masses and convective heat transfer units that reproduce the ways of heat propagation in parts: winding, stator, housing, rotor, front and rear bearing supports and flange. The engine exchanges heat with the atmosphere through the contacts housing-atmosphere, flange-atmosphere and bearing 1 -atmosphere. Environmental conditions are simulated using an ideal temperature source set at 300 K.
Model diagram:
Defining the function to load and run the model:
function start_model_engee()
try
engee.close("motor_thermal_circuit", force=true) # closing the model
catch err # if there is no model to close and engee.close() is not executed, it will be loaded after catch.
m = engee.load("$(@__DIR__)/motor_thermal_circuit.engee") # loading the model
end;
try
engee.run(m) # launching the model
catch err # if the model is not loaded and engee.run() is not executed, the bottom two lines after catch will be executed.
m = engee.load("$(@__DIR__)/motor_thermal_circuit.engee") # loading the model
engee.run(m) # launching the model
end
end
Running the simulation
try
start_model_engee() # running the simulation using the special function implemented above
catch err
end;
Recording temperature and heat flow signals from simout to variables:
t = collect(simout["The thermal mass of the stator.T"].time[:])
Температура_ротора = collect(simout["The thermal mass of the rotor.T"].value[:])
Температура_обмоток = collect(simout["The thermal mass of the windings.T"].value[:])
Температура_статора = collect(simout["The thermal mass of the stator.T"].value[:])
Температура_корпуса = collect(simout["Thermal mass of the housing.T"].value[:])
Тепловыделение_ротора = collect(simout["The thermal mass of the rotor.T"].value[:])
Тепловыделение_обмоток = collect(simout["The thermal mass of the windings.T"].value[:])
Тепловыделение_статора = collect(simout["The thermal mass of the stator.T"].value[:]);
Visualization of simulation results
using Plots
plot(t[:,1], Температура_ротора[:,1], label="Rotor temperature, K", linewidth=2)
plot!(t[:,1], Температура_статора[:,1], label="Stator temperature, K", linewidth=2)
plot!(t[:,1], Температура_обмоток[:,1], label="Winding temperature, K", linewidth=2)
plot!(t[:,1], Температура_корпуса[:,1], label="Case temperature, K", linewidth=2, legend=:bottomright)
plot(t[:,1], Тепловыделение_ротора[:,1], label="Heat dissipation of the rotor, W", linewidth=2)
plot!(t[:,1], Тепловыделение_статора[:,1], label="Stator heat dissipation, W", linewidth=2)
plot!(t[:,1], Тепловыделение_обмоток[:,1], label="Heat dissipation of windings, W", linewidth=2, legend=:bottomright)