Simulation of car braking
This example will demonstrate the simulation of car braking.
The movement of the car and its inertia are described by the Car block. The resulting force from two pairs of wheels connected to the braking mechanism comes to the left port of this unit. The air resistance force described by the subsystem of the same name is applied to the right port.
Model diagram:
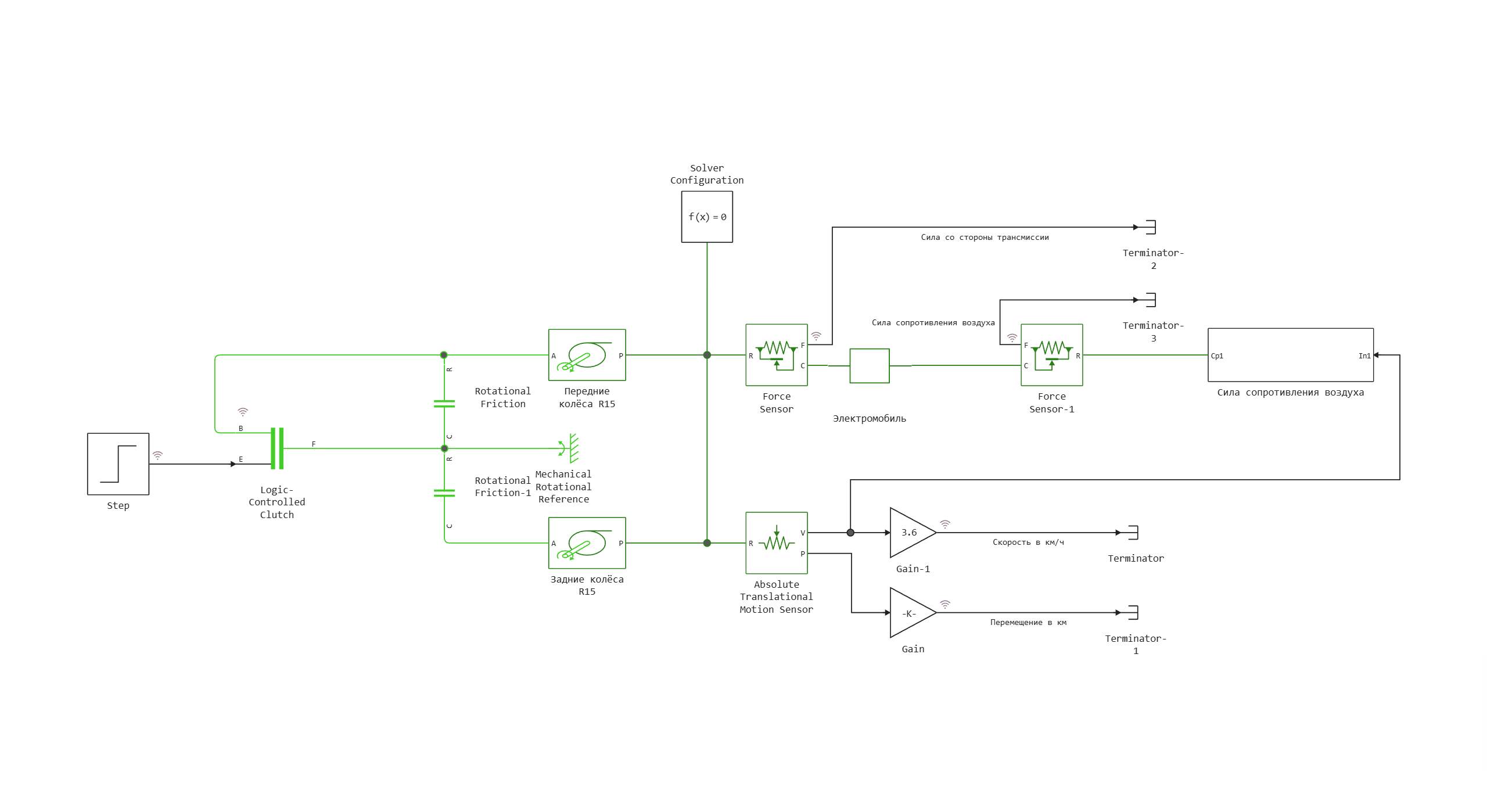
Defining the function to load and run the model:
In [ ]:
function start_model_engee()
try
engee.close("braking_distance", force=true) # closing the model
catch err # if there is no model to close and engee.close() is not executed, it will be loaded after catch.
m = engee.load("$(@__DIR__)/braking_distance.engee") # loading the model
end;
try
engee.run(m) # launching the model
catch err # if the model is not loaded and engee.run() is not executed, the bottom two lines after catch will be executed.
m = engee.load("$(@__DIR__)/braking_distance.engee") # loading the model
engee.run(m) # launching the model
end
end
Out[0]:
Running the simulation
In [ ]:
try
start_model_engee() # running the simulation using the special function implemented above
catch err
end;
Recording speed, displacement, and force signals from simout to variables:
In [ ]:
t = simout["braking_distance/Speed in km/h"].time[:]
distance = simout["braking_distance/Movement in km"].value[:]
speed = simout["braking_distance/Speed in km/h"].value[:]
forces_left = simout["braking_distance/Power from the transmission"].value[:]
forces_right = simout["braking_distance/Air resistance force"].value[:];
Visualization of simulation results
In [ ]:
using Plots
In [ ]:
plot(t, forces_left, label="Force from the transmission, N", linewidth=2)
plot!(t, forces_right, label="Air resistance, N", linewidth=2)
plot!(t, (forces_left+forces_right), label="The sum of forces, N", linewidth=2, title="Forces acting on the car")
Out[0]:
In [ ]:
plot(t, speed, label="Speed, km/h", linewidth=2)
plot!(t, distance*1000, label="Displacement, m", linewidth=2)
Out[0]:
Definition of a function for calculating the braking distance of a car and its application to movement data:
In [ ]:
function braking_distance(distance, t)
index = findfirst(x -> x < 0.00001, distance)
if index != nothing
return println("Braking distance: ", round(maximum(distance)*1000, digits=2), " m")
end
end
braking_distance(distance, t)
Conclusions:
In this example, a simulation of car braking was demonstrated. Using the function braking_distance The braking distance was calculated for a car with an initial speed of 100 km/h.