Simulation of the discharge and charge cycle of a battery
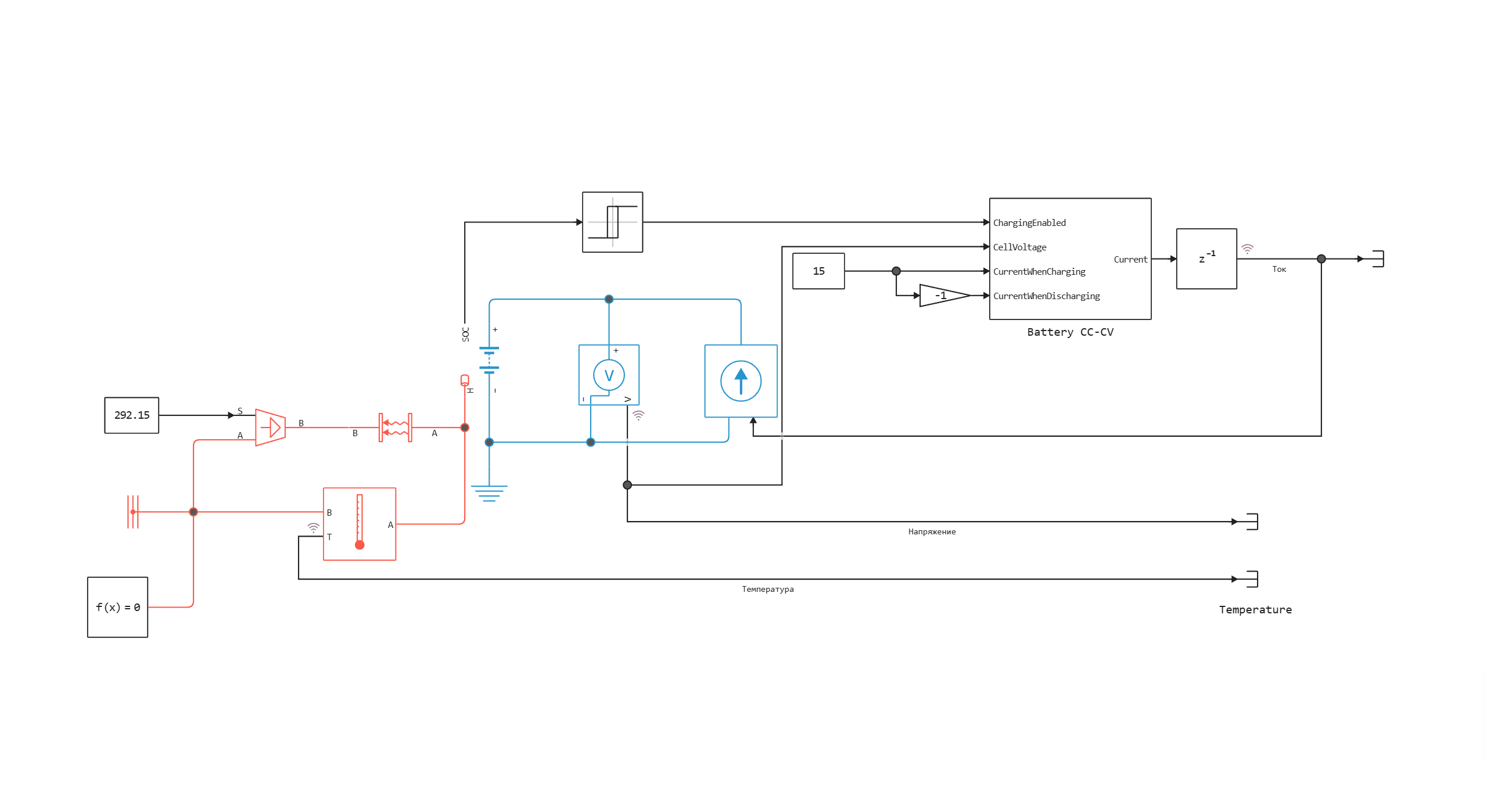
This example shows how to use the battery charge and discharge algorithm at constant current and constant voltage. The CC-CV unit charges and discharges the battery within 10 hours. The initial charge level is 0.3. During charging, the current remains constant until the battery voltage reaches its maximum value and the current decreases to 0. Direct current is used during discharge.
Model diagram:
Defining the function to load and run the model:
In [ ]:
function start_model_engee()
try
engee.close("battery_cccv", force=true) # closing the model
catch err # if there is no model to close and engee.close() is not executed, it will be loaded after catch.
m = engee.load("$(@__DIR__)/battery_cccv.engee") # loading the model
end;
try
engee.run(m) # launching the model
catch err # if the model is not loaded and engee.run() is not executed, the bottom two lines after catch will be executed.
m = engee.load("$(@__DIR__)/battery_cccv.engee") # loading the model
engee.run(m) # launching the model
end
end
Out[0]:
Running the simulation
In [ ]:
try
start_model_engee() # running the simulation using the special function implemented above
catch err
end;
Output of a variable simout:
In [ ]:
simout
Out[0]:
Recording voltage, current, and temperature signals from simout to variables:
In [ ]:
res = collect(simout)
V = collect(res[1])
I = collect(res[2])
T = collect(res[3])
Out[0]:
Visualization of simulation results
In [ ]:
using Plots
In [ ]:
plot(V[:,1], V[:,2], label="Voltage, V", linewidth=2, title="Battery voltage")
Out[0]:
In [ ]:
plot(I[:,1], I[:,2], label="Current, A", linewidth=2, title="Discharge/charge current")
Out[0]:
In [ ]:
plot(T[:,1], T[:,2], label="Battery temperature", linewidth=2, title="Battery temperature")
Out[0]: