In1
Subsystem input port or external input.
blockType: Inport
Path in the library: |
Description
Block In1 connects signals outside the system to the system.
The software assigns the block port numbers In1 according to these rules:
-
Blocks In1 in a top-level system or subsystem, they are numbered sequentially, starting with
1. -
If you are adding a block In1, it is added with the next available number.
-
If you are copying a block In1 Its port number is not renumbered unless its current number conflicts with an input port that already exists in the system.
Blocks of input ports in subsystems
Blocks In1 The inputs to the subsystem are represented in the subsystem. The signal coming to the input port in the block Subsystem, exits the linked block In1 in this subsystem.
Duplicate input ports
A duplicate input port is a special copy of an existing input port (In1). All duplicates created from the same port represent the same signal. This allows you to separate the same input signal into different parts of the model without creating multiple connecting lines through the entire circuit.
To create duplicates of the input port:
-
Select an existing block on the canvas In1 (input port).
-
Hold down the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+LKM on the block.
-
Pull the mouse to the side and a context menu will appear.
-
In the menu, select the Duplicate option.
After creating a duplicate, the system switches to identifying ports by program names. The appearance of all ports associated with this signal will change.:
-
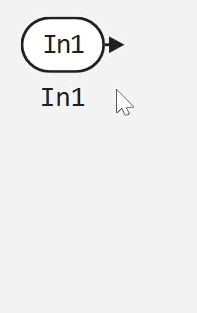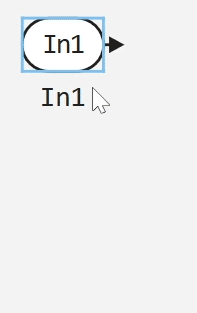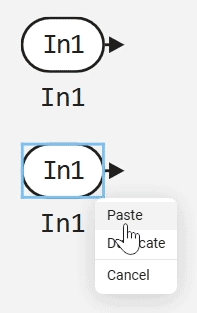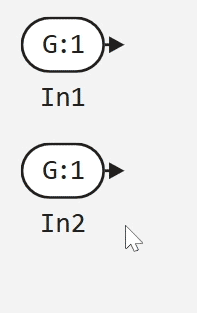
Source port
Inport1turns intoG:1; -
The created duplicate is displayed as
G:2; -
Subsequent duplicates receive IDs
G:3,G:4etc.
All blocks G:1, G:2, G:3 they are equal representations of the same port. There is no difference between them — it is a single port with several connection points in the diagram. Learn more about working with duplicates:
| Highlight |
When any duplicate is selected, all associated ports of this signal are highlighted in orange. |
| Edit |
To change the properties of the signal (name, data type), edit any of the duplicates. The changes will be automatically applied to all associated ports. |
| Deletion |
Deleting any duplicate does not affect the original signal. The signal (and all its duplicates) is deleted only when the last remaining port is deleted. |
| Usage |
Place duplicate ports in different parts of the circuit to supply the same input signal to different blocks. |
The same identification system is used for duplicates of input ports of subsystems and state machines.
Ports
Output
#
OUT_1
—
output signal
scalar | vector | matrix | bus
Details
A signal that enters the system through the input port.
You can use the In1 block in a subsystem to provide fixed-point data in a structure or any other format.
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
Parameters
Main
#
Interpolate —
possibility of linear interpolation of output data
Logical
Details
When loading data from the workspace into the Root Level Input Unit, specify whether the unit performs linear interpolation and extrapolation of output data at time steps for which no corresponding data exists.
To load individual data from the workspace, in the block dialogue box In1:
-
Uncheck the parameters Interpolate, if active.
-
Set the Sample time parameters to a discrete value, e.g.
2.
Specifying a discrete sample time causes the simulation to have hit times exactly when the data is sampled. You specify data values, not time values.
Disabling interpolation avoids unexpected data values at other times in the simulation as a result of double precision arithmetic.
The software uses the following interpolation and extrapolation methods:
-
For time steps between the first specified data point and the last specified data point, zero-order retention.
-
For time steps before the first specified data point and after the last specified data point, prime.
-
For variable size signals for time steps up to the first specified data point - `NaN' value is registered for single or double data types and grounded for other data types. For time steps after the last specified data point, the software uses the basic values.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Sample Time —
interval between calculation steps
SampleTime (real number / vector of two real numbers)
Details
Specify the interval between calculation steps as a non-negative number. To inherit a calculation step, set this parameter to -1.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Partition —
selecting the input port signal to be split
Logical
Details
Select this check box if you want to split the signal (only for subsystems For Each). Checking this box adds parameters from For Each to the settings menu of In1.
If the checkbox is selected:
-
Select the signals of the input ports connected to the For Each block to be split into subarrays or elements.
-
For each port listed in the Port column, select the corresponding check box to split that signal.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Partition Dimension —
input signal array slicing measurement
Int64 integer
Details
Specify the dimension along which the selected input signal array will be sliced. The resulting slices are perpendicular to the specified dimension. The slices divide the array into subarrays or items as appropriate:
-
Situation 1 - slicing the input array by columns.
-
Situation 2 - slicing the input array by rows.
-
Situation 3 - input array slicing by dimension.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, select the check box Partition.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Partition Width —
signal width
Int64 integer
Details
Specify the width of each section slice of the selected input signal.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, select the Partition check box.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Partition Offset —
partition offset
Int64 integer
Details
Set the offset for each partition slice of the selected input signal:
-
0- no offset between the partitions, i.e. the partitions have no gaps between them and do not overlap. -
` integer` - specify the offset of the partition, using a positive integer to specify the gap between the fragments or a negative integer to specify the overlap. The sum of the Partition Offset and Partition Width parameters must be a positive integer.
For example, Partition Width of 3 and Partition Offset of -2 means that each three-element fragment overlaps neighbouring fragments by two elements; while Partition Width of 2 and Partition Offset of 1 means that there is a one-element-wide gap between each pair of neighbouring two-element-wide fragments.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, select the Partition check box .
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Signal Attributes
#
Output data type —
output data type
Inherit: auto | Float64 | Float32 | Float16 | Int8 | UInt8 | Int16 | UInt16 | Int32 | UInt32 | Int64 | UInt64 | Int128 | UInt128 | Bool | Fixed-point | BusSignal
Details
Specify the type of output data.
The type can be inherited or specified directly.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Output fixed-point type —
fixed-point output data type
Data type
Details
Specify the fixed-point output type.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set the Output data type parameters to Fixed-point.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Output bus type —
output bus type
Data type
Details
Specify the output bus type.
For details on busbar operation, refer to Working with custom tires BusSignal in the equipment blocks.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set the parameters Output data type to . BusSignal.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Port dimensions — port dimension
Details
Specify the dimensionality of the output signal:
-
-1- The port can load data for a signal of any dimension. The port inherits the dimension from the connected signal. -
()- the port can load data for a scalar signal, i.e. a signal representing a single value (number). -
(N,)- the port can load data for a signal representing a vector of dimensionN. -
(R, C)- the port can load data for a matrix signal having `R rows and `C columns.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Signal type —
output signal type
auto | real | complex
Details
Specify the output signal type. To inherit the type of signal connected to its input, select auto. Otherwise, select real or complex signal type.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
