Enable
Creating an input port for the subsystem.
blockType: EnablePort
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Enable allows an external signal to control the execution of the subsystem. To use this block, add it to the subsystem block. Subsystem.
Adding to the subsystem of the block Enable creates activated subsystem 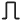 .
.
Adding both blocks to the subsystem Enable and Trigger creates triggered and activated subsystem 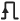 .
.
Ports
Output
#
OUT_1
—
an external permission signal for the subsystem
scalar
Details
The permission signal enters a special port and is transmitted inside the subsystem.
Dependencies
To use this port, check the box Show output port.
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
Parameters
Main
#
States —
select the block states when the subsystem or model is disabled
held | reset
Details
When the subsystem or model is disabled, select what happens to the block states inside the subsystem or model.:
-
held— block states are kept at their previous values. -
reset— the states of the blocks are reset to their initial conditions (zero if they are not defined).
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
# Show output port — controlling the display of the output port for the resolution signal
Details
The output port transmits a permission signal connected externally to the external unit Subsystem, which contains a block Enable.
Select this option to display the output port on the block. Enable. Selecting this parameter allows the subsystem to process the resolution signal.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
Verilog Code generation
In the current implementation, only the held mode is supported, in which the subsystem saves the state of registers between activations.
The Verilog module generated from the activated subsystem includes an additional input enable. Updating of register states (sequential logic) occurs only when enable = 1. Combinatorial logic is constantly being calculated.
- This approach is synchronous and provides the following advantages
-
-
More productive and cleaner Verilog code;
-
No need to save previous states of combinatorial logic when
enable = 0.
-
The signal enable It functions as a signal valid:
-
By
enable = 0The output values may change and are invalid.; -
By
enable = 1The output signals are guaranteed to be correct and correspond to the simulation results.
By verification there may be discrepancies between the generated code and the simulation when enable = 0. However, when enable = 1 The output values completely match the simulation results.
