Switch Case
Selecting a subsystem for execution using usage logic similar to the operator switch.
blockType: SwitchCase
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Switch Case with a block Subsystem, containing blocks Action Port, implements switching logic to control the execution of the subsystem.
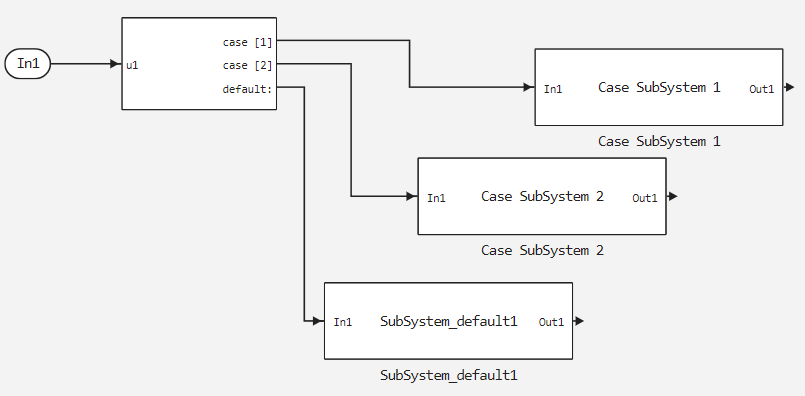
Block Switch Case It has one entrance. To select an option, correlate it with the value of the input signal using the parameter Case conditions (e.g. [1, 2, 3]). Options are evaluated from top to bottom, starting with the first one.
Each option is associated with an output port that is attached to the unit Subsystem. When an option is selected, its associated output port sends an action signal to execute the subsystem.
Option default It is selected after all other conditions are evaluated as false. Availability of the option default is optional even if the other conditions do not exhaust all possible input values.
Options for the block Switch Case already contain an analogue of the operator break after executing the Switch Case Action Subsystem block. Therefore, for the block Switch Case you do not need to specify it explicitly, as in standard operators switch the C language.
Ports
Input
#
u1
—
the value for selecting an option
scalar
Details
Input signal for selecting an option
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
I don’t |
Parameters
Main
# Case conditions (e.g. [1, 2, 3]) — variant values
Details
Sets the values corresponding to the options.
[1] — means that the output port marked as case[1], outputs an action signal when the input port value is 1.
You can use the colon notation to specify a range of integer register conditions. For example, the value {[1:5]} indicates that the output port option [1 2 3 4 5] is executed when the input value is 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5.
Depending on the block size, options from a long list of option states are displayed in a shortened form on the front of the block Switch Case in the form of an ellipsis (…).
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Show default case —
controlling the display of the output port
Logical
Details
Control the display of the output port by default.
If this check box is checked, the output port is default: displayed as the last option in the block Switch Case. This allows you to specify a by default option that is executed when the input value does not match any of the other values.
If this check box is not checked, then the output port is default: Hidden.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
