Parametric audio equalizer
In this demo, we will analyze a parametric audio equalizer that supports three configurable bands. Each band is implemented using a different biquadrate filter structure.
An equalizer is an electronic device or computer program that allows you to selectively adjust the amplitude of a signal depending on the frequency characteristics.
Also in this demo, we will compare the operation of the Engee and MATLAB models.
To do this, we will connect the necessary libraries and consider the device of the implemented model.
Pkg.add(["Statistics", "CSV"])
using Plots
using MATLAB
using CSV
using DataFrames
using Statistics
plotlyjs();
mat"start_simulink"
mat"p = genpath('/user/start/examples'); addpath(p);"
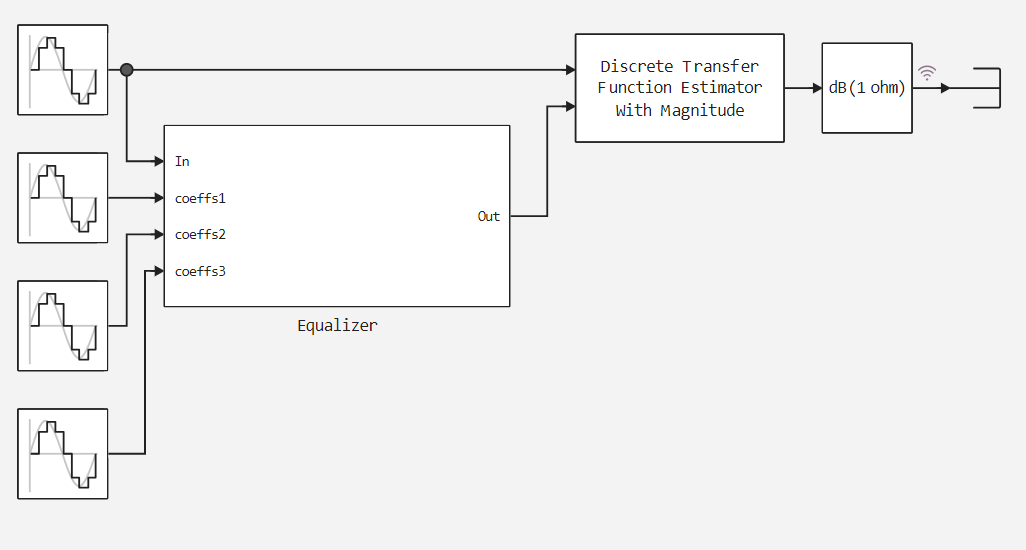
The model consists of two main blocks: the equalizer itself, which includes 3 filtering units with filter coefficients at the upper level, and the discrete transfer function estimator. The figures below show the appraiser's model and settings.
.png)
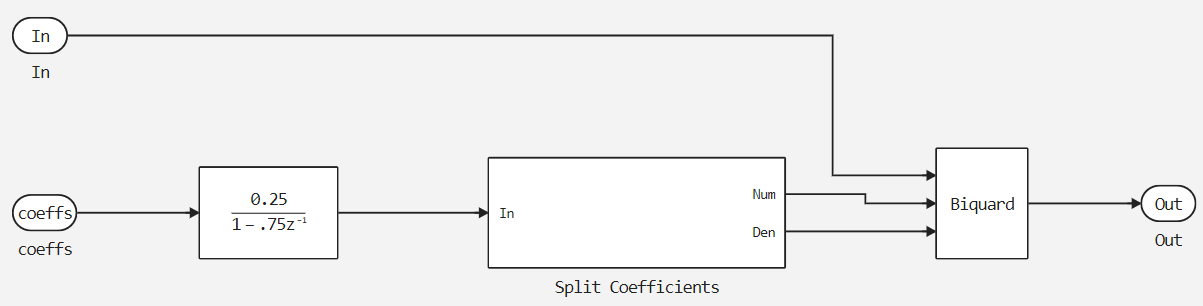
If we consider each of the filters, they are implemented in the same way and include a discrete filter, a coefficient sampling unit, and a biquad filter.
Now let's move on to the launch and comparison of the implementation of this model in Engee and Simulink.
Launching and analyzing the Engee model
Let's look at the simulation results in Engee:
function rum_model(NemeModel,Path_to_folder)
Path = Path_to_folder * "/" * NemeModel * ".engee"
if NemeModel in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] # Checking the condition for loading a model into the kernel
model = engee.open(NemeModel) # Open the model
engee.run(model, verbose=true); # Launch the model
else
model = engee.load(Path, force=true) # Upload a model
engee.run(model, verbose=true); # Launch the model
engee.close(NemeModel, force=true); # Close the model
end
end
# Launching the model
rum_model("Equalizer","/user/start/examples/dsp/equalizer")
function parse_csv_engee(filename :: String)
file = open(filename)
line = readline(file)
name_idx = vcat(0,findall(',', line), length(line)+1)
names = collect([line[(name_idx[it-1]+1):(name_idx[it]-1)] for it ∈ 2:length(name_idx)])
data = collect([it for it ∈ (line -> eval(Meta.parse(line)))(readline(file))])
while !eof(file)
data = ((a, b) -> [a;;;b]).(data, collect([it for it ∈ (line -> eval(Meta.parse(line)))(readline(file))]))
end
close(file)
return Dict(names .=> data)
end
# Reading CSV
out = parse_csv_engee("/user/start/examples/dsp/equalizer/out.csv");
out_t = out["time"];
out_data = out["1"];
# Plotting graphs
Eng_data = reshape(out_data,808)
plot(Eng_data[1:8:end])
plot!(Eng_data[2:8:end])
plot!(Eng_data[3:8:end])
plot!(Eng_data[4:8:end])
plot!(Eng_data[5:8:end])
plot!(Eng_data[6:8:end])
plot!(Eng_data[7:8:end])
plot!(Eng_data[8:8:end])
plot!(title = "Simulation results in Engee", ylabel = "Data", xlabel="Time, c")
Launching and analyzing the Simulink model
Let's compare the simulation results in Engee and Simulink. To do this, we will first run a simulation of the model.
mat"run_test_model('Equalizer')";
Let's look at the results in Simulink:
mat"whos" # Output all variables stored in the workspace
# Reading the model output
sim = mat"SysOutput.Data";
# Plotting graphs
Sim_data = reshape(sim,808)
plot(Sim_data[1:8:end])
plot!(Sim_data[2:8:end])
plot!(Sim_data[3:8:end])
plot!(Sim_data[4:8:end])
plot!(Sim_data[5:8:end])
plot!(Sim_data[6:8:end])
plot!(Sim_data[7:8:end])
plot!(Sim_data[8:8:end])
plot!(title = "Simulation results in Simulink", ylabel = "Response", xlabel="Time, c")
Now let's plot the difference between the output data of Simulink and Engee, and also calculate the average error value.
plot(Sim_data-Eng_data)
print("Error rate: " * string((sum(abs.(Sim_data-Eng_data)))/length(Eng_data)))
As we can see from the graphs presented above and the result of calculating the average error, the models work almost identically.
Conclusion
In this example, we implemented an equalizer, and also compared the capabilities of Engee regarding modeling in Simulink and showed the options for connecting the MATLAB core to solve problems inside the Engee development environment.