The averaging filter
An averaging filter is a type of digital filter widely used in digital signal and image processing to reduce noise levels. The median filter is a nonlinear FIR filter.
In this example, we will look at its simplified implementation and see how well it works. The figure below shows the model of the implemented filter.
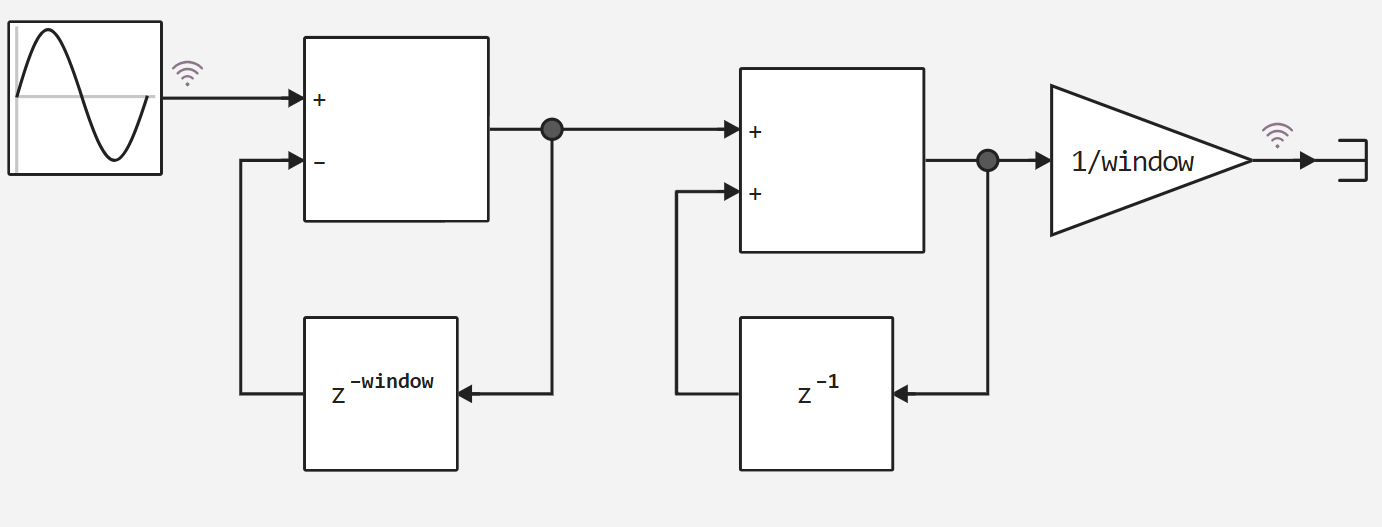
In this model, the window parameter determines the size of the filtering window.
Next, we will define the function of launching the model and declare several options for the dimension of the filtering window.
# Enabling the auxiliary model launch function.
function run_model( name_model)
Path = (@__DIR__) * "/" * name_model * ".engee"
if name_model in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] # Checking the condition for loading a model into the kernel
model = engee.open( name_model ) # Open the model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
else
model = engee.load( Path, force=true ) # Upload a model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
engee.close( name_model, force=true ); # Close the model
end
sleep(5)
return model_output
end
window_arr = Int64[10,20,100,1e3];
Next, let's run this model in a loop with different parameters of the averaging window and compare the results.
out_arr = zeros(1001,4)
window = 0;
for i in 1:4
window = window_arr[i]
run_model("Averaging_filter") # Launching the model.
out = collect(simout["Averaging_filter/out"]);
out_arr[:,i] = out.value
end
plot(out_arr, label=["window = 10" "window = 20" "window = 100" "window = 1000"])
Conclusion
As we can see from the resulting graph, the larger the thinning window, the lower the signal amplitude, this is due to the fact that a sine wave is applied to the input and with a larger averaging window we find averages between all possible signal values, including the maxima and minima of the function, the filter itself works correctly and performs its main function.