Spectral classifier
This example shows a model of a spectral classifier.
This model, developed at Engee, demonstrates the use
of a system of blocks and masks to implement digital
signal processing algorithms. This approach allows for efficient data processing and analysis
, providing flexibility and convenience when designing complex systems.
The spectral classifier
is used to isolate and identify the frequency components of a signal,
which is a key element in the recognition and analysis of various types
of signals. In this example, speech became such a signal.
By changing the parameters – band widths and
thresholds – you can adapt the algorithm to specific requirements, increasing
the accuracy of the result.
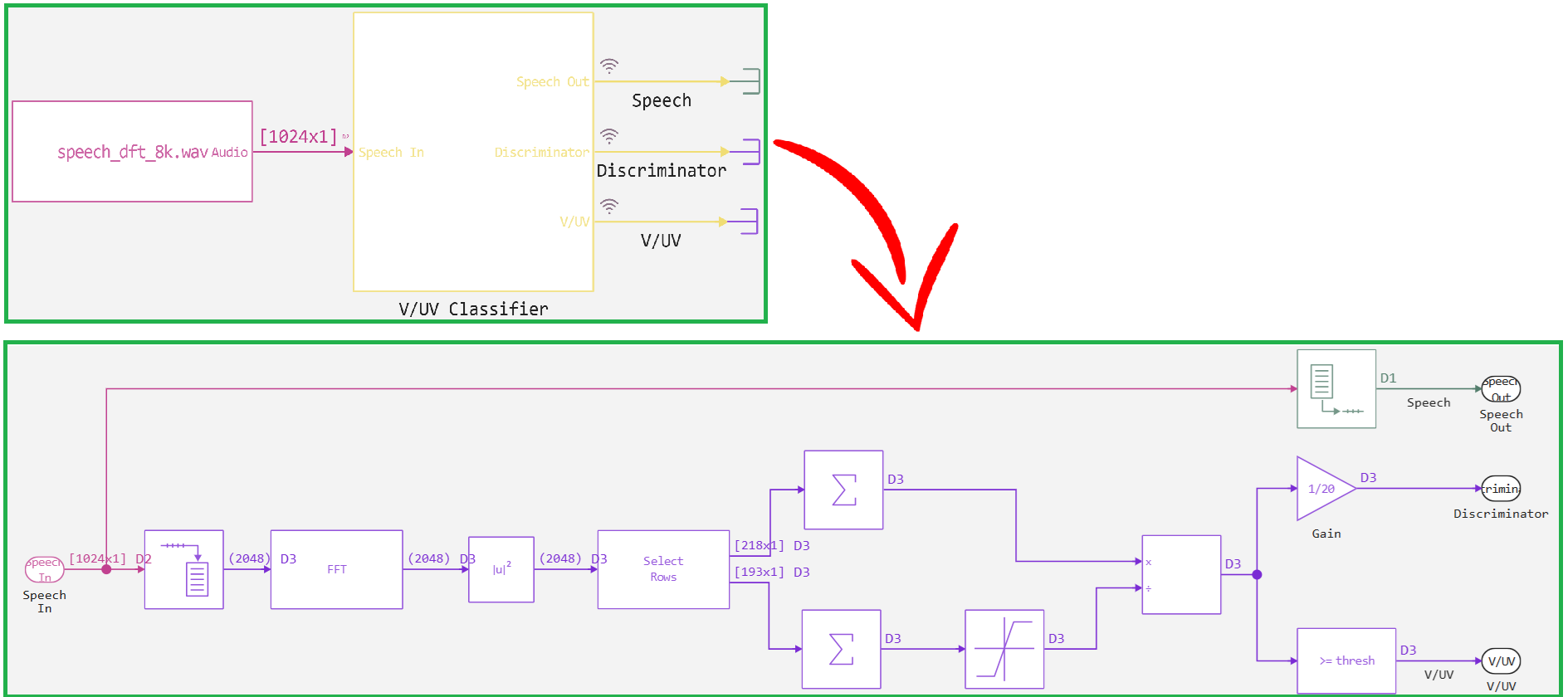
The implemented model is shown in the figure below.
Auxiliary functions
Pkg.add("WAV")
# Enabling the auxiliary model launch function.
function run_model( name_model)
Path = (@__DIR__) * "/" * name_model * ".engee"
if name_model in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] # Checking the condition for loading a model into the kernel
model = engee.open( name_model ) # Open the model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
else
model = engee.load( Path, force=true ) # Upload a model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
engee.close( name_model, force=true ); # Close the model
end
sleep(5)
return model_output
end
using FFTW
# Calculation of the signal spectrum
function compute_spectrum(signal, fs)
n = length(signal)
spectrum = abs.(fft(signal)) / n
freqs = (0:n-1) .* (fs / n)
spectrum[1:Int(n/2)], freqs[1:Int(n/2)] # Return half of the spectrum (for convenience)
end
using WAV;
using .EngeeDSP;
function audioplayer(patch, Samples_per_audio_channel);
s, fs = wavread(patch);
buf = IOBuffer();
wavwrite(s, buf; Fs=fs);
data = base64encode(unsafe_string(pointer(buf.data), buf.size));
display("text/html", """<audio controls="controls" {autoplay}>
<source src="data:audio/wav;base64,$data" type="audio/wav" />
Your browser does not support the audio element.
</audio>""");
return s
end
Launching the model and analyzing the results
Let's listen to the input signal and analyze its spectrum.
signal = audioplayer("$(@__DIR__)/speech_dft_8k.wav", 256);
gr()
spectrum_inp, freqs_inp = compute_spectrum(signal, 8000)
plot(freqs_inp, spectrum_inp, xlabel="Frequency (Hz)", ylabel="Amplitude")
This audio contains a speech recording. The useful frequencies are within 1 MHz.
Let's try to classify them using our model.
First, let's set the settings for our block.
fs = 8000; # Sampling rate
framesize = 2048; # The size of the analysis segment
nfft = 1024; # FFT Size
df = fs/nfft; # Bin width FFT
f1 = 200; # The lower limit of the first band (Hz)
f2 = 1900; # The upper limit of the first band (Hz)
f3 = 2000; # The lower limit of the second band (Hz)
f4 = 3500; # The upper limit of the second band (Hz)
indx1 = round(Int,f1/df); # Indexes in the FFT output data array
indx2 = round(Int,f2/df);
indx3 = round(Int,f3/df);
indx4 = round(Int,f4/df);
Now let's run the model and analyze the results.
run_model("simple_classifier") # Launching the model.
Speech = collect(simout["simple_classifier/V/Speech"])
V_on_UV = collect(simout["simple_classifier/V/V/UV"])
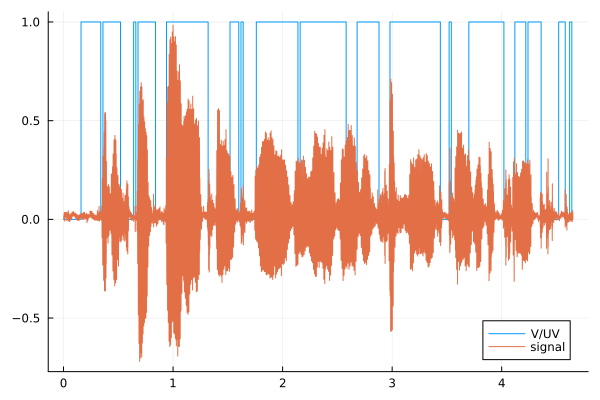
plot(V_on_UV.time, V_on_UV.value, seriestype=:steppost, label="V/UV")
plot!(Speech.time, Speech.value, label="signal")
As we can see, areas have been selected from the signal
that meet the spectral
characteristics set in
the mask settings of our block.
Conclusion
In this example
, the spectral classifier model and the possibilities
of its application for audio signal processing were analyzed.