Value added tax (VAT)
VAT is an indirect tax. The calculation is made by the seller when selling goods (works, services, property rights) to the buyer.
This model allows us to calculate VAT on any purchases by specifying them as an array of prices.
The model itself is shown in the picture below.
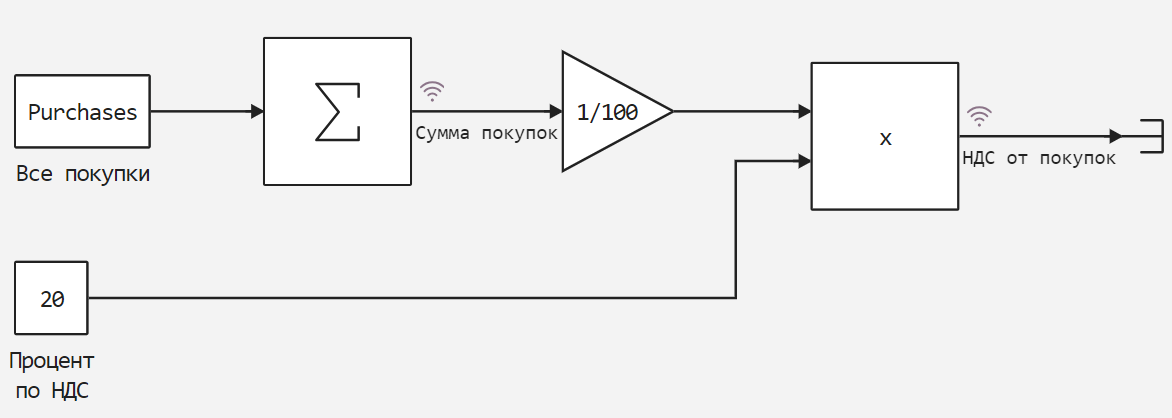
Next, we will add an auxiliary function of the model and specify the shopping list.
In [ ]:
# Enabling the auxiliary model launch function.
function run_model( name_model)
Path = (@__DIR__) * "/" * name_model * ".engee"
if name_model in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] # Checking the condition for loading a model into the kernel
model = engee.open( name_model ) # Open the model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
else
model = engee.load( Path, force=true ) # Upload a model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
engee.close( name_model, force=true ); # Close the model
end
sleep(5)
return model_output
end
Out[0]:
In [ ]:
Purchases = [100, 120, 12.55];
Let's run the model and output the calculated tax amount.
In [ ]:
run_model("NDS") # Launching the model.
Sum = collect(simout["NDS/Amount of purchases"]);
NDS = collect(simout["NDS/VAT on purchases"]);
println("Amount of purchases: " * string(Sum.value))
println("VAT on purchases: " * string(NDS.value))
Conclusion
In this example, we have demonstrated the possibilities of using Engee for everyday tasks.