Rod
Axially flexible rod or cable.
blockType: Engee1DMechanical.Elements.Translational.Rod
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Rod It is an axially flexible rod or cable that stretches or contracts.
Model
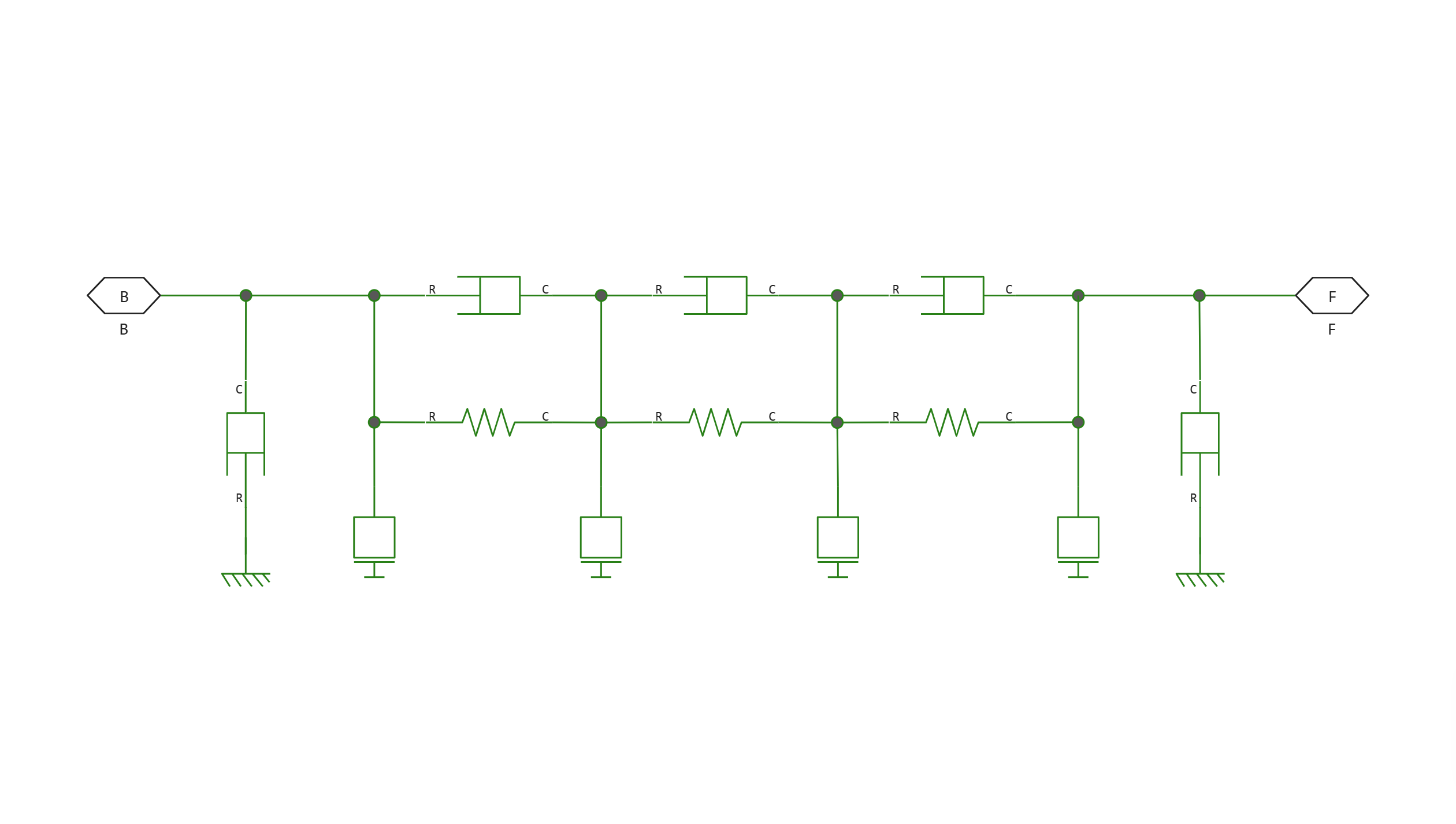
To represent a rod or cable, the block uses a model with concentrated parameters. The model consists of concentrated masses connected in series by means of sets of parallel connected spring and damper circuits. The spring represents elasticity. A damper represents damping in a material.
The model with one flexible element has a natural frequency close to the first natural frequency of the model with distributed parameters. For a more accurate analysis, select 2, 4, 8 or more flexible elements.
An equivalent physical network contains spring and damper circuits and blocks of masses. The total mass of the rod is evenly distributed over the mass blocks. The stiffness of the spring in each spring and damper chain is equal to the stiffness of the rod material multiplied by .
The equations
Defining equations for the model:
where
-
— rod damping;
-
— the damping coefficient of the rod material;
-
— stiffness of the rod;
-
— the cross-sectional area of the rod;
-
— the outer diameter of the rod;
-
— the inner diameter of the rod, where
-
for a solid rod,
-
for an annular, i.e. hollow, rod;
-
-
— Young’s modulus, that is, the modulus of elasticity of the rod material;
-
— the length of the rod;
-
— the mass of the rod;
-
— the density of the rod material.
Ports
Conserving
#
B
—
drive shaft
Translational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the drive shaft or rod inlet.
| Program usage name |
|
#
F
—
driven shaft
Translational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to a driven shaft or rod outlet.
| Program usage name |
|
Parameters
Rod
#
Parameterization —
parameterization method
By stiffness and inertia | By material and geometry
Details
The parameterization method.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Stiffness —
stiffness of the material
N/m | mN/m | kN/m | MN/m | GN/m | kgf/m | lbf/ft | lbf/in
Details
The rigidity of the material.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Parameterization meaning By stiffness and inertia.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Mass —
rod weight
kg | mg | g | t | lbm | oz | slug
Details
The mass of the rod.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Parameterization meaning By stiffness and inertia.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Damping ratio — material damping coefficient
Details
The damping coefficient of the material.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Number of flexible elements —
Details
Number of flexible elements for an approximation.
More flexible elements increases the accuracy of the model, but reduces the simulation performance, i.e. the simulation speed. Single-element model ( ) demonstrates a natural frequency close to the first natural frequency of a continuous model with distributed parameters.
If accuracy is more important than performance, choose 2, 4, 8 or more flexible elements. For example, the four lowest natural frequencies are represented with precision 0.1, 1.9, 1.6 and 5.3%, respectively, in the 16-element model.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Geometry —
cross section of the rod
Solid | Annular
Details
The shape of the cross-section of the rod.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Parameterization meaning By material and geometry.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Length —
rod length
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The length of the rod.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Parameterization meaning By material and geometry.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Outer diameter —
the outer diameter of the rod
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The outer diameter of the rod.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Parameterization meaning By material and geometry.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Density —
material density
kg/m^3 | g/m^3 | g/cm^3 | g/mm^3 | lbm/ft^3 | lbm/gal | lbm/in^3
Details
The density of the material.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Parameterization meaning By material and geometry.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Young's modulus —
Young’s module
Pa | uPa | hPa | kPa | MPa | GPa | kgf/m^2 | kgf/cm^2 | kgf/mm^2 | mbar | bar | kbar | atm | ksi | psi | mmHg | inHg
Details
Young’s modulus for the rod material.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Parameterization meaning By material and geometry.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Inner diameter —
inner diameter of the rod
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
The inner diameter of the rod. If the rod is solid, specify the value `0'.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Parameterization meaning By material and geometry, and for the parameter Geometry meaning Annular.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Viscous Losses
#
Viscous friction coefficients at base (B) and follower (F) —
coefficients of viscous friction
N*s/m | kgf*s/m | lbf*s/ft | lbf*s/in
Details
Coefficients of viscous friction in ports B and F.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Initial Conditions
#
Initial deflection —
initial deviation
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
Rod deflection at the beginning of the simulation.
A positive initial deviation leads to a positive displacement of the end of the rod with port B relative to the end of the rod with port F.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial velocity —
initial velocity
m/s | mm/s | cm/s | km/s | m/hr | km/hr | in/s | ft/s | mi/s | ft/min | mi/hr | kn
Details
The longitudinal velocity of the end of the rod with port B relative to the end of the rod with port F at the beginning of the simulation.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |



