decimate
Decimation is a decrease in the sampling rate by an integer number of times.
| Library |
|
Arguments
Input arguments
# x — input signal
+
vector
Details
The input signal is in the form of a vector.
| Data types |
|
# r is the decimation coefficient
+
scalar
Details
The decimation coefficient, set as a positive integer. To get the best results when r more 13, divide r use smaller multipliers and call decimate several times.
| Data types |
|
# n — filtering order
+
scalar
Details
The filtering order is specified as a positive integer. It is not recommended to use the higher filtering order for the IIR filter. 13 due to numerical instability. In such cases, the function outputs a warning.
| Data types |
|
Output arguments
# y is a signal with a reduced sampling rate
Details
A signal with a reduced sampling rate.
| Data types |
|
Examples
Signal decimation
Details
Generate a sinusoidal signal with a sampling frequency 4 kHz. Reduce the sampling rate by four times.
import EngeeDSP.Functions: decimate
t = 0:1/4e3:1
x = sin.(2*pi*30*t) + sin.(2*pi*60*t)
y = decimate(x, 4)Let’s draw graphs of the source and the signal with a reduced sampling rate.
p1 = plot(0:120, x[1:121],
seriestype = :stem,
marker = :circle,
markersize = 3,
xlabel = "Sample Number",
ylabel = "Original",
grid = true,
legend = false)
p2 = plot(0:30, y[1:31],
seriestype = :stem,
marker = :circle,
markersize = 3,
xlabel = "Sample Number",
ylabel = "Decimated",
grid = true,
legend = false)
plot(p1, p2, layout = (2, 1))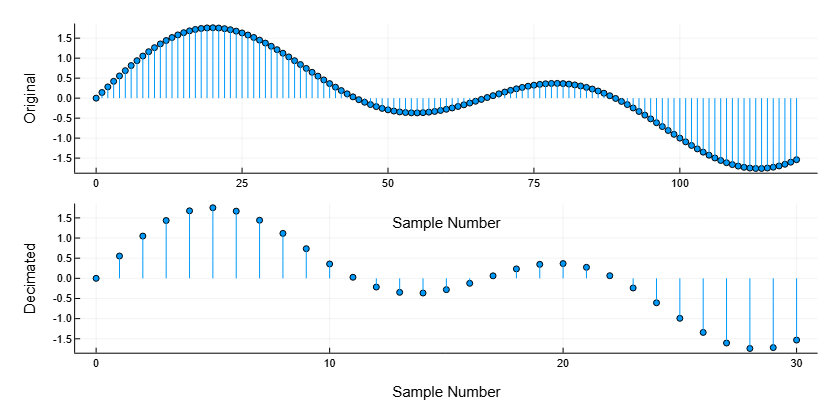
Decimation of the signal using a Chebyshev filter
Details
We will generate a signal from two sinusoids. We will reduce the sampling rate by a factor of 13 using the Chebyshev filter of the fifth order. Let’s plot the source and output signals.
import EngeeDSP.Functions: decimate
r = 13
n = 16:365
lx = length(n)
x = sin.(2*pi*n/153) + cos.(2*pi*n/127)
y = decimate(x, r, 5)
plot(0:lx-1, x,
seriestype=:scatter,
marker=:circle,
label="Original",
framestyle=:origin,
grid = true)
plot!(lx-1:-r:0, reverse(y),
seriestype=:scatter,
marker=:circle,
color=:red,
markersize=4,
label="Decimated",
grid = true)
xlabel!("Sample number")
ylabel!("Signal")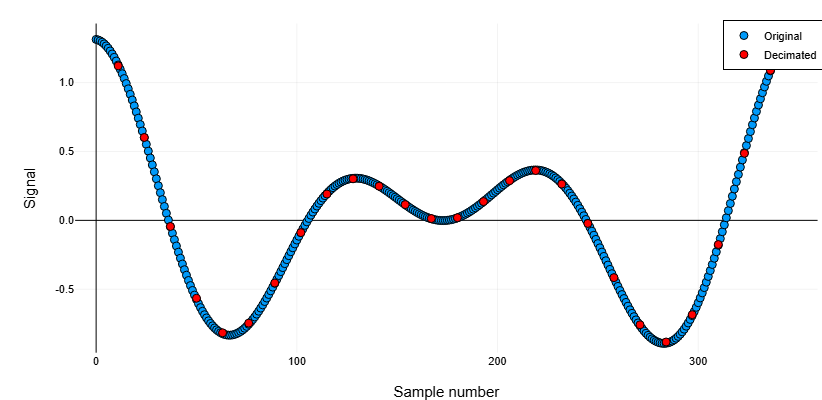
Decimation of the signal using an FIR filter
Details
Generate a sinusoidal signal with a sampling frequency 4 kHz. Reduce the sampling rate by four times.
We will generate a signal from two sinusoids. Reduce the sampling rate by a factor of 13 using an FIR filter. Let’s plot the source and output signals.
import EngeeDSP.Functions: decimate
r = 13
n = 16:365
lx = length(n)
x = sin.(2*pi*n/153) + cos.(2*pi*n/127)
y = decimate(x, r, 82, "fir")
plot(0:lx-1, x,
seriestype=:scatter,
marker=:circle,
label="Original",
framestyle=:origin,
grid=true)
plot!(0:r:lx-1, y,
seriestype=:scatter,
marker=:circle,
color=:red,
markersize=4,
label="Decimated",
grid=true)
xlabel!("Sample number")
ylabel!("Signal")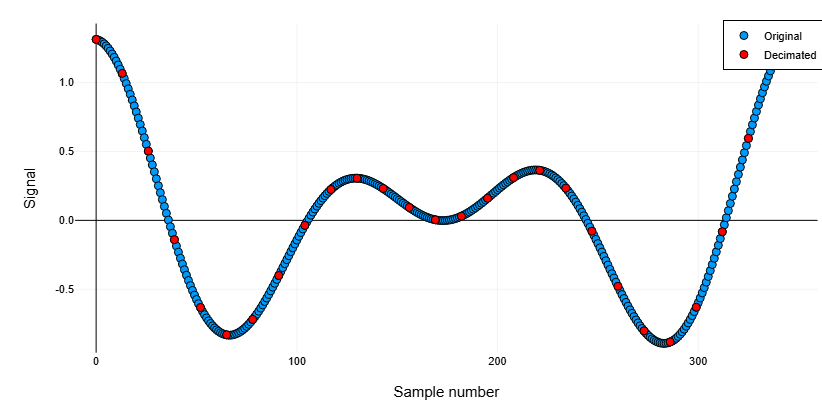
Algorithms
Decimation reduces the initial sampling rate of the sequence to a lower one. This is the opposite of interpolation. Function decimate applies low-pass filtering to the input signal to protect against spectrum aliasing and decimates the result. The function uses the decimation algorithms 8.2 and 8.3 from [1].
-
decimatecreates a low-pass filter. By default, the Chebyshev I BIH filter is used. This filter has a normalized cutoff frequency equal to0.8/r, and a bandwidth ripple equal to0.05dB. Sometimes the specified filtering order leads to bandwidth distortion due to rounding errors accumulated as a result of the convolutions required to create the transfer function. Functiondecimateautomatically reduces the filtering order when distortion causes the amplitude response at the cutoff frequency to differ from the ripple by more than10-6.When selecting an option
"fir"functiondecimateuses the functionfir1for designing a low-pass FIR filter with a cutoff frequency1/r. -
When using an FIR filter, the function
decimatefilters the input sequence in only one direction. This saves memory and is useful for working with long sequences. In the case of an IIR filter, the functiondecimateapplies the filter in the forward and reverse directions usingfiltfiltto eliminate phase distortion. In effect, this process doubles the filtering order. In both cases, the function minimizes transient effects at both ends of the signal by matching endpoint conditions. -
And finally, the function
decimateresamples the data, selecting allr-e points inside the filtered signal. In the re-sampling sequence (y),y(end)respondx(end)when an IIR filter is used, andy(1)respondx(1)when using the FIR filter.