Masks of code cells
| Working with code cell masks is also discussed in detail in the example. Masking code cells of interactive scripts |
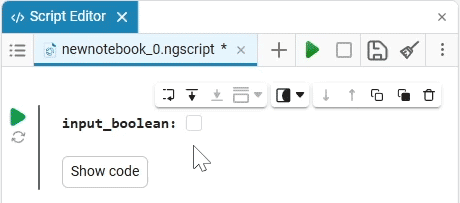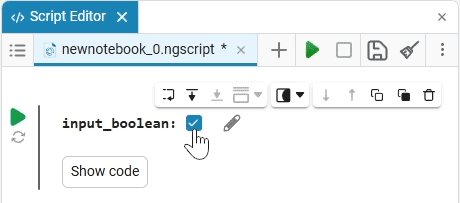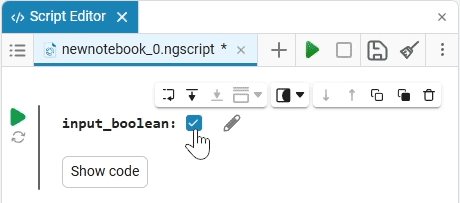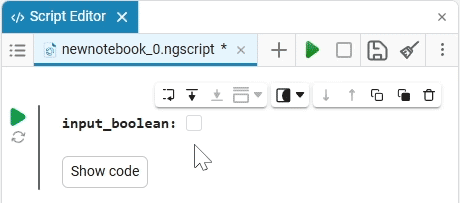
Interactive controls are often used for more convenient parameterization and visual representation of the code. They can be various data entry fields, lists, sliders, etc. In Engee, such elements are implemented in script editor ![]() using masks of code cells.
using masks of code cells.
Mask of code cells  — it is a tool that turns variables in code cells of Engee scripts into interactive controls. Applying a mask allows you to completely hide the code of the cells, while maintaining their full functionality.
— it is a tool that turns variables in code cells of Engee scripts into interactive controls. Applying a mask allows you to completely hide the code of the cells, while maintaining their full functionality.
Creating a code cell mask
To create a code cell mask, hover over the code cell and select in the tools Mask  and Add field:
and Add field:

Adding a field will open an interactive menu. Depending on the type of field, the add menu changes its options (the available variable types change and/or additional settings appear). There are four types available in total:
-
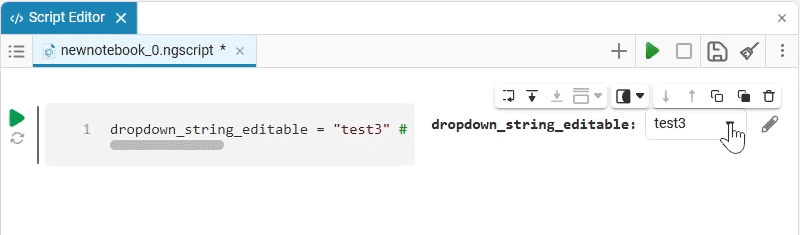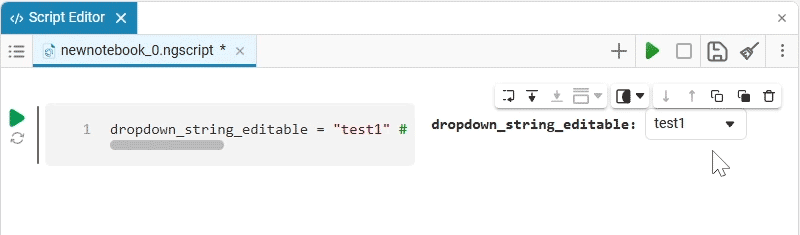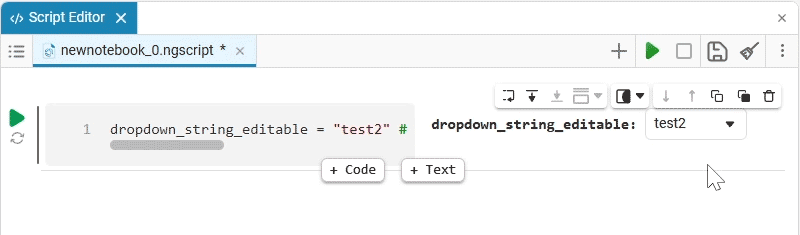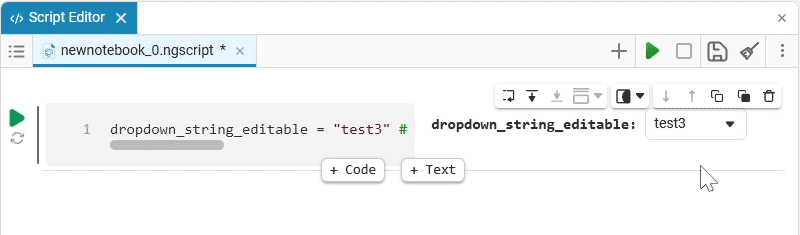
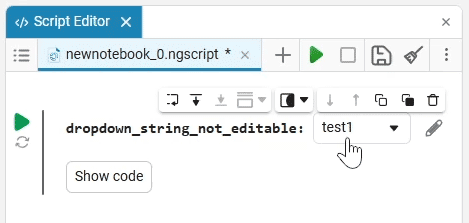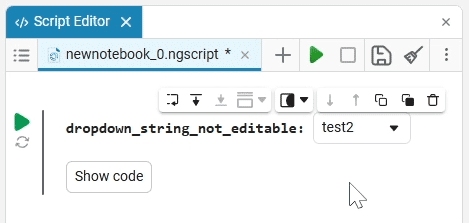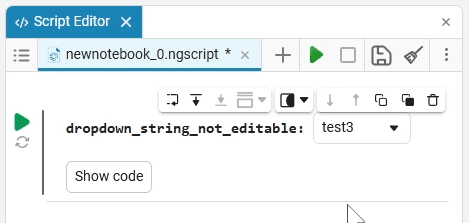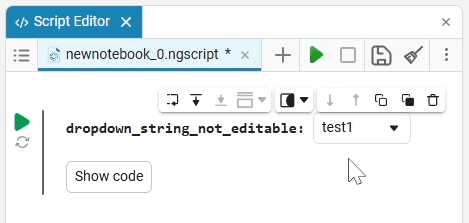
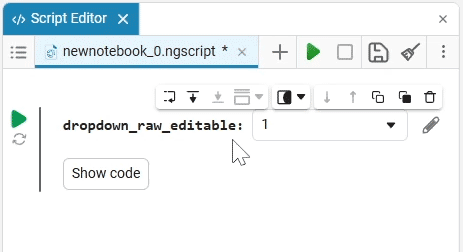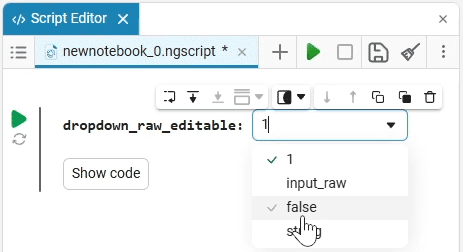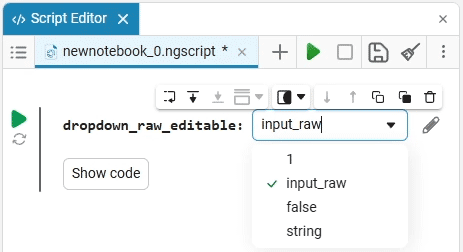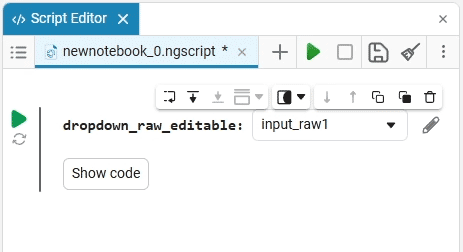
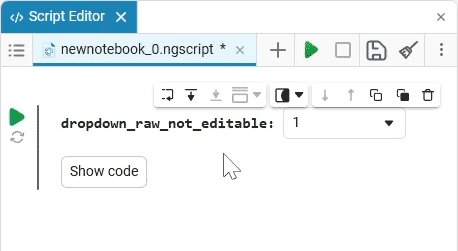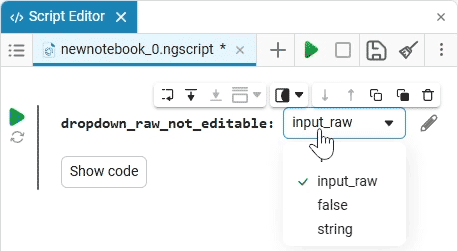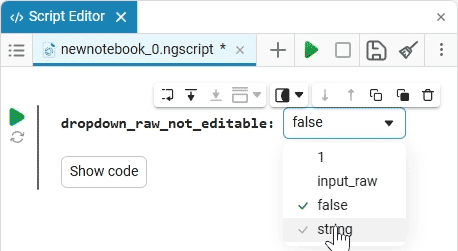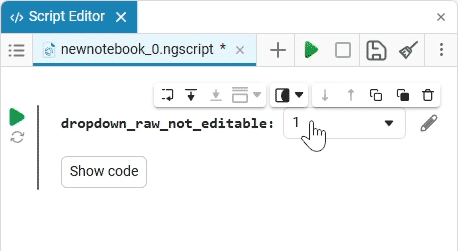
Select (dropdown) is a drop—down list of options with a choice of one option. When you click on the drop-down list, you can select the desired option.
example of the drop-down list
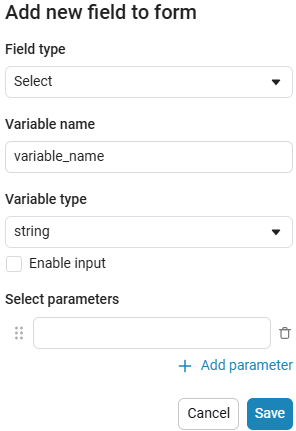
Create an empty code cell and add a drop-down list mask with the following settings:
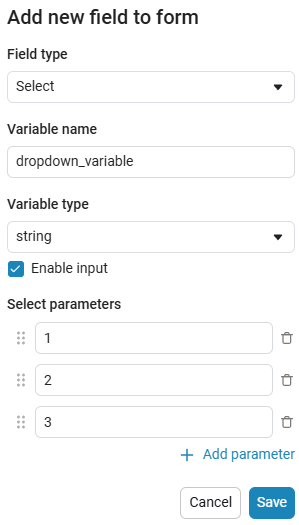
After saving, the code cell will change its appearance.:
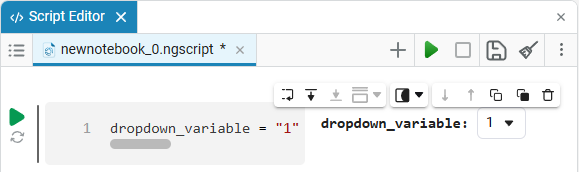
In this case, the following code will fill in the contents of the code cell:
dropdown_variable = "1" # @param ["1","2","3"] {allow-input:true}By changing this code, you can change the contents of the mask without accessing the tool. Mask
 .
. -
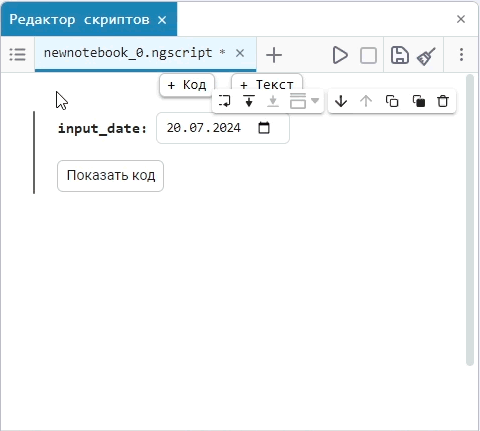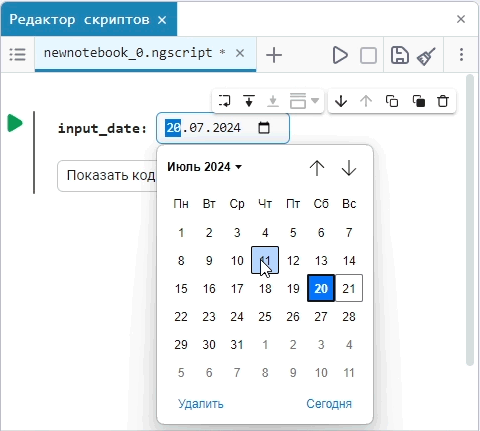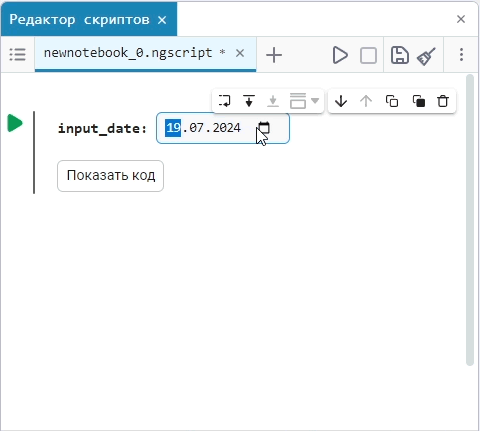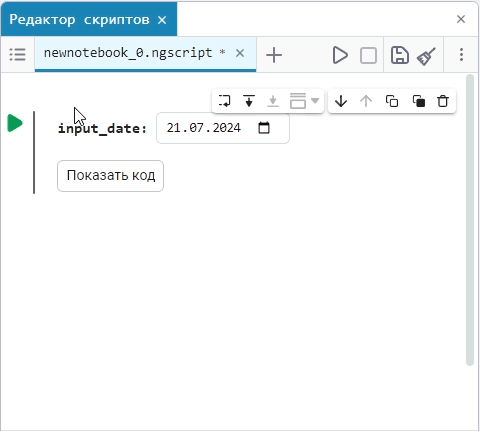
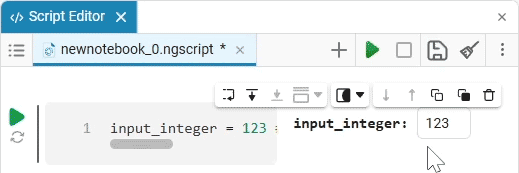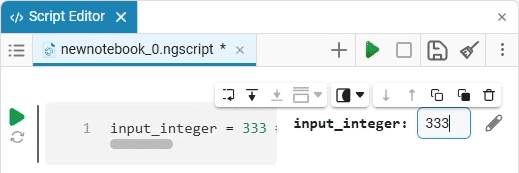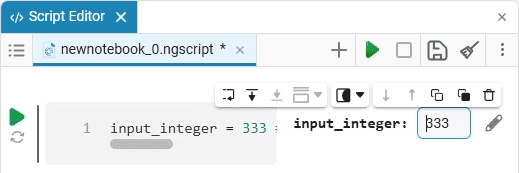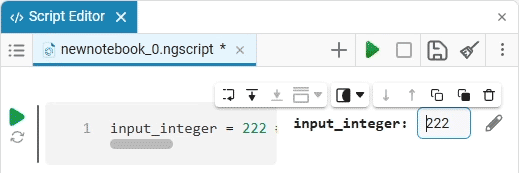
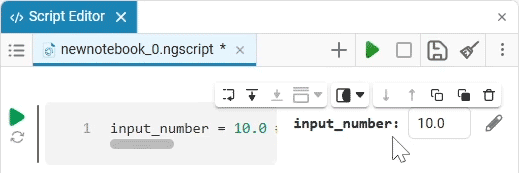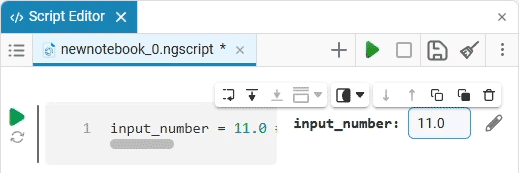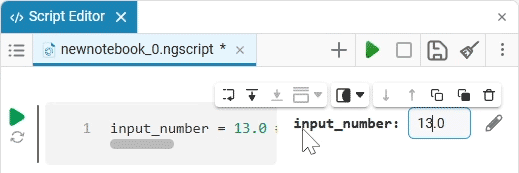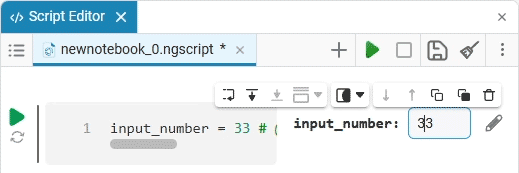
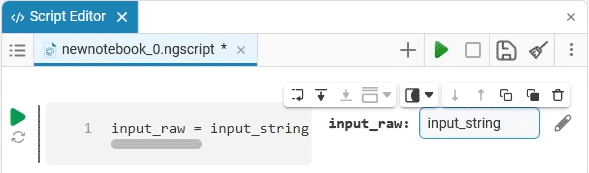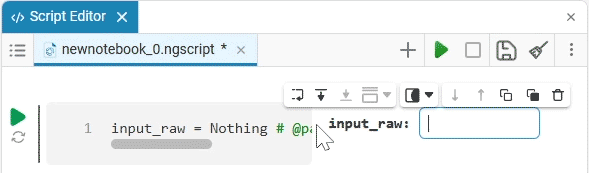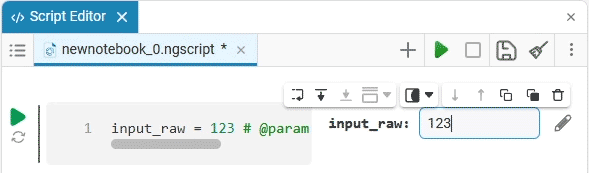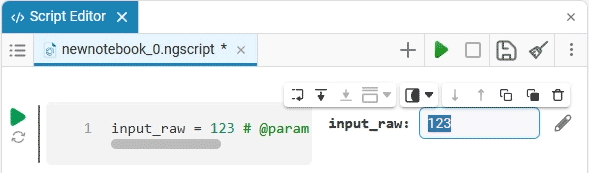
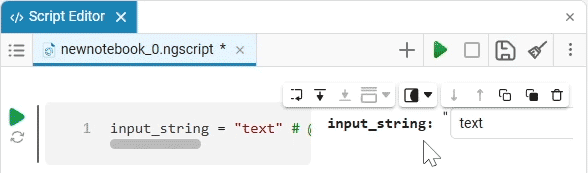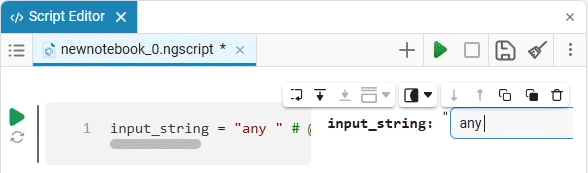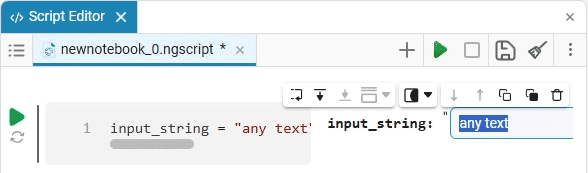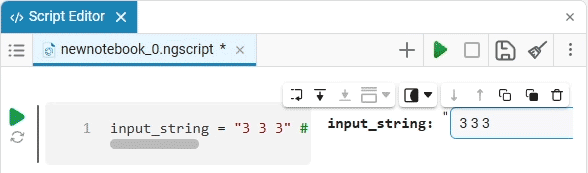
Input (input) is a window for entering data.
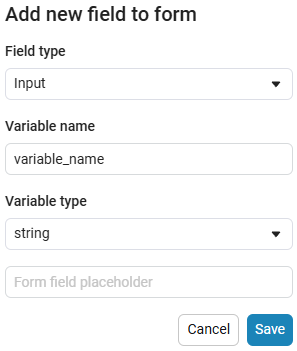
example of the input field
Create an empty code cell and add an input field mask with the following settings:
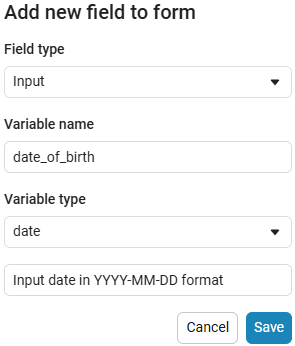
Here, the placeholder is the text that is displayed inside the input field until any data is entered. It is usually used to give a hint about what information needs to be entered. For example, for the date field, the option
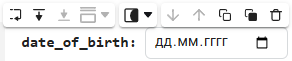
Enter the date in the YYYY-MM-DD formatis perfect.We get the following option:
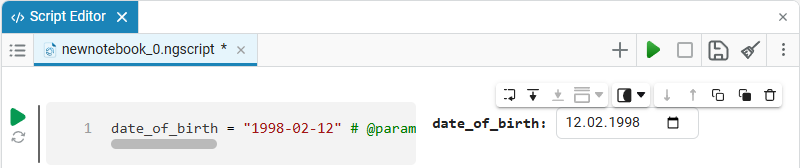
In this case, the following code will fill in the contents of the code cell:
date_of_birth = "2025-01-16" # @param {type:"date",placeholder:"Enter the date in the YYYY-MM-DD format"}Based on the name of the variable, we need the date of birth, not today’s date (set automatically by the system), so we’ll change the date to the desired one. You can change the date both in the mask and in the code cell itself. When you remove the date mask, you can see that the placeholder is working correctly and improving the user experience.:
-
Markdown — this is a Markdown markup representation for implementing code masks.
example of Markdown
Create an empty code cell and add a Markdown mask with the following settings:
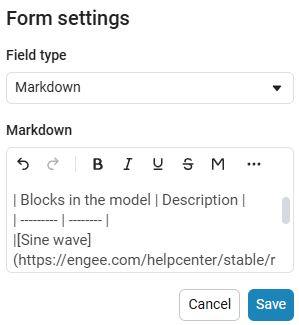
# Building a sine wave To build a simple sine wave, use the following blocks: |Blocks in the model|Description| | --------- | -------- | |[Sine wave](https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/ru/base-lib-sources/sine-wave.html)|A sinusoidal signal generator.| |[Terminator](https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/ru/base-lib-sinks/terminator.html)|Output port plug.|We get the following option:
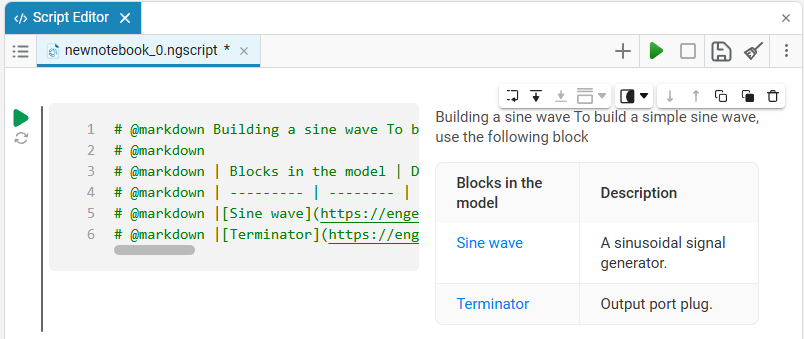
In this case, the following code will fill in the contents of the code cell:
# @markdown # Constructing a sine wave # @markdown # @markdown To build a simple sinuoside, use the following blocks: # @markdown # @markdown |Blocks in the model|Description| # @markdown | --------- | -------- | # @markdown |[Sine wave](https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/ru/base-lib-sources/sine-wave.html)|A sinusoidal signal generator.| # @markdown |[Terminator](https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/ru/base-lib-sinks/terminator.html)|Output port plug.| -
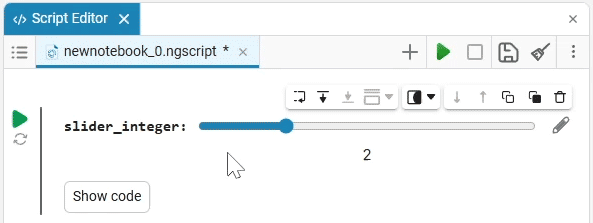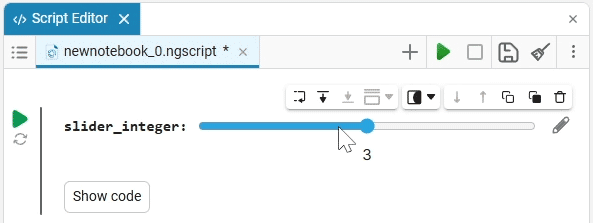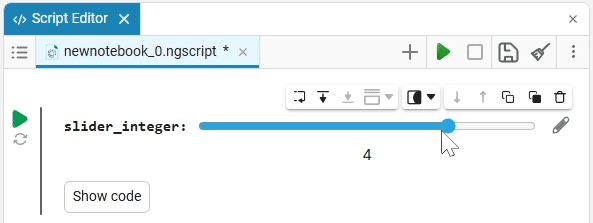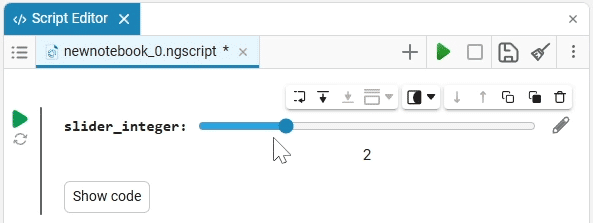
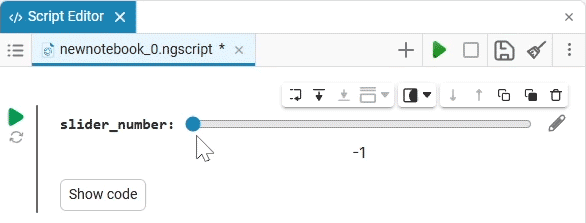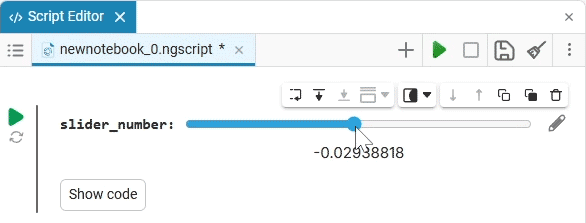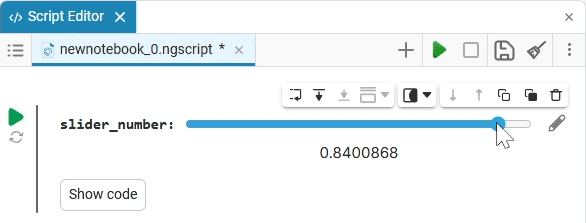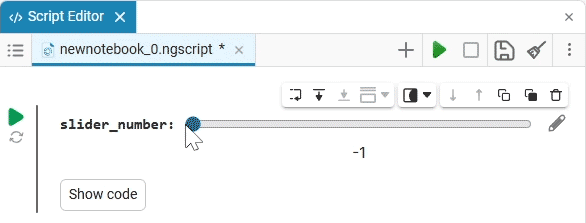
Slider slider is a representation of a slider with a selection of values from a given range. The selection of a value from the range is realized by moving the slider on the scale.
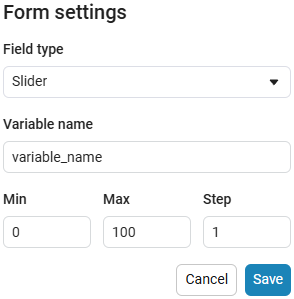
The slider example
Create an empty code cell and add a slider mask with the following settings:
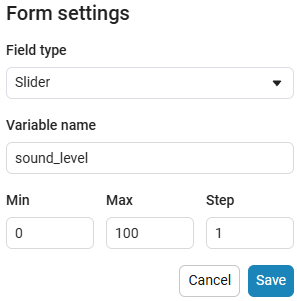
We get the following option:
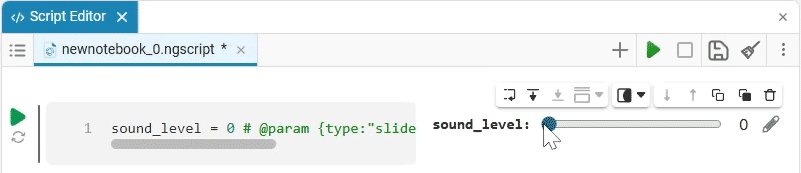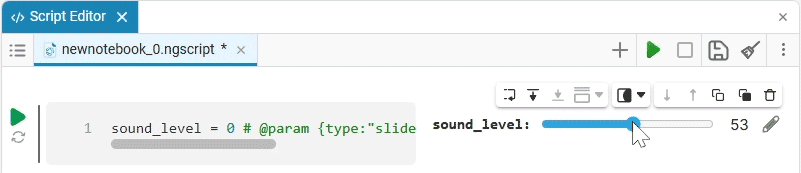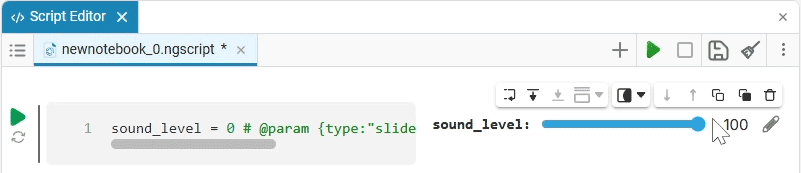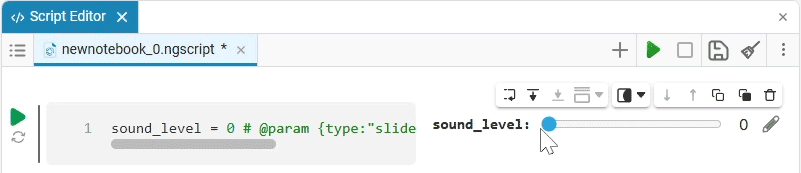
In this case, the following code will fill in the contents of the code cell:
volume_level = 0 # @param {type:"slider",min:0,max:100,step:1}
To edit the applied mask, hover the mouse cursor over it and click the icon  . Since the code of the masked cells is fully operational, you can edit not only the mask, but also the cell code.
. Since the code of the masked cells is fully operational, you can edit not only the mask, but also the cell code.
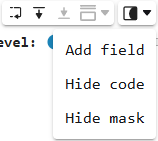
To add a new field, hide the code, or hide the mask, use the context menu of the mask again.  :
:
Creating masks without an editor interface
| This section describes some of the syntax features of masked cells that may be useful in your practice. We recommend that you read this section even if you do not plan to create masks manually. |
In some cases, it may be more convenient to create a mask without using the mask creation context menu.  Therefore, let’s look at this process in more detail.
Therefore, let’s look at this process in more detail.
To create masks manually, you need to recreate the syntax yourself, consisting of:
-
The name of the control. Some of the elements have their own parameters for customizing behavior.;
-
The comment
#and the parameter starting with `@'.
The controls for code cell masks have already been described above, there are only four of them. Each element has its own approach for manual creation. Let’s look at examples for each of them.:
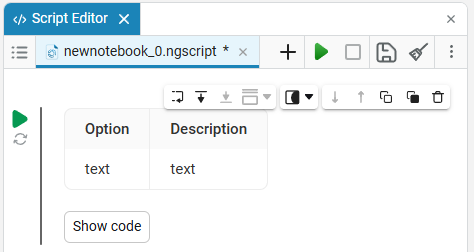
description of drop-down list types and subtypes
|
description of input window typesYou can use different types of input fields to collect information, and each type is suitable for a specific type of data.
|
A description of slider types
|
'markdown` is a Markdown markup representation for implementing code masks. description of markdown featuresUsing the code mask
|