nuttallwin
The minimum four—term Blackman-Harris window defined by Nuttall.
| Library |
|
Syntax
Function call
-
w = nuttallwin(L)— returnsL`is a point-symmetric four—membered Blackman-Harris window defined by Nuttall. The coefficients of this window differ from the coefficients of the Blackman—Harris window calculated using `blackmanharris, and produce slightly smaller side lobes.
Arguments
Input arguments
# L — window length
+
scalar
Details
The length of the window, set as a real positive number.
| Типы данных |
|
# sflag — window selection
+
"symmetric" (by default) | "periodic"
Details
The window selection method, set as "symmetric" or "periodic". For the equations defining symmetric and periodic windows, see Algorithms.
| Типы данных |
|
Output arguments
# w — The Blackman—Harris window, defined by Nuttall
+
column vector
Details
The Blackman—Harris window defined by Nuttall, returned as a column vector of length L. The function minimizes the maximum side lobes of the window. For the equations defining the window, see Algorithms.
Examples
Nuttall and Blackman—Harris Windows
Details
Let’s compare the Nuttall and Blackman—Harris windows generated by 64 points. Let’s display the result using plot.
import EngeeDSP.Functions: blackmanharris
import EngeeDSP.Functions: nuttallwin
using Plots
w = blackmanharris(64)
y = nuttallwin(64)
plot(w,
label = "Blackman-Harris Window",
xlabel = "Sample Number",
ylabel = "Amplitude",
linewidth = 2,
color = :blue,
grid = true)
plot!(y,
label = "Nuttall Window",
linewidth = 2,
color = :red)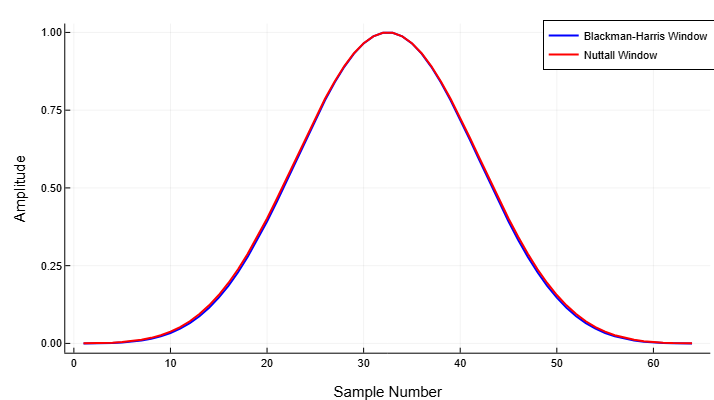
Calculate the maximum difference between the two windows.
max_diff = maximum(abs.(y - w))0.009894115670254444Algorithms
The equation for a symmetric four—term Blackman-Harris window defined by Nuttall has the form:
where , — the length of the window.
The equation for the periodic four—term Blackman-Harris window defined by Nuttall has the form:
where . The periodic window has a period .
The window coefficients are shown in the table.
| Ratio | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|