n-D Lookup Table
Approximate -dimensional function.
blockType: Lookup_n-D
Path in the library: |
Description
Block n-D Lookup Table calculates a sample representation of a function from variables:
,
where is the function it can be empirical.
The block icon n-D Lookup Table displays a graph of the function specified in the block.
The block maps the input data to the output value by searching or interpolating a table of values that are defined by the block parameters. The block supports the following interpolation methods: Flat, Linear point-slope, Linear Lagrange, Nearest and Cubic spline. You can apply these methods to a table of any dimension from 1 to 30.
You can read more about the interpolation methods here.: Methods for approximating function values
In the next block, the first input identifies the reference points of the first dimension (row), the second input identifies the reference points of the second dimension (column), and so on.
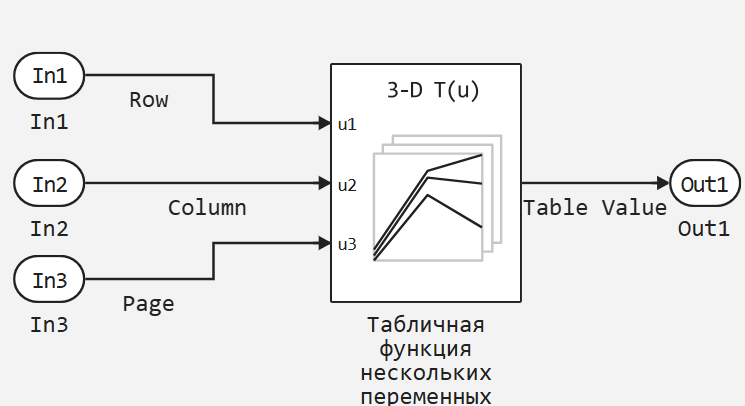
Specification of reference points and tabular data
These block parameters define the reference points and the data of the table.
| Block Parameter | Appointment |
|---|---|
Number of dimensions |
Specifies the number of dimensions in the table. |
Breakpoints 1 |
Sets the vector of reference points corresponding to each dimension of the table. |
Table data |
Defines a related set of output values. |
How the block generates output data
Block n-D Lookup Table generates output data by searching or evaluating table values based on input values.
| Block inputs | Block behavior n-D Lookup Table |
|---|---|
Match the values of the indexes in the vectors of the reference points. |
Outputs a tabular value at the intersection of rows, columns, and higher dimensions. |
They do not match the index values in the reference point datasets, but they are within the range. |
Interpolates the corresponding table values using the selected Interpolation method. |
They do not correspond to the index values in the reference point datasets and are out of range. |
Extrapolates the output value using the selected Extrapolation method. |
Other blocks that perform equivalent operations
You can use the block Interpolation Using Prelookup with a block Prelookup to perform an equivalent operation with n-D Lookup Table. This combination of blocks provides more flexibility, which can lead to more efficient modeling for linear interpolations.
Ports
Output
#
OUT_1
—
output data calculated by searching or evaluating table values
scalar | vector | matrix
Details
Output data generated by searching or evaluating table values based on input values.
| When the input data of a block… | Then the block n-D Lookup Table… |
|---|---|
Compares index values in sets of reference points. |
Outputs a tabular value at the intersection of rows, columns and higher dimensions of the reference points. |
Do not match the index values in the reference point sets, but are within range. |
Interpolates the corresponding table values using the one you selected Interpolation method. |
Do not match the index values in the reference point sets and are out of range. |
Extrapolates the output value using the one you selected Extrapolation method. |
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
Input
#
u1
—
input data of the first dimension (rows)
scalar | vector | matrix
Details
_No description._The real input data to port u1, matched to an output value by searching or interpolating a table of values you define.
Example: collect(1:10).
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
#
u2
—
input data of the 2nd measurement
scalar | vector | matrix
Details
Real input data to port u2, matched to an output value by searching or interpolating a table of values you define.
Example: collect(1:10).
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
#
uN
—
input data of the Nth measurement
scalar | vector | matrix
Details
Real input data on port uN, matched to an output value by searching or interpolating a table of values you define.
Example: collect(1:10).
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
Parameters
Main
#
Number of dimensions —
number of table measurements
Real number
Details
Enter the number of dimensions in the lookup table. This parameters defines:
-
The number of independent variables for the table and the number of block inputs.
-
The number of reference point sets to specify.
| To specify… | Need to do… |
|---|---|
1, 2, 3, or 4. |
Enter a positive integer directly into the field. |
A larger number of table sizes. |
Enter a positive integer directly in the field. The maximum number of table sizes supported by this block is |
For example, a table with dimension to to means that dimension size 1 is equal to , dimension size 2 is equal to and so on. must match the first anchor point, must match the second anchor point and so on.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Table data —
defining the output value table
Array of real and/or complex numbers
Details
Enter the output value table.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
Yes |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Main
#
Breakpoints 1 —
reference point values for the nth measurement
Array of real numbers
Details
Reference points for the nth dimension.
The number of parameters for specifying the reference point values depends on the value of the parameter Number of dimensions.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
Yes |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Lookup method
#
Interpolation method —
method of interpolation between the values of reference points
Flat | Nearest | Linear point-slope | Linear Lagrange | Cubic spline
Details
When the input signal falls between the reference point values, the unit interpolates the output value using the neighbouring reference points.
Read more about interpolation methods here: Methods for approximating function values
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Extrapolation method —
method of processing input values that go beyond the reference points
Clip | Linear | Cubic spline
Details
Choice of extrapolation method.
Read more about extrapolation methods here: Methods for approximating function values
Dependencies
To choose Cubic spline for Extrapolation method, you must also select Cubic spline for Interpolation method.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
No |
