sawtooth
A sawtooth or triangular wave.
| Library |
|
Arguments
Input arguments
# t — time values
+
vector | matrix
Details
Time values set as a vector or matrix. Function sawtooth works with the first dimension of the array from t with a larger size 1.
| Data types |
|
# xmax — maximum wave value
+
1 (by default) | scalar from 0 to 1
Details
The maximum value of the wave, given as a scalar of 0 before 1. Value xmax defines the point between 0 and , in which the wave reaches its maximum. The function increases with -1 before 1 on the interval from 0 before xmax, then linearly decreases from 1 before -1 on the interval xmax before . Then the form is repeated with a period in .
For example, xmax = 0.5 defines a standard triangular wave, symmetrical with respect to the time value , with peak-to-peak amplitude equal to 1.
| Data types |
|
Output arguments
# x — sawtooth wave
+
vector | matrix
Details
A sawtooth wave returned as a vector or matrix.
| Data types |
|
Examples
Sawtooth wave 50 Hz
Details
Generate 10 periods of a sawtooth signal with a fundamental frequency 50 Hz. Sampling rate — 1 kHz.
import EngeeDSP.Functions: sawtooth
T = 10 * (1/50)
fs = 1000
t = 0:1/fs:T-1/fs
x = sawtooth.(2*pi*50 .* t)
plot(t, x, grid = true)
xlabel!("Time (s)")
ylabel!("Amplitude")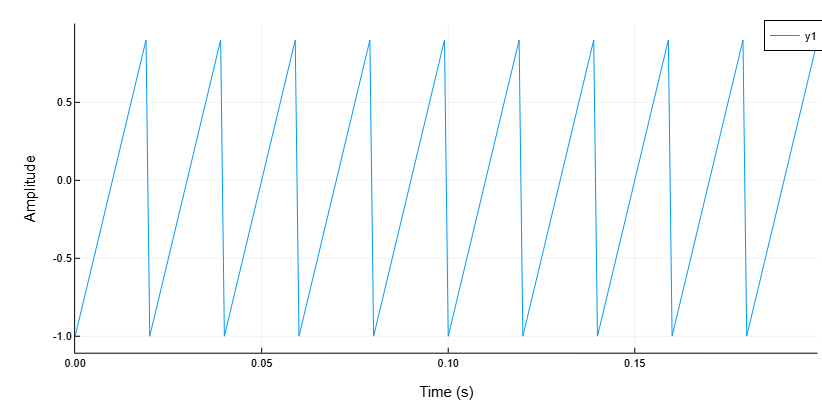
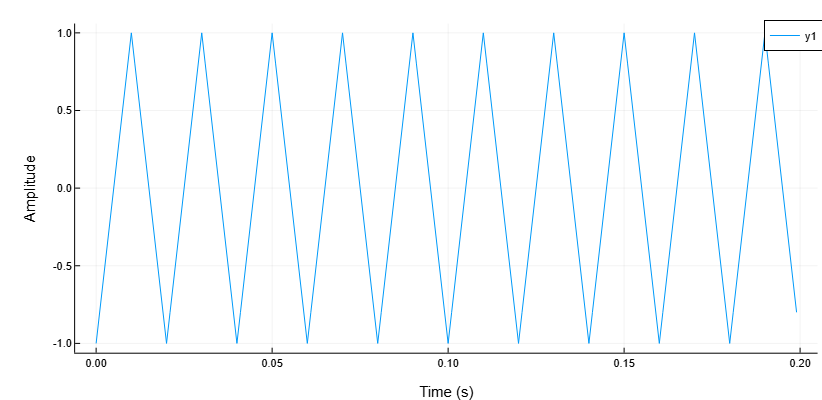
50 Hz triangle wave
Details
Generate 10 periods of a triangular signal with a fundamental frequency 50 Hz. Sampling rate — 1 kHz.
import EngeeDSP.Functions: sawtooth
T = 10 * (1/50)
fs = 1000
t = 0:1/fs:T-1/fs
x = sawtooth.(2*pi*50 .* t, 0.5)
plot(t, x, grid = true)
xlabel!("Time (s)")
ylabel!("Amplitude")