Eddy Current
Eddy currents.
blockType: AcausalElectricPowerSystems.Passive.EddyCurrent
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Eddy Current simulates the effect of eddy currents by creating a magnetomotive force (MDS) that counteracts changes in the magnetic flux. In addition, the unit simulates parasitic effects using series resistance and parallel scattering resistance, as well as thermal effects using an additional thermal port H.
Eddy currents in magnetic cores arise under the influence of time-varying magnetic fields. The changing flow induces an EMF in the material, causing a current in closed circuits. Such currents are usually undesirable and cause heating of the magnetic circuit.
This unit is used to add eddy current losses in the magnetic field to a custom transformer or other magnetic component.
Eddy current is sometimes called magnetic inductance because it is the magnetic analog of an electric inductor.
The equations
Equivalent magnetic circuit of the unit, including an eddy current circuit (bottom) and a parallel scattering circuit (top):
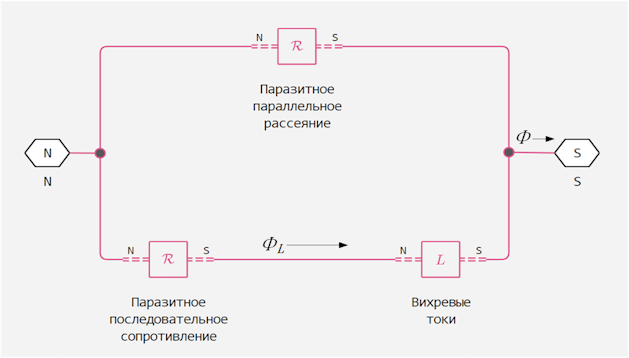
On the diagram:
-
— the total flow at the terminals. This flow consists of an eddy current flow and a parallel scattering flow.
-
— flow through a loop of eddy currents.
The unit calculates the MDS of the terminals, , and the stream, Like:
where:
-
— the conductivity of the eddy current circuit.
-
— parasitic series resistance of the eddy current circuit.
-
— parallel scattering.
Since the parasitic series resistance and parallel resistance have no losses, the total power dissipation in the unit is:
The relationship between the electrical and magnetic transformer models
In the electrical field, eddy current losses are modeled using the parallel resistance of the primary winding. The equivalent circuit of an imperfect two-winding transformer:
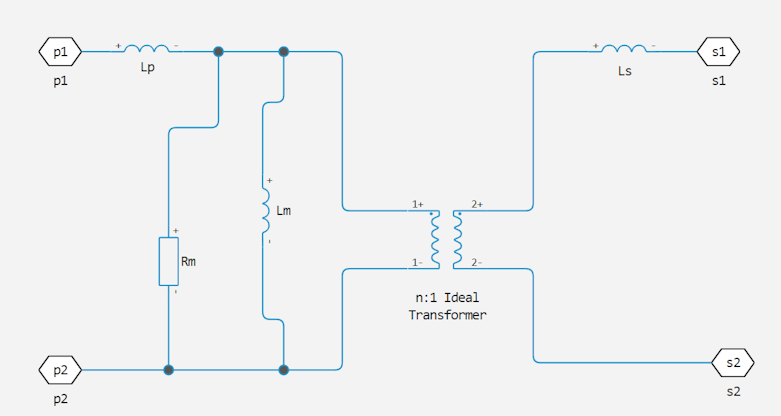
On the diagram:
-
and — the intrinsic inductance of the primary and secondary windings, respectively.
-
— the mutual inductance of the two windings.
-
— the mutual resistance of the two windings due to eddy current losses.
This two-winding transformer can be similarly represented in the magnetic field. The equivalent scheme:
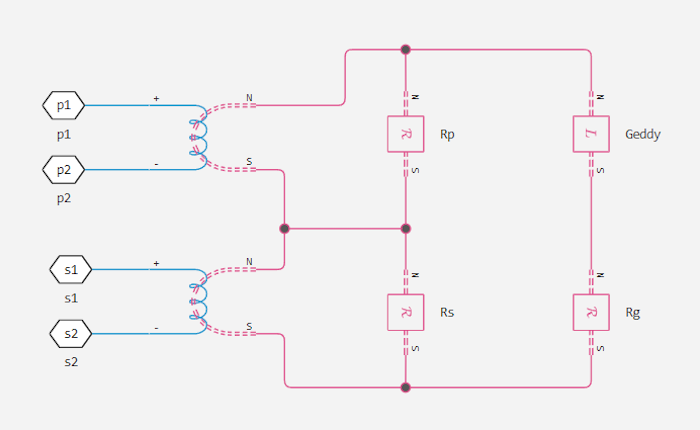
On the diagram:
-
and — the resistances associated with the primary and secondary windings, respectively.
-
— the resistance associated with the magnetic coupling of the two windings.
-
— the ratio of turns between the two windings.
Electric and magnetic circuits are equivalent if:
These relations can be used to calculate the equivalent properties of a two-winding transformer for one area based on the other.
Ports
Non-directional
N — north terminal
Magnetism
The magnetic port corresponding to the northern terminal of the unit.
S — south terminal
Magnetism
The magnetic port corresponding to the southern terminal of the unit.
H — thermal port
warm
Thermal port
Dependencies
To use this port, select the Enable thermal port checkbox.
Parameters
Conductivity of eddy current loop — eddy current loop conductivity
1 1/Ohm (default) | a positive number
Eddy current loop conductivity, . This component is an analog of magnetic inductance in the electrical field.
Parasitic series reluctation — sequential resistance
1e−3 1/Gn (default) | a non-negative number
Parasitic resistance eddy current circuits.
Parasitic parallel permeance — permeability of parallel scattering
1e−6 Gn (default) | a non-negative number
Parasitic permeability parallel scattering contour. To facilitate the convergence of modeling in some circuit topologies, a small value of this parameter should be set.
Enable thermal port — visibility of the thermal port
disabled (by default) | enabled
Select this option to enable the thermal port H
Thermal mass — thermal mass
0.1 J/K (default) | a positive number
The thermal mass of the unit. This parameter controls the absorption and accumulation of thermal energy in the unit.
Dependencies
To use this option, select the Show thermal port checkbox.
