Double-Pinion Planetary Gear
A planetary mechanism with two sets of engaged planetary gears.
blockType: Engee1DMechanical.Transmission.Gears.Planetary.DoubleStage
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Double-Pinion Planetary Gear It is a planetary mechanism with two sets of planetary gears engaged between the solar and corona gears. A single carrier holds two sets of planetary gears at different radii relative to the centerline of the solar gear, while allowing the individual gears to rotate relative to each other. The gear model takes into account the power losses caused by friction between the teeth of the gears engaged and the viscous damping of the rotating gear shafts.
Structurally, the planetary gear with two gears resembles the Ravigno gear, but without the second, large solar gear. The inner satellites engage with the solar gear, while the outer ones engage with the corona. Due to the presence of two sets of planetary gears, a planetary gear with two gears reverses the relative direction of rotation of the corona and solar gears.
The gear ratio of a pair of engaged gears determines the relative angular velocities of the two gears in this pair. In the block Double-Pinion Planetary Gear You can set the gear ratios between the corona and solar gears, as well as between the outer and inner planetary gears. The geometric constraint defines the remaining gear ratios: the crown gear is connected to the outer planetary gear and the inner planetary gear is connected to the solar gear. This limits the radius of the crown gear to the sum of the radius of the sun gear and the diameters of the inner and outer planetary gears.
where
-
— radius of the crown gear;
-
— radius of the solar gear;
-
— the radius of the inner planetary transmission;
-
— the radius of the outer planetary transmission.
The gear ratio of the crown gear and the outer planetary gear is
The gear ratio of the inner planetary gear and the solar gear is
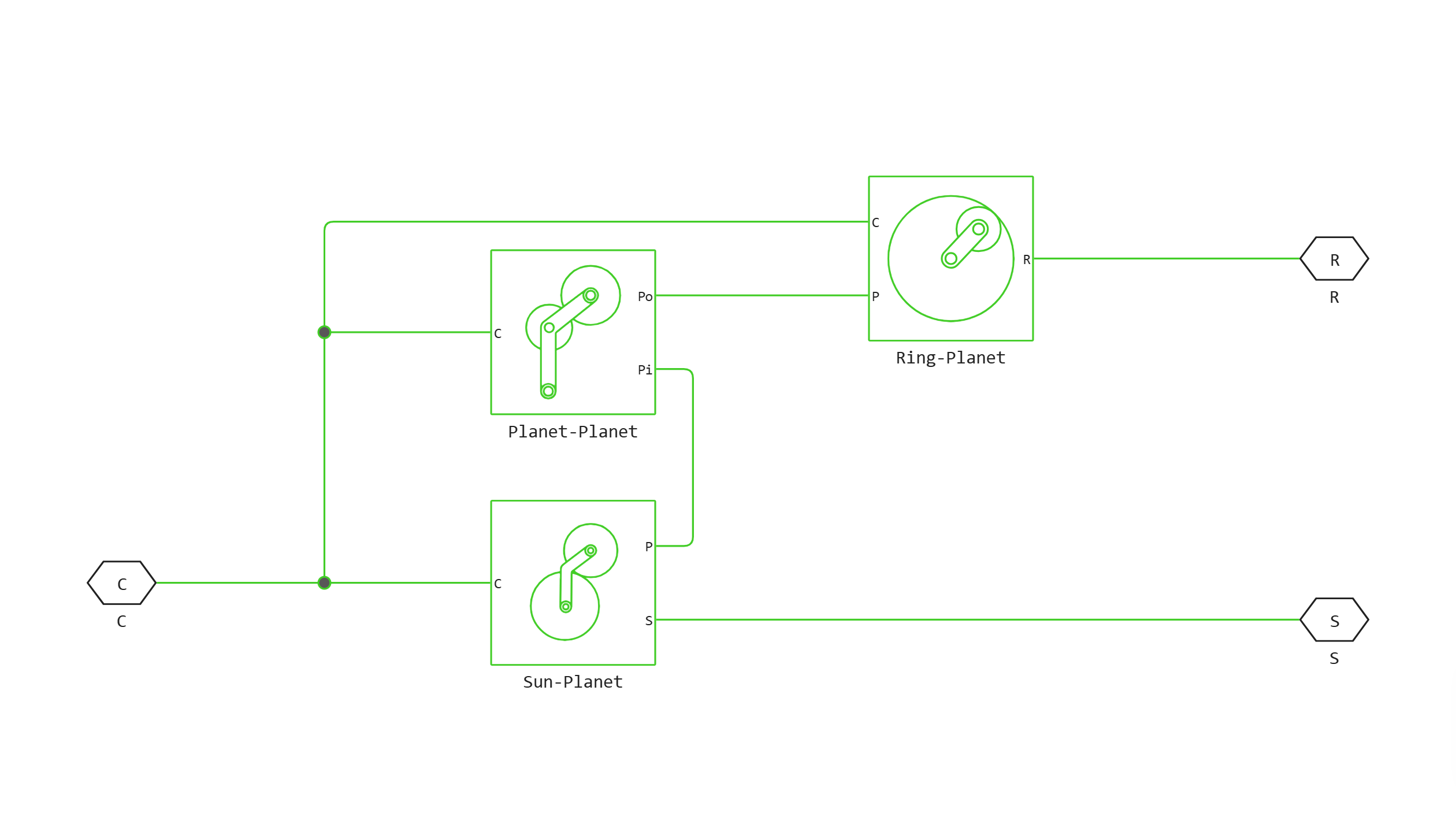
Block Double-Pinion Planetary Gear It consists of three main blocks: Ring-Planet, Planet-Planet and Sun-Planet, connected as shown in the figure. Each unit is connected to a separate driveshaft via a non-directional port.
The thermal model
You can simulate the effects of heat flow and temperature changes by turning on an additional heat port. To enable this port, set the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
Assumptions and limitations
-
The inertia of the gears is negligible.
-
Gears are treated as solids.
-
Coulomb friction slows down the simulation (for more information, see here).
Ports
Conserving
#
C
—
planetary transmission satellite carrier
rotational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the satellite carrier of the planetary transmission.
| Program usage name |
|
#
S
—
The solar gear
rotational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the solar gear.
| Program usage name |
|
#
R
—
crown gear
rotational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the crown gear.
| Program usage name |
|
#
H
—
heat flow
warm
Details
A non-directional port connected to the heat flow. The heat flow affects the efficiency of power transmission by changing the temperature of the gears.
Dependencies
To use this port, set the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Program usage name |
|
Parameters
Parameters
# Ring (R) to sun (S) teeth ratio (NR/NS) — gear ratio of the crown gear to the solar one
Details
The fixed gear ratio of the crown gear to the solar gear, determined by the ratio of the number of teeth of the satellite to the number of teeth of the solar gear.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Outer planet (Po) to inner planet (Pi) teeth ratio (NPo/NPi) — gear ratio of external and internal planetary gears
Details
A fixed gear ratio of the outer and inner planetary gears, determined by the ratio of the number of teeth of the planetary gear to the number of teeth of the solar gear.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Meshing Losses
#
Friction model —
the friction model
No meshing losses - Suitable for HIL simulation | Constant efficiency | Temperature-dependent efficiency
Details
The friction model for the block:
-
No meshing losses - Suitable for HIL simulation— perfect gear engagement. -
Constant efficiency— the transmission of torque between pairs of gears is reduced by a constant efficiency , such that . -
Temperature-dependent efficiency— the transmission of torque between pairs of gears is determined by the temperature interpolation table.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
# Sun-planet, ring-planet and planet-planet ordinary efficiencies — Torque transmission efficiency
Details
Vector efficiency of torque transmission for the gearing of the sun-satellite, corona-satellite and satellite-satellite pairs, respectively. The elements of the vector must be in the range (0,1].
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Constant efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Sun-carrier, ring-carrier and planet-carrier power thresholds —
minimum power thresholds for gear couplings: solar gear — driver, crown gear — driver and satellite — driver
W | uW | mW | kW | MW | GW | V*A | HP_DIN
Details
A vector of power thresholds, over which full efficiencies are applied. Enter the threshold values in the following order: solar gear — driver, crown gear — driver, satellite — driver.
If for the parameter Friction model the value is set Constant efficiency, the unit reduces efficiency losses to zero in the absence of power transfer. If for the parameter Friction model the value is set Temperature-dependent efficiency, then the unit smooths the efficiency from zero at rest to the values indicated in the interpolation tables of temperature and efficiency at power thresholds.
The power threshold should be lower than the expected transmitted power during the simulation. Higher values may lead to underestimation of efficiency losses by the block. Very low values can increase computational costs.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Constant efficiency or Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Temperature —
temperature
K | degC | degF | degR | deltaK | deltadegC | deltadegF | deltadegR
Details
The temperature vector used to construct a one-dimensional interpolation table of temperature and efficiency correspondence. The elements of the vector should increase from left to right.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Sun-planet efficiency — EFFICIENCY of torque transmission from solar transmission to internal planetary transmission
Details
A vector of output and input power ratios describing the power flow from the solar gear to the internal planetary gears . The block uses these values to build a one-dimensional interpolation table of temperature versus efficiency.
Each element represents an efficiency related to the temperature in the vector Temperature. The length of the vector must be equal to the length of the vector Temperature. Each element of the vector must be in the range (0,1].
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Ring-planet efficiency — EFFICIENCY of torque transmission from corona transmission to external planetary gears
Details
A vector of output and input power ratios describing the power flow from the crown gear to the external planetary gears . The block uses these values to build a one-dimensional interpolation table of temperature versus efficiency.
Each element represents an efficiency related to the temperature in the vector Temperature. The length of the vector must be equal to the length of the vector Temperature. Each element of the vector must be in the range (0,1].
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Planet-planet efficiency — EFFICIENCY of torque transmission from internal planetary gears to external ones
Details
A vector of output and input power ratios describing the power flow from an internal planetary transmission to an external one . The block uses these values to build a one-dimensional interpolation table of temperature versus efficiency.
Each element represents an efficiency related to the temperature in the vector Temperature. The length of the vector must be equal to the length of the vector Temperature. Each element of the vector must be in the range (0,1].
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Viscous Losses
#
Sun-carrier, ring-carrier and planet-carrier viscous friction coefficients —
viscous friction of gears
N*m/(rad/s) | ft*lbf/(rad/s)
Details
Vector of viscous friction coefficients for the movement of the solar, coronal, and planetary gears, respectively.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Inertia
# Inertia — the inertia model
Details
Inertia model for the block:
-
The check box is set to simulate the inertia of a gear train.
-
Unchecked — ignore the inertia of the gear train.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Inner planet gear inertia —
the moment of inertia of the internal planetary transmission
kg*m^2 | g*m^2 | kg*cm^2 | g*cm^2 | lbm*in^2 | lbm*ft^2 | slug*in^2 | slug*ft^2
Details
The moment of inertia of the internal planetary gears. This value must be positive.
Dependencies
To use this option, check the box next to the option Inertia.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Outer planet gear inertia —
the moment of inertia of the external planetary transmission
kg*m^2 | g*m^2 | kg*cm^2 | g*cm^2 | lbm*in^2 | lbm*ft^2 | slug*in^2 | slug*ft^2
Details
The moment of inertia of the external planetary gears. This value must be positive.
Dependencies
To use this option, check the box next to the option Inertia.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Thermal Port
#
Thermal mass —
thermal mass
J/K | kJ/K
Details
The thermal energy required to change the temperature of a component by one unit of temperature. The greater the thermal mass, the more resistant the component is to temperature changes.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial temperature —
Initial temperature
K | degC | degF | degR | deltaK | deltadegC | deltadegF | deltadegR
Details
The temperature of the block at the beginning of the simulation. The initial temperature sets the initial efficiencies of the components according to their efficiency vectors.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |


