Limited-Slip Differential
Reducing the speed difference between two connected shafts.
blockType: Engee1DMechanical.Transmission.Gears.Differentials.LimitedSlip
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Limited-Slip Differential It is a differential with increased internal resistance (DPVS), a gear mechanism that limits the speed difference between two connected shafts. The block models the DPVS mechanism as a structural component combining a differential and a clutch.
Differential in the block Limited-Slip Differential It is an open differential. An open differential is a gear mechanism that allows two driven shafts to rotate at different speeds. In a car, the differential allows the inner wheels to rotate more slowly than the outer wheels when cornering. A vehicle in which the wheel shafts are connected by an open differential can get stuck when one of the wheels slips and rotates freely due to loss of traction. Such a vehicle stops because the driveshaft transmits less power to a wheel with good traction than to a rotating wheel.
In the same case, a vehicle with a high-speed transmission is less likely to get stuck, since it has a clutch assembly that can transfer power to a wheel that retains traction. Coupling in the block Limited-Slip Differential It is a friction clutch with two sets of flat friction discs. The coupling is activated when the applied pressure exceeds the threshold value. In the DPVS, the tension of the spring, which separates the solar gears, presses the disks of both sets against each other. When the shafts experience a thrust difference, the planetary gear satellites exert additional force in the direction of the cross-country shaft. If the additional pressure exceeds the threshold value, the clutch assembly is activated. Gearing allows the driveshaft to transfer more power to a slower rotating all-terrain wheel. The additional power reduces the difference in the rotation speed of the two shafts. As the off-road wheel continues to rotate, the vehicle continues to move.
The figure shows the location of the main components of the DPVS mechanism. The gear of the driveshaft is not visible in this image.
Block Limited-Slip Differential models the DPVS mechanism as a block-based structural component Differential and Disc Friction Clutch. Differential mechanism modeled by the block Differential, is a structural component based on the other two blocks: Simple Gear and Sun-Planet Bevel. The block diagram shows the structural components of the DPVS.
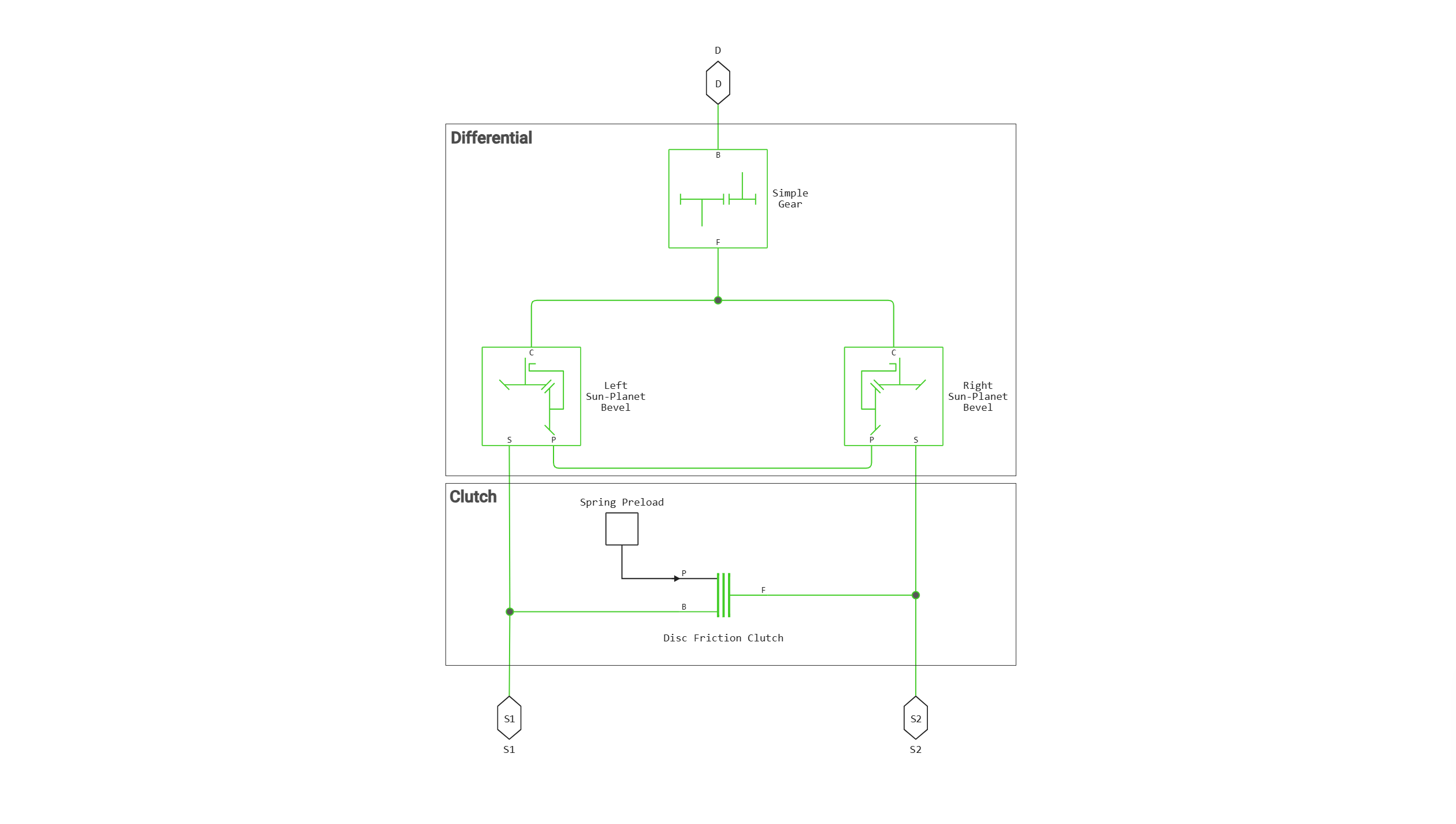
Block Ports Limited-Slip Differential They are connected to a driveshaft (port D) and two driven shafts (ports S1 and S2) that connect the solar gears to the wheels.
Block Limited-Slip Differential allows you to set the moments of inertia only for the differential housing and internal planetary gear satellites. By default, the moments of inertia of the external gears are considered negligible. To simulate the moments of inertia of the external gears, connect the blocks Inertia to ports D, S1 and S2.
The table shows the direction of rotation of the driven shaft ports for various block parameterizations and input conditions.
| Direction of rotation of the driven shaft ports (S1 and S2) | Location of the driven gear relative to the centerline | Direction of rotation of the driveshaft, port D | Relative slip in the differential |
|---|---|---|---|
Positive |
On the right |
Positive |
|
|
On the right |
Positive |
|
Negative |
On the right |
Negative |
|
|
On the right |
Negative |
|
Negative |
Leftward |
Positive |
|
|
Leftward |
Positive |
|
Positive |
Leftward |
Negative |
|
|
Leftward |
Negative |
|
Ports
Conserving
#
S1
—
solar gear 1
rotational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the shaft of the solar gear 1.
| Program usage name |
|
#
S2
—
solar gear 2
rotational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the shaft of the solar gear 2.
| Program usage name |
|
#
D
—
the cardan shaft
rotational mechanics
Details
A non-directional port connected to the driveshaft.
| Program usage name |
|
#
H
—
heat flow
warm
Details
A non-directional port connected to the heat flow.
Dependencies
To use this port, in the parameter group Differential set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Program usage name |
|
Parameters
Differential
#
Crown gear located —
location of the driven gear
To the left of centerline | To the right of centerline
Details
The location of the bevel driven gear relative to the centerline of the gear mechanism.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
# Carrier (C) to driveshaft (D) teeth ratio (NC/ND) — gear ratio of the driven gear to the drive gear of the driveshaft
Details
The fixed ratio the number of teeth of the driven gear the number of teeth of the drive gear of the driveshaft . This gear ratio must be strictly greater. 0. The driven gear is rigidly fixed on the driver.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Friction model —
the friction model
No meshing losses - Suitable for HIL simulation | Constant efficiency | Temperature-dependent efficiency
Details
The friction model for the block:
-
No meshing losses - Suitable for HIL simulation— perfect gear engagement. -
Constant efficiency— the transmission of torque between pairs of gears is reduced by a constant efficiency , such that . -
Temperature-dependent efficiency— the transmission of torque between pairs of gears is determined by the temperature interpolation table.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Sun-carrier and driveshaft-casing viscous friction coefficients —
coefficients of viscous friction
N*m/(rad/s) | ft*lbf/(rad/s)
Details
Vector of viscous friction coefficients for the movement of the solar carrier and the longitudinal movement of the driveshaft and housing, respectively.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Inertia — the inertia model
Details
Inertia model for the block:
-
The check box is set to simulate the inertia of a gear train.
-
Unchecked — ignore the inertia of the gear train.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Carrier inertia —
the moment of inertia of the planetary transmission satellite carrier
kg*m^2 | g*m^2 | kg*cm^2 | g*cm^2 | lbm*in^2 | lbm*ft^2 | slug*in^2 | slug*ft^2
Details
The moment of inertia drove the planetary gear satellites, including the driven gear. This value must be positive.
Dependencies
To use this option, check the box next to the option Inertia.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Planet gear inertia —
the moment of inertia of the planetary transmission satellite
kg*m^2 | g*m^2 | kg*cm^2 | g*cm^2 | lbm*in^2 | lbm*ft^2 | slug*in^2 | slug*ft^2
Details
The moment of inertia of all satellites of planetary transmissions. This value must be positive.
Dependencies
To use this option, check the box next to the option Inertia.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Sun-sun and carrier-driveshaft ordinary efficiencies — differential torque transmission coefficients with constant efficiency
Details
Vector of torque transmission coefficients . Here
-
— the ratio of output power to input power, describing the power flow from the driving solar gear to the driven solar gear;
-
— the ratio of output power to input power, describing the power flow from the driven gear to the drive gear of the driveshaft.
The driver is rigidly fixed on the driven gear. The elements of the vector must be in the range (0,1].
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Constant efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Sun-carrier and driveshaft-casing power thresholds —
minimum power efficiency thresholds for solar gear, driven gear, and driveshaft gear couplings
W | uW | mW | kW | MW | GW | V*A | HP_DIN
Details
Vector of power thresholds for the solar gear and the longitudinal body of the driveshaft respectively. If these values are exceeded, a complete loss of efficiency is applied. Below these values, the efficiency is smoothed out by the hyperbolic tangent function.
If set for the parameter Friction model meaning Constant efficiency The unit reduces efficiency losses to zero in the absence of power transfer. If set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency The unit smooths the efficiency from zero at rest to the values indicated in the interpolation tables of temperature and efficiency at power thresholds.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Constant efficiency or Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Temperature —
temperature
K | degC | degF | degR | deltaK | deltadegC | deltadegF | deltadegR
Details
The temperature vector used to construct a one-dimensional interpolation table of temperature and efficiency correspondence. The elements of the vector should increase from left to right.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Sun-sun efficiency — The efficiency of torque transmission from the driving solar gear to the driven solar gear
Details
A vector of output and input power ratios describing the power flow from the driving solar gear to the driven solar gear . The block uses these values to build a one-dimensional interpolation table of temperature versus efficiency.
Each element represents an efficiency related to the temperature in the vector Temperature. The length of the vector must be equal to the length of the vector Temperature. Each element of the vector must be in the range (0,1].
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Carrier-driveshaft efficiency — The efficiency of torque transmission from the driven gear to the drive gear of the driveshaft
Details
A vector of output and input power ratios describing the power flow from the driven gear to the drive gear of the driveshaft . The block uses these values to build an interpolation table of temperature versus efficiency. The driver is rigidly fixed on the driven gear.
Each element represents an efficiency related to the temperature in the vector Temperature. The length of the vector must be equal to the length of the vector Temperature. Each element of the vector must be in the range (0,1].
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Clutch
# Number of friction surfaces — number of contact surfaces
Details
Quantity contact surfaces inside the clutch that create friction.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Effective torque radius —
radius of application of the friction force
m | um | mm | cm | km | in | ft | yd | mi | nmi
Details
Effective radius of the torque arm , which determines the moment of kinetic friction inside the clutch.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Preload force —
clutch disc engagement pressure
N | nN | uN | mN | kN | MN | GN | dyn | lbf | kgf
Details
The force with which the spring tension acts on the clutch discs. Must be greater than or equal to zero.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Static friction coefficient — coefficient of friction at rest
Details
Static or peak value of the coefficient of friction. The coefficient of friction at rest must be greater than the kinetic coefficient of friction.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning No meshing losses - Suitable for HIL simulation.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Kinetic friction coefficient relative velocity vector —
vector of relative velocities
rad/s | deg/s | rad/min | deg/min | rpm | rps
Details
Vector of input values of relative velocity. The values in the vector should increase from left to right. The minimum number of values depends on the chosen interpolation method. For linear interpolation, specify at least two values for each dimension. For smooth interpolation, specify at least three values for each dimension.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Kinetic friction coefficient vector — Coulomb friction coefficient
Details
The vector of the output values of the kinetic friction coefficient. All values must be greater than zero.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, in the parameter group Differential set for the parameter Friction model meaning No meshing losses - Suitable for HIL simulation or Constant efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Friction coefficient interpolation method —
the interpolation method
Linear | Smooth
Details
Interpolation methods for approximating the output value when the input value is between two consecutive grid points. To optimize performance, select the value Linear. To construct a continuous curve with continuous first-order derivatives, select the value Smooth.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Friction coefficient extrapolation method —
the extrapolation method
Linear | Nearest | Error
Details
Extrapolation methods for approximating the output value when the input value falls outside the range specified in the argument list. To plot a curve with continuous first-order derivatives in the extrapolation domain and on the boundary with the interpolation domain, select the value Linear. To get an extrapolation that does not go beyond the highest data point and beyond the lowest data point, select the value Nearest.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Velocity tolerance —
the limit of the slip rate lock
rad/s | deg/s | rad/min | deg/min | rpm | rps
Details
The maximum slip rate at which the clutch can lock. The slip rate is the sign difference between the angular velocities of the drive and driven shafts., . If the movement friction moment is non-zero and the transmitted torque is within the permissible resting friction moment, the clutch is locked if the actual slip rate falls below the permissible speed value.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial state —
the initial state of the clutch
Unlocked | Locked
Details
The state of the coupling at the beginning of the simulation. The clutch can be in one of two states: locked and unlocked. A locked clutch causes the drive and driven shafts to rotate at the same speed, that is, as a single unit. The unlocked clutch allows the two shafts to rotate at different speeds, which causes the clutch discs to slip.
| Values |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
# Static friction coefficient vector — coefficient of friction at rest
Details
A vector of static or peak values of the coefficient of friction at a given temperature. The length of the vector must match the length of the vector Temperature. Each element must be greater than the maximum value of the corresponding row in the matrix. Kinetic friction coefficient matrix.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
# Kinetic friction coefficient matrix — Coulomb friction coefficient
Details
A matrix of kinetic friction coefficient values. All values must be greater than zero.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, in the parameter group Differential set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Thermal Port
#
Thermal mass —
thermal mass
J/K | kJ/K
Details
The thermal energy required to change the temperature of a component by one unit of temperature. The greater the thermal mass, the more resistant the component is to temperature changes.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Initial temperature —
Initial temperature
K | degC | degF | degR | deltaK | deltadegC | deltadegF | deltadegR
Details
The temperature of the block at the beginning of the simulation. The initial temperature sets the initial efficiencies of the components according to their efficiency vectors.
Dependencies
To use this parameter, set for the parameter Friction model meaning Temperature-dependent efficiency.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |

