Generating Promela in Engee
Formal verification in Engee is based on the automatic generation of formal models in the Promela (PROcess MEta LAnguage) supported by the Spin system.
The Promela generator converts diagrams of finite automata (Chart), incoming and output ports, and virtual subsystems of the Engee model into a textual formal specification — .pml- the file.
This specification describes the behavior of the model in the form of states, transitions, and logical conditions, which can then be checked by the Spin tool against specified LTL formulas. This approach allows you to use the existing Engee model without manually rewriting it into a separate formal notation.
Running the code generator
Code generation in Promela from the Engee model file is performed by accessing the Engee API, for example, from a window command line  :
:
engee.generate_code(source, destination, target="promela")where
-
source— string, the path to the model file .engee; -
destination— string, the path to the directory where the generated file will be placed.
The API uses the model file name as the name of the generated file (the suffix ".engee" is excluded), ending with the new suffix ".pml".
For example, if the path to the model file is source — "/user/models/large_model.engee", and the directory for generating files destination — "/user/spin", then the generated code in Promela language will be placed in a file, the path to which — "/user/spin/large_model.pml".
The formal verification process at Engee
-
Creating a finite state machine model (inside the block Chart) in Engee.
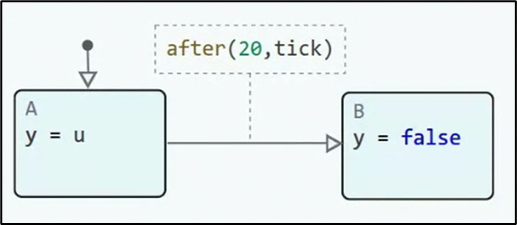
-
Generating a formal Promela model using the function
generate_codespecifying the target language:engee.generate_code(source, destination, target="promela").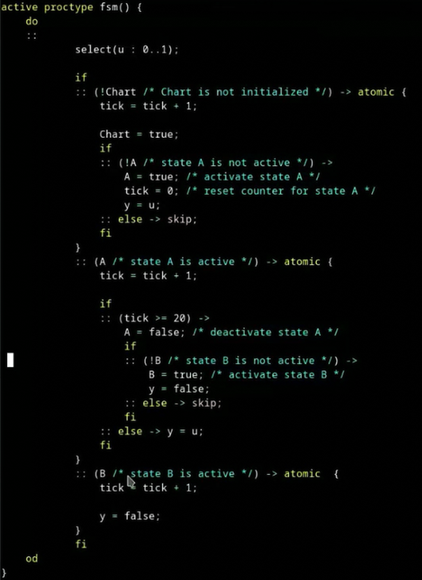
-
Adding formal properties in the form of LTL formulas.
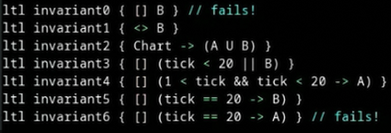
-
Checking the model using Spin tools.
-
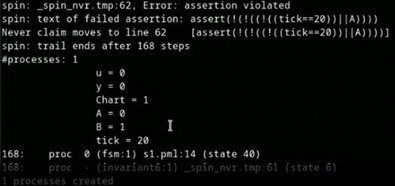
Analysis of the results: successful proofs, counterexamples, execution routes.
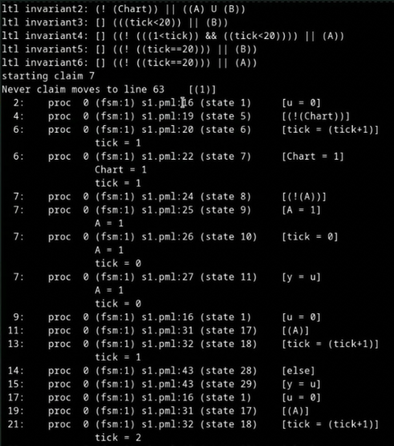 →
→ 
Limitations of the model
If the model contains blocks or types that are not in the list, an attempt to call the API to generate Promela code will fail.
Not supported:
-
Multiple sampling step;
-
Temporal operators of the Chart block (
t,before,after…); -
Operators of the Chart block
countandduration; -
Julia library functions such as
pow,floor,ceil… .
Block support
Currently, the functionality of the Promela generator is limited to supporting several types of model blocks.:
Data type support
In addition, only those data types and arrays consisting of elements of these types that have analogues in Promela are supported.:
Type Julia |
Promela Type |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Julia syntax support
The Promela code generator supports almost all Julia syntax found in the code inserts of the Chart block and supported by the C language code generator.
A number of designs have no direct analogues in Promela and therefore are not supported.:
-
Operator
continue; -
Nested loops
for(or cycles with complex conditions); -
Cycles
forin increments other than 1; -
Operator
,.
Additional syntax is implemented:
-
@goto -
@label