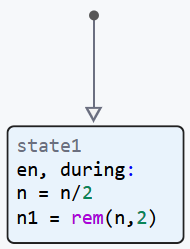
Groups of state machine operators
Groups of operators are the conditions that trigger the model’s actions inside states.
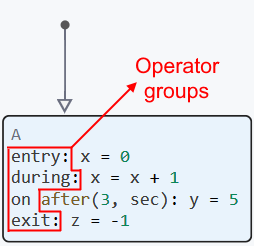
Operator groups are used when it is necessary to configure more complex model behavior. For more information about the logic of operator groups, see The logic of finite automata operation.
Operator groups only support operations in the Julia language and can contain several parts that alternate in any order. For example:
during: du1
entry: en1
during: du2In this case, when the state is activated, the code will be executed entry: en1. After that, at each subsequent step, while the state remains active, the combined code of the operator group will be executed. during, represented as "du1; du2". This means that du1 and du2 they are combined and executed sequentially, as if they are connected together within the same during.
|
You can use short names for groups of operators. —
When enumerating, it is important that the same word is not repeated. Example of an incorrect enumeration: |
The Julia code in the status blocks can be multi-line and continue until the keyword occurs at the beginning of the line. entry, during, exit or on. For example:
during:
if x > 10
y = 1
else
y = 2
end
exit: y = 3
The code in the state without operator groups is executed both when the state is activated and at each step while the state remains active. Thus, he combines the actions specific to the sections. entry and during, but it does not include logic related to deactivating the state (as the section does exit).
|
The entry group
entry (input) — is used to determine the actions that are performed when entering the state. Actions specified in entry, are executed each time the state becomes active.
The band during
during (during) — is used to determine the actions that are performed at each stage of the model calculation step (except the first one) if the state is active. Actions specified in during, are executed while the state is active.
Exit group
exit (exit) — is used to determine the actions that are performed when exiting the state. These actions are performed once when the state becomes inactive, and occur after all the actions of the transitions that initiated the exit from this state are completed. After exiting the state, the operators during are no longer running because the state is no longer active. For example, there is the following finite state machine:
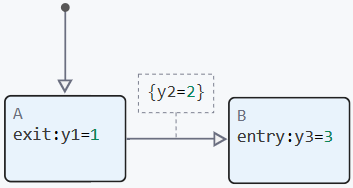
Here, the state machine activates state "A" in the first step, and in the second it performs the actions in the following order:
y2 = 2
y1 = 1
y3 = 3The on group
on — is performed when the specified action occurs in the active state. Operator Group on allows you to use temporal logic within states. For example:
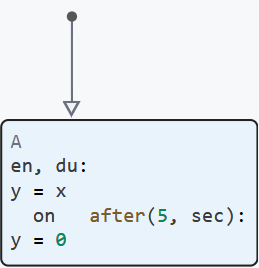
Here:
-
on after(5, sec)determines that execution will start from the fifth second (and run after 6, 7, etc. seconds). -
y = 0defines what needs to be assigned to a variableymeaning0.
The logic of operator groups
In the state machine, the order of working with transitions and groups of operators is entry, during, exit, and on it happens as follows:
Types of logic for executing groups of operators |
entry |
during |
exit |
on |
The order of execution |
|
|
|
|
Activation Features |
|
|
|
|
Interaction with traffic |
|
Before completing the section |
|
|