Condition
State (State)  — this is one of the blocks of a finite state machine (SC). The block contains actions describing the behavior of the system in this state in the form of a program code based on Julia, transition graph or nested KA and can be configured using groups of operators.
— this is one of the blocks of a finite state machine (SC). The block contains actions describing the behavior of the system in this state in the form of a program code based on Julia, transition graph or nested KA and can be configured using groups of operators.
The state blocks obey the logic of the spacecraft:
-
In the spacecraft model, one or more states can be active at any given time if a hierarchy of states is used. In this case, the states from the most nested to its outermost parent state are active (for more information, see Hierarchy of the state machine);
-
The state is activated if the condition for switching to it is met. If the state is the only one in the model or the only one among the nested states, then it can be activated without an incoming transition.
| States maintain a hierarchy (for more information, see Hierarchy of the state machine). |
Syntax of states
| The rule | Error in violation of the condition |
|---|---|
Each state should have a name. |
Error in the router’s result loop: ErrorException('model name/Chart': state name ' ' is incorrect.) |
|
Error in the router’s result loop: ErrorException('model name/Chart': state name 'example of an incorrect name' is incorrect.) |
Operator groups only support operations in the Julia language. |
Model initialization error: [EXEC] Initialization error of the id_model id_simulation: UndefVarError(:incorrect syntax) |
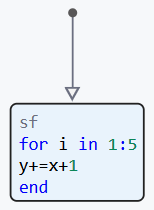
Code written in a state without specifying prefixes entry:, during:, exit: and on, is executed both when the state is activated and at each step of the model, while the state remains active and is called a code with an anonymous group of operators. This group of operators combines the behavior of prefixes. entry: and during:. For example, a status block with a loop for it looks like this:
|
You can leave comments in the status blocks, just like in any Julia code.:
|