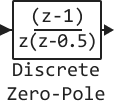Discrete Zero-Pole
Simulates a discrete transfer function with specified poles and zeros.
blockType: DiscreteZeroPole
|
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Discrete Zero-Pole models a discrete system given by the zeros, poles and gain of the transfer function in the -region. This block assumes that the transfer function has the following form:
,
where
-
- vector of zeros;
-
- vector of poles;
-
- gain factor of the transfer function.
The number of poles must be greater than or equal to the number of zeros . If poles and zeros are complex, they must be complex-conjugate pairs.
Modelling a system with a single output
For a single output system, the input and output of a block are scalar signals in the time domain. To model this system:
-
Enter a vector for the zeros of the transfer function in the box Zeros.
-
Enter a vector for the poles of the transfer function in the field Poles.
-
Enter a scalar for the gain of the transfer function in the field Gain.
Modelling a system with multiple outputs
For a system with multiple outputs, the input of a block is a scalar and the output is a vector where each element is an output of the system. To model this system:
-
Enter the matrix of zeros in the box Zeros.
Each column of this matrix contains the zeros of the transfer function linking the input of the system to one of the outputs.
-
Enter the vector or matrix of poles common to all transfer functions of the system in the field Poles.
-
Enter the value of the gain of the transfer function in the field Gain. The gain Gain can be specified as a scalar, vector or matrix.
Each element is the gain of the corresponding transfer function in the . Zeros.
Each element of the output vector or matrix corresponds to a column in . Zeros.
Ports
Input
#
IN_1
—
input signal
scalar
Details
Input signal, scalar real value.
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
Output
#
OUT_1
—
discrete system model
scalar | vector | matrix
Details
A model of a system given by the zeros, poles and gain of a discrete transfer function. The width of the output signal is equal to the number of columns in the matrix Zeros or one if Zeros is a vector.
| Data types |
|
| Complex numbers support |
Yes |
Parameters
Main
#
Zeros —
matrix of zeros
Arbitrary type
Details
Specifies a vector or matrix of zeros. The number of zeros must be less than or equal to the number of poles. If the poles and zeros are complex, they must be complex-conjugate pairs.
-
For a system with one output, a vector for the zeros of the transfer function is specified.
-
For a system with multiple outputs, a matrix is specified. Each column of the matrix contains the zeros of the transfer function linking the input of the system to one of the outputs.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
Yes |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Poles —
pole vector
Arbitrary type
Details
Specifies a scalar, vector or matrix of poles. The number of poles must be greater than or equal to the number of zeros. If poles and zeros are complex, they must be complex-conjugate pairs.
-
For a system with one output, a vector for the poles of the transfer function is specified.
-
For a system with multiple outputs, a vector or matrix for the poles common to all transfer functions of the system is specified.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
Yes |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Gain —
transfer function gain
Scalar / array of real numbers
Details
Specifies a vector or matrix of gain factors.
-
For a system with a single output, it is a scalar.
-
For a system with multiple outputs, a vector or matrix of coefficients is specified. Each of its elements is a gain coefficient of the corresponding transfer function in parameters Zeros.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
Yes |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Sample time —
interval between calculation steps
SampleTime (real number / vector of two real numbers)
Details
Specify the interval between calculation steps.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Tunable |
No |
| Evaluatable |
Yes |