Cauer Thermal Model
blockType: AcausalElectricPowerSystems.Passive.Thermal.CauerModel
Path in the library: |
Description
Block Cauer Thermal Model It represents heat transfer through several layers of semiconductor modules. Cauer Thermal Model It consists of several elements of the Kauer model. The figure below shows an equivalent circuit for one element of the Kauer model.
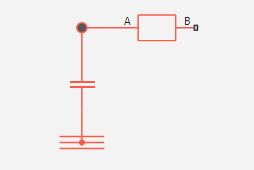
Multiple layers Cauer Thermal Model They include a chip, solder, substrate, and base. Other terms describing Cauer Thermal Model:
-
Continuous fractional scheme.
-
The T-model.
-
Staircase network.
The figure below shows an equivalent circuit for Cauer Thermal Model.
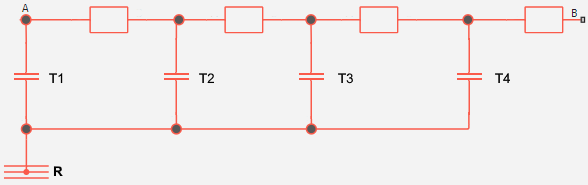
The temperature at point R is absolute zero.
The equations
Defining equations for each element Cauer Thermal Model are:
,
,
,
where
-
— heat capacity;
-
— thermal time constant;
-
— thermal resistance;
-
— heat flow through the material;
-
— the temperature difference between the layers of the material;
-
— heat flow through the heat capacity;
-
— temperature difference through heat capacity.
Parameterization of the Kauer model based on Foster coefficients
Foster coefficients are often used in semiconductor device specifications to determine the thermal model. However, Kauer’s thermal models are more useful because they can be expanded with additional thermal components such as radiators and radiation or convection elements.
To use the block Cauer Thermal Model based on Foster’s thermal model data, select the parameter Parameterize Cauer model using Foster coefficient data.
| It is not recommended to use vectors longer than 10 elements for parameters. Thermal resistance data (Foster) and Thermal time constant data (Foster). This can lead to large errors in the results. |
Ports
Conserving
#
A
—
the primary surface of a single semiconductor layer
warm
Details
A thermal port connected to the primary surface of a separate semiconductor layer.
| Program usage name |
|
#
B
—
the secondary surface of the last semiconductor layer
warm
Details
A thermal port connected to the secondary surface of the last semiconductor layer.
| Program usage name |
|
Parameters
Main
# Parameterize Cauer model using Foster coefficient data — parameterization of the Kauer model based on Foster coefficients
Details
Select this option to enable parameterization of the Kauer model based on Foster coefficients.
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
No |
#
Thermal resistance data —
thermal resistances
K/W
Details
The vector of thermal resistances.
Dependencies
To use this option, uncheck the box. Parameterize Cauer model using Foster coefficient data.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Thermal time constant data —
thermal time constants
s | ns | us | ms | min | hr | d
Details
A vector of thermal time constants.
Dependencies
To use this option, uncheck the box. Parameterize Cauer model using Foster coefficient data.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Thermal resistance data (Foster) —
thermal resistances parameterized based on Foster coefficients
K/W
Details
A vector of thermal resistances parameterized based on Foster coefficients.
Dependencies
To use this option, check the box Parameterize Cauer model using Foster coefficient data.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
#
Thermal time constant data (Foster) —
thermal time constants
s | ns | us | ms | min | hr | d
Details
A vector of thermal time constants parameterized based on Foster coefficients.
Dependencies
To use this option, check the box Parameterize Cauer model using Foster coefficient data.
| Units |
|
| Default value |
|
| Program usage name |
|
| Evaluatable |
Yes |
Literature
-
Schutze, T. AN2008-03: Thermal equivalent circuit models. Application Note. V1.0. Germany: Infineon Technologies AG, 2008.
-
T. G. Subhash Joshi and V. John, Combined transient thermal impedance estimation for pulse-power applications. 2017 National Power Electronics Conference (NPEC), 2017, pp. 42-47, doi: 10.1109/NPEC.2017.8310432.
