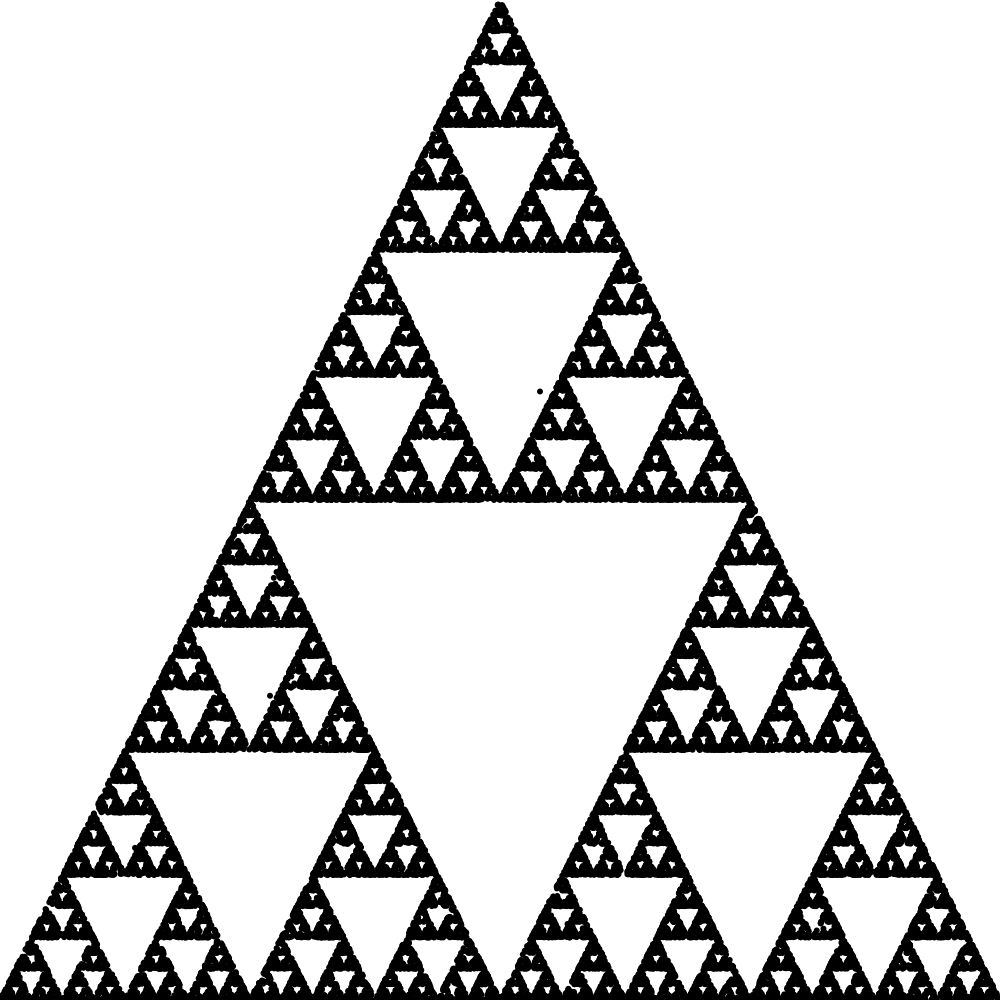
Sierpinski's Triangle (Chaos Game)
This example discusses the implementation of an algorithm for constructing a Sierpinski triangle in Julia using the Luxor graphics library for visualization.
Introduction
The Sierpinski triangle algorithm is a simple iterative process that is used to generate fractals. Despite its apparent simplicity, this method allows you to create complex and beautiful geometric structures. The algorithm is based on the random selection of one of the predefined points (vertices) and the subsequent construction of a new point at a certain distance from the current position. By repeating this process many times, we get a visualization of the fractal set.
The main part
Installing an external Luxor package, if it is not already installed
import Pkg; Pkg.add("Luxor")
Connecting the Luxor library for working with graphics
using Luxor
Definition of the function implementing the Chaos game algorithm
function chaos()
# Setting the image size (width and height in pixels)
width = 1000
height = 1000
# Creating a new drawing with the specified dimensions and file name
Drawing(width, height, "./chaos.png")
# Creating a "turtle" (Turtle object) that will draw dots
# Parameters: initial coordinates (0, 0), visibility (true), direction (0 degrees), color (black)
t = Turtle(0, 0, true, 0, (0., 0., 0.))
# Randomly setting the initial coordinates of a point
x = rand(1:width)
y = rand(1:height)
# Iteration cycle: the longer the number, the more accurately the fractal is formed
for l in 1:30_000
# Random selection of one of three possible vertices (1, 2 or 3)
v = rand(1:3)
# Depending on the selected vertex, we recalculate the coordinates of the point.
if v == 1
# The first vertex is located at the origin (0,0) — the point "shrinks" to the origin
x /= 2
y /= 2
elseif v == 2
# The second vertex is located in the upper—right corner - the point is shifted there.
x = width/2 + (width/2 - x)/2
y = height - (height - y)/2
else
# The third vertex in the lower right corner is the point that moves there.
x = width - (width - x)/2
y = y / 2
end
# Moving the turtle to the new coordinates (the Y-axis is inverted due to the coordinate system of the image)
Reposition(t, x, height-y)
# Draw a small circle (dot) with a radius of 3 pixels
Circle(t, 3)
end
end
Calling the function and completing the drawing
Calling the main function that executes the algorithm, completing the drawing, saving and opening the created file
chaos()
finish()
preview()
Conclusion
In this example, we implemented an algorithm for constructing the Sierpinski triangle using the Luxor library in the Julia programming language. We have generated a random set of points, which gradually forms a fractal. This implementation demonstrates the power of simple iterative methods and makes it possible to visually see the emergence of complex geometric structures from chaotic actions. This example can be useful as a demonstration of the basics of fractal graphics, Julia programming, and working with graphics.
The example was developed using materials from Rosetta Code