Importing and exporting variables
Engee supports recording and uploading variables in formats.mat and .jld2:
-
.mat is a format that is used in the MATLAB software.
-
.jld2 is a format that is used in the Julia programming language.
To write variables to .mat or .jld format, select them in the variables window 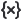 and right-click on the context menu. In the menu, tap Save as…:
and right-click on the context menu. In the menu, tap Save as…:
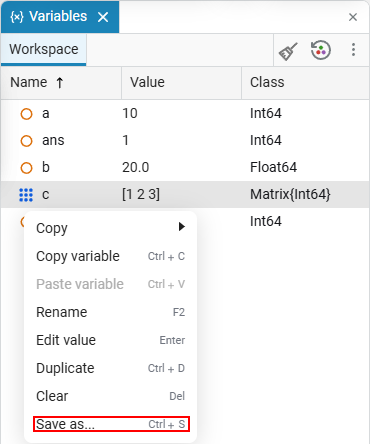
This will open the variable export window:
-
Specify the name of the file that will contain the variables.
-
Select the format of the exported file — MAT or JLD2.
-
Track the directory where the file will be saved.
-
Specify the path where the file will be saved. All folders of the Engee file browser will be displayed in this area.
-
Return from the current directory to the levels above, up to
/user(the beginning of the Engee file browser path). -
Create a new folder in the directory of item 3.
The saved file in MAT or JLD2 format will be displayed in file browser  . Double-clicking with the left mouse button on the saved file imports variables into the Engee workspace. Imported variables will be automatically added to variable window
. Double-clicking with the left mouse button on the saved file imports variables into the Engee workspace. Imported variables will be automatically added to variable window  .
.
MAT
| Use the MAT package.jl for working with data in the format .mat in Julia (more in MAT). |
You can work with the MAT format programmatically, through the script editor or the command line. For example, consider the following code for reading one variable from MAT:
using MAT # connecting the MAT library to work with .mat files
a = 1 # setting the variable a with a value of 1
file = matopen("/user/mat_file.mat") # open the mat_file.mat file for reading using the matopen function and create a file object
variable_mat = read(file, "a") # reads the variable "a" from a file of type MAT and assigns its value to the variable variable_mat
close(file) # closes the fileTo write a variable to a MAT file, use the code:
variable_1 = 1 # let's set the variable variable_1 and assign it the value 1
file = matopen("/user/new_mat_file.mat", "w") # opens the new_mat_file.mat file in writing mode ("w")
write(file, "variable_mat", variable_1) # writes the value of the variable variable_1 to the variable variable_mat in the file new_mat_file.mat
close(file) # closes the fileUsing the code, we wrote the variable to a MAT file. Similarly, through the matwrite function, we can write Dict (dictionary) to the MAT format, using its keys as variable names:
mat_Dict = Dict(
"variable_1" => 1,
"variable_2" => -2,
"variable_3" => "Hello, world")
matwrite("/user/Dict.mat", mat_Dict)The code will create a Dict.mat file containing a dictionary with variable names.
|
You can use the data compression argument |
JLD2
| Use the JLD2.jl package to work with data in the format.jld2 in Julia (more in JLD2.jl). |
Download the JLD2 module:
import Pkg; # importing a package manager
Pkg.add("JLD2") # adding the JLD2 packageThe JLD2.jl package supports function interfaces like jldsave. For example:
using JLD2 # loading the module
x = 1
y = 2
z = 42
# The simplest case:
jldsave("example.jld2"; x, y, z)
# this is equivalent to
jldsave("example.jld2"; x=x, y=y, z=z)
# New names can be assigned only to parts of the arguments.
jldsave("example.jld2"; x, a=y, z)
# and to create complete confusion, you can do this
jldsave("example.jld2"; z=x, x=y, y=z)If you want to save only one object in the file for later loading, you can use the save_object and load_object functions. For example:
save_object(filename, x) # saves the x object in a new JLD2 file in filename, if the file exists in this path, it will be overwritten.
load_object(filename, x) # loads object x