Testing UDP data transmission using an echo server in socat
This example discusses the use of UDP blocks in the Engee model, which allow you to connect external hardware/software to exchange data with the model. Data is received and transmitted in the model via an echo server in the socat utility running on a personal computer.
Introduction
UDP (English User Datagram Protocol) is one of the main protocols for data transmission. Computer applications use UDP datagrams to forward IP messages to other hosts on the network.
Engee, with the ability to work with external hardware, allows you to use UDP transmission to interact models with software.
Preparation for work
Before launching the model in Engee, several preparatory steps must be performed, as described in the manual.
In addition, similar preparation steps can be found in an example of working with COM-портом. After successfully connecting to Engee, you can switch to working with the external environment.
Launching the echo server in socat
Socat (SOcket CAT) is a command—line utility designed for two-way data transfer between two points. For example, you can run emulation of COM ports or create a TCP proxy. The installation of the utility is available in almost all Linux distributions.
To run the UDP echo server on Linux, run the command on the command line:
socat UDP-RECV:5150 UDP-SEND:127.0.0.1:5151
On Windows, the utility can be launched using the Cygwin command-line shell. The necessary instructions for installing Cygwin and running socat on Windows can be found at link. After installing socat, just use the command above.
The example model
The model used in this example - udp_socat_echo_server.engee. Conventionally, the model can be divided into two parts:
-
Signal generation, processing, and transmission over UDP,
-
Receiving UDP signals, processing them, and displaying them on graphs.
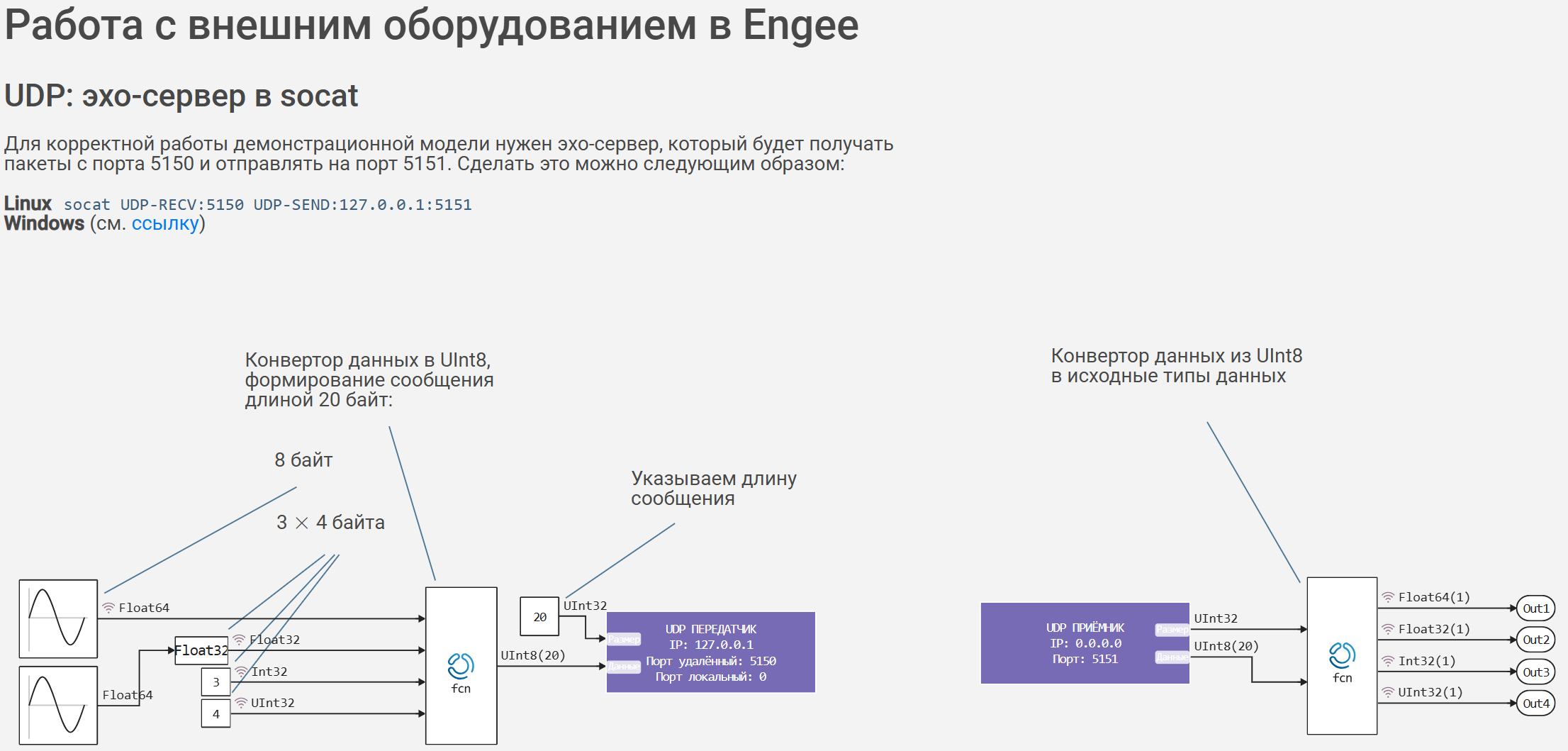
The generated signals are sinusoidal with a period types of data Float64 and Float32, as well as constant - types Int32 and UInt32.
The [Engee Function] block(https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/ru/base-lib-user-defined-function/engee-function.html ) embeds Julia code into the model, which converts 4 signals of various input formats into one variable for transmitting a data packet in the format UInt8.
The received variable is sent to the second input of the [UDP transmitter] block (https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/ru/hardware-udp/udp-tx.html ), and the value of the data packet is transmitted to the first input of the block. Also in the block it is necessary to define an IPv4 address in the format for sending messages to the local machine. - 127.0.0.1, remote port - 5150, as well as the maximum size of the transmitted message, in our case - 20 bytes.
UDP signals are captured using the [UDP receiver] block (https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/ru/hardware-udp/udp-rx.html ). At its first output, it generates the size of the received packet, and at the second, the data itself is of the type UInt8. IPv4 specified in the block - 0.0.0.0, port - 5151, maximum message size - 20 bytes.
The Engee Function block at the output of the UDP receiver converts the received messages into the original data types. - Float64, Float32, Int32 and UInt32. The received signals are recorded for display in graphs.
Simulation results
After completing all the steps to prepare for the simulation, we will start executing the model. Data transmission and reception over UDP can be checked using Engee graphs. In addition, you can run a traffic analysis program (sniffer), such as WireShark. In the traffic capture window, you can observe packet reception and transmission over the specified IP and port numbers.
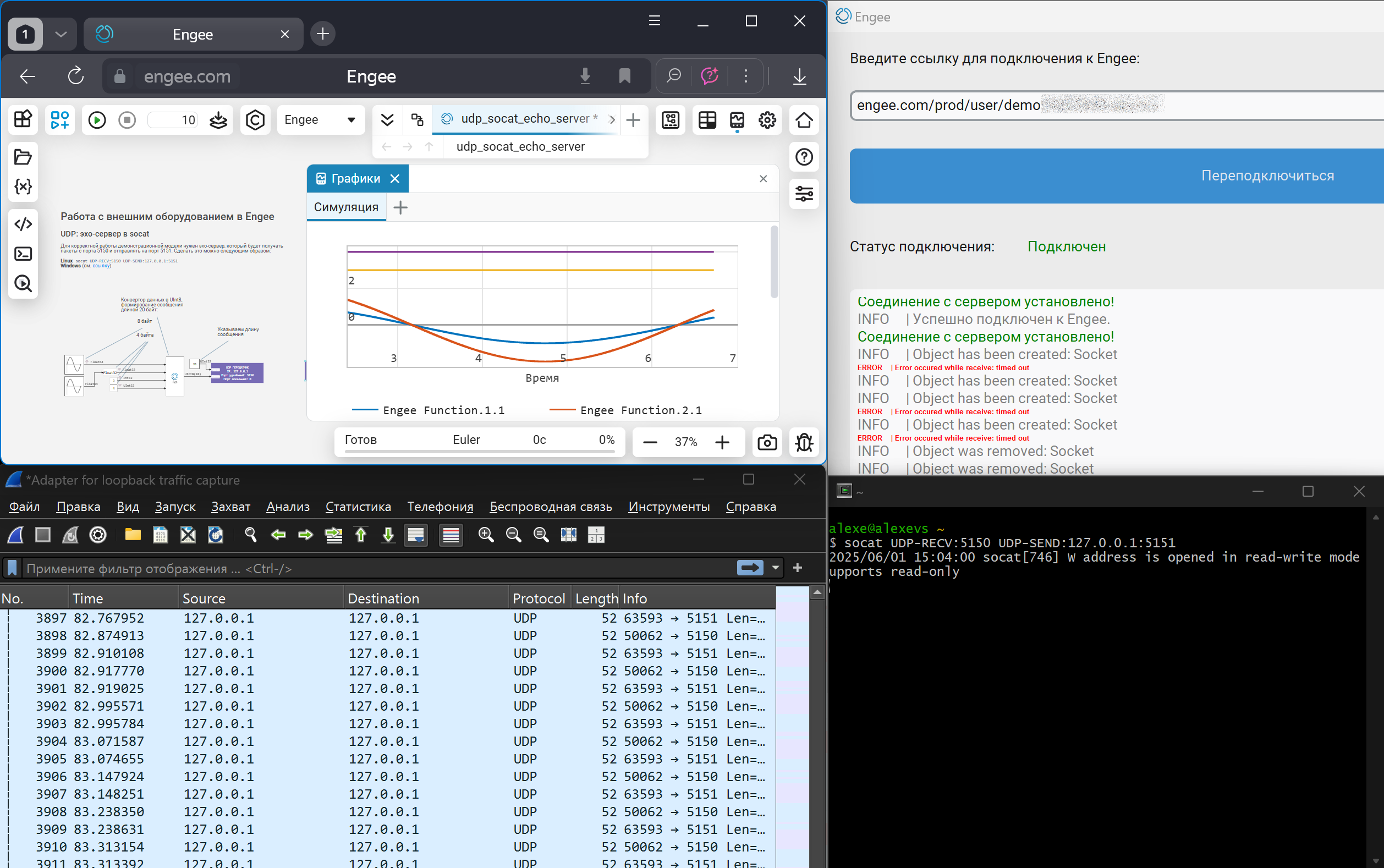
As can be seen from the Engee graphs and the output in the traffic analysis window, data transmission over UDP is performed correctly.
Conclusion
We looked at a simple example of how Engee works with an external environment - an echo server running in the socat utility on a personal computer. The Engee model transmits and receives data over the UDP protocol using the appropriate blocks.