The Scrambler
A scrambler is a software or hardware device (algorithm) that performs scrambling, that is, the reversible transformation of a digital stream without changing the transmission rate in order to obtain the properties of a random sequence.
This example implements scrambling with a "Pseudo Random Binary Sequence" (PRBS). This sequence is calculated due to the LFSR of length 15, given by the associated polynomial 1+ x14+x15 and the initial value 100101010000000. Also below is a picture describing the formula for the operation of a pseudorandom sequence generator.
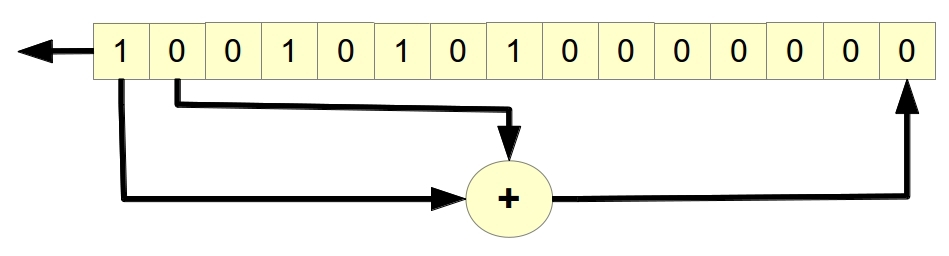
Next, let's look at the implemented scrambling and descrambling scheme. It and a bitwise comparison of the operation of this algorithm are shown in the figure below.
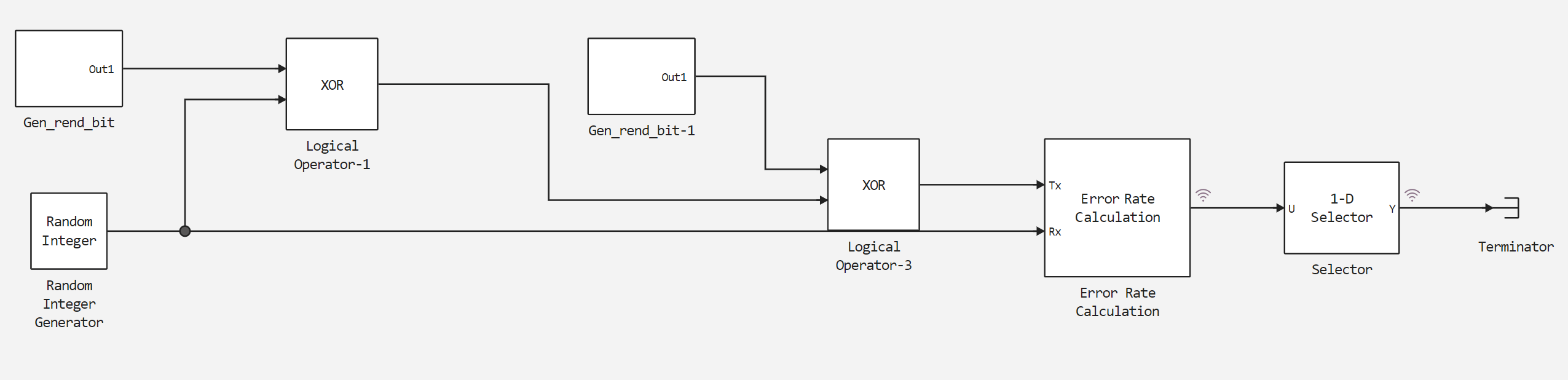
Let's run this model using the startup function described by us and save the results of the bit error.
function run_model(name_model)
Path = string(@__DIR__) * "/" * name_model * ".engee"
if name_model in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] # Checking the condition for loading a model into the kernel
model = engee.open( name_model ) # Open the model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
else
model = engee.load( Path, force=true ) # Upload a model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
engee.close( name_model, force=true ); # Close the model
end
return model_output
end
run_model("Scrambler_descrambler")
Let's analyze the stored values. BER is zero for 1001 steps.
# Reading stored signals from simout
BER = simout["Scrambler_descrambler/Error Rate Calculation.Out"];
BER = collect(BER)
BER[end-3:end,:]
Conclusion
Based on the results of this demonstration, we explored the possibilities of implementing the scrambling method used in the DVB video transmission protocols of the second generation.