Checksum calculation in Engee
Let's generate a CRC-8 checksum for an example from the 802.11-2016 standard in section 21.3.10.3 and compare it with the expected checksum.
Description of the model
To implement a variant of the checksum algorithm described in the 802.11-2016 standard, configure the block General CRC Generator to work with a polynomial . set the initial state of the bits to 1, set the XOR bit to 1, and select the direct method.
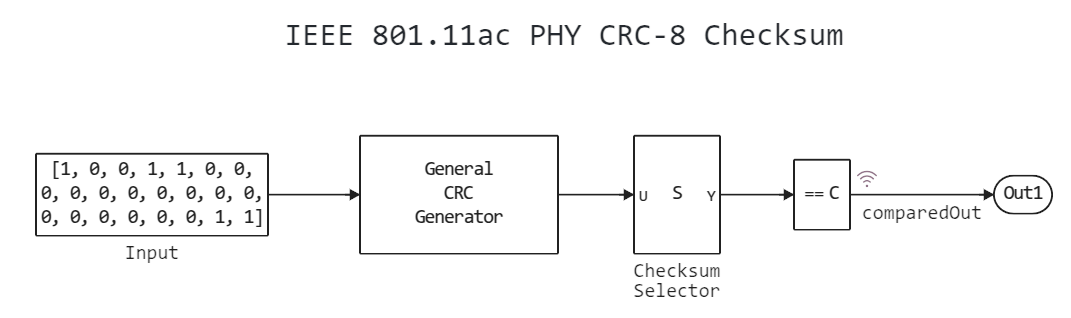
The length of the simulation is 0, meaning that one input message from the block will be processed. Input. This block is given as an example in the 802.11-2016 standard section 21.3.10.3. The message includes bits {m0, ... m22} with values [1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1], the expected checksum for them {c7, ..., c0} is [0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0]. The model has blocks for bitwise comparison of the calculated and expected checksum. Each time the comparator input matches the checksum embedded in it, the corresponding output bit takes on the value 1.
model_name = "generate_crc_8_checksum";
model_name in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] ? engee.open(model_name) : engee.load( "$(@__DIR__)/$(model_name).engee");
res = engee.run( model_name );
collect(res["comparedOut"]).value[end]
Conclusion
We have checked the operation of the block General CRC Generator and implemented the checksum calculation according to 802.11-2016.