What’s new in 24.9
_ Release date: September 2024_
 General
General
 The ability to "drag" a folder or file to the desired location
The ability to "drag" a folder or file to the desired location
Now you can move files or folders to the desired location by dragging them to the navigation bar. Look at the gif and you’ll immediately understand what it’s about.
 Keyboard control of the file browser
Keyboard control of the file browser
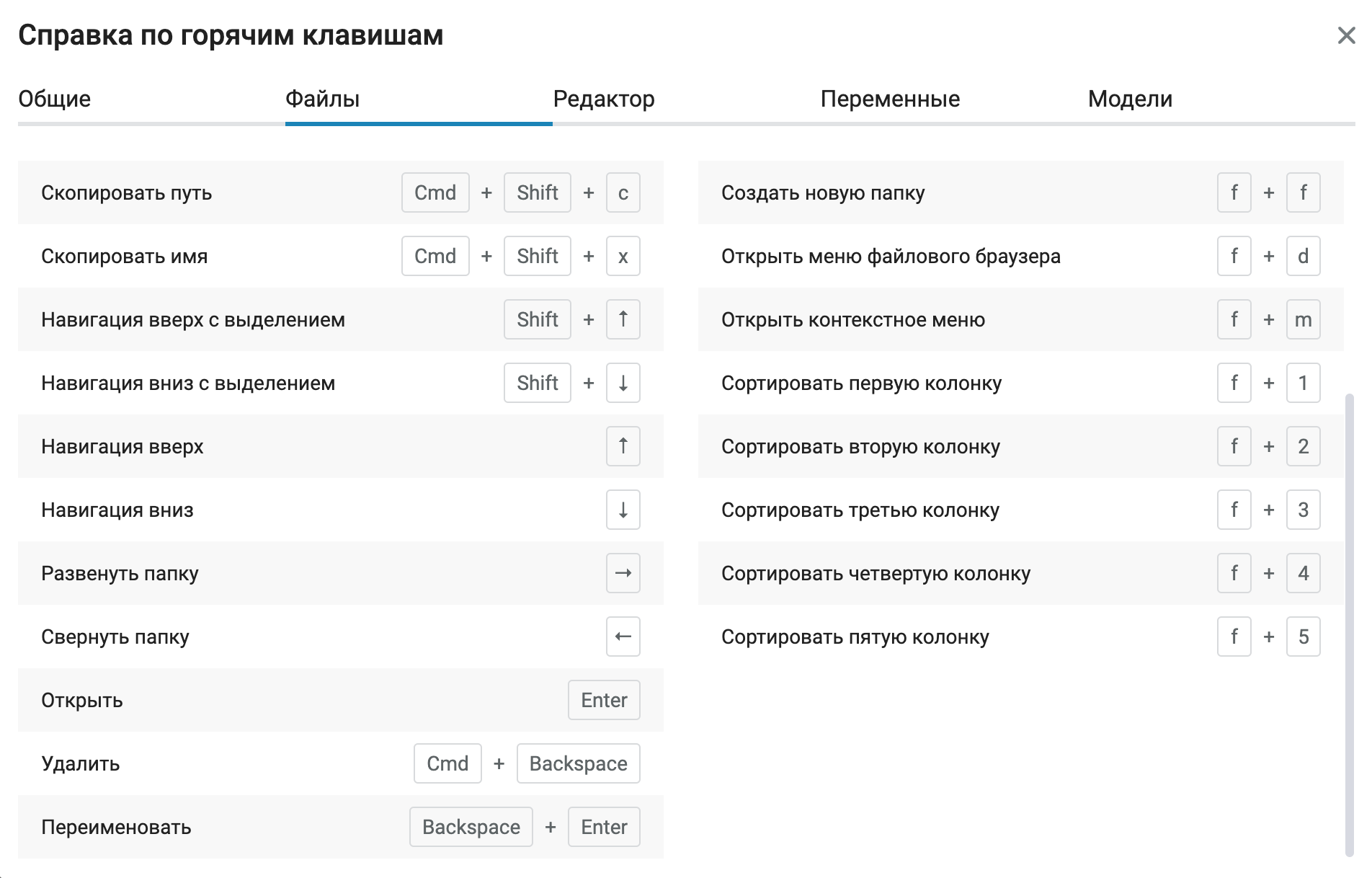
Added the ability to manage your folders and files using the keyboard. You can navigate through folders or navigate. We also added useful ones keyboard shortcuts for various actions. You can find the full list in the keyboard shortcuts menu (Shift+?).
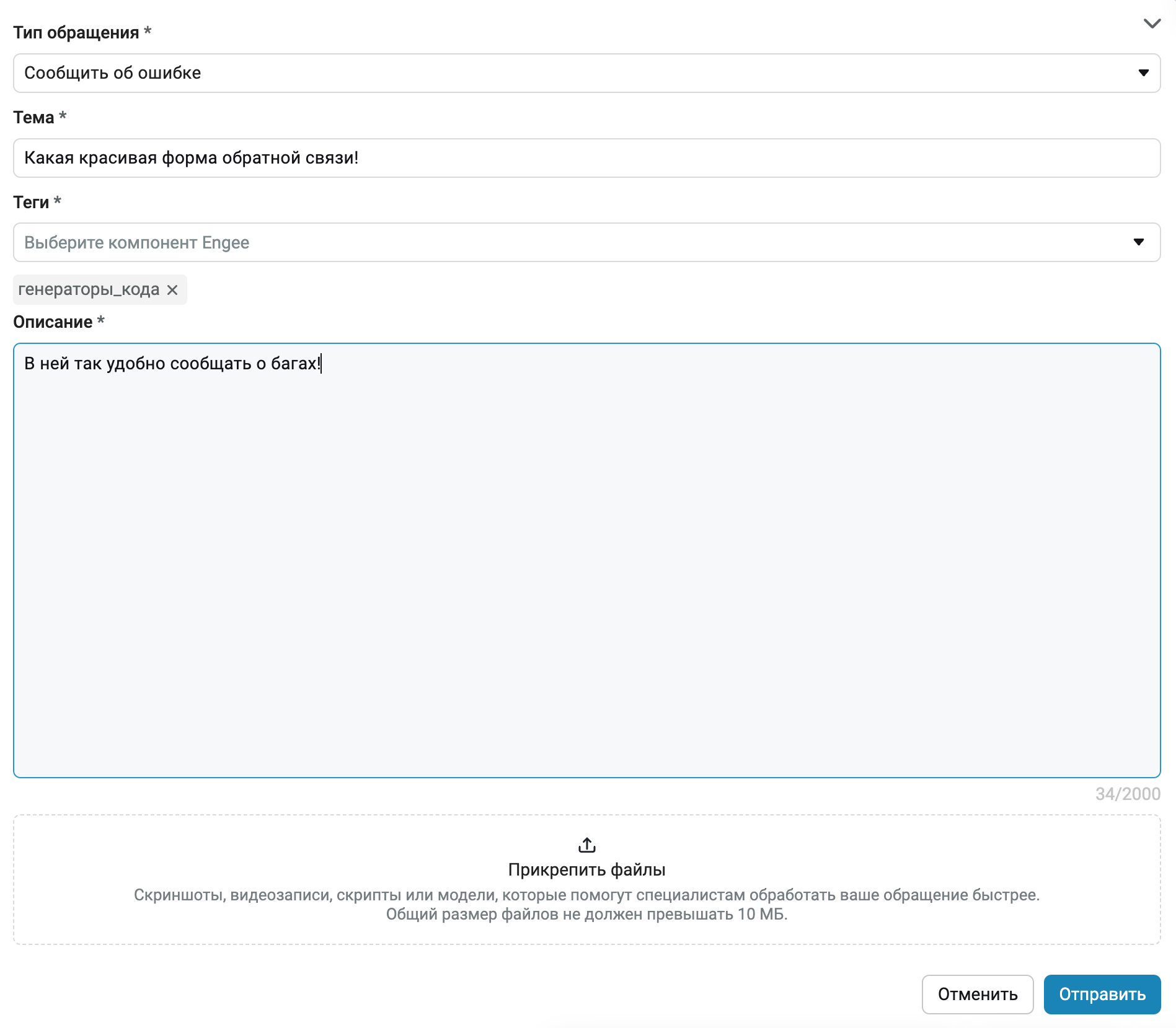
 New feedback form
New feedback form
The feedback menu has been completely redesigned. It has become faster, clearer and more convenient. We have reduced the number of types of requests, removed restrictions on attached files, and implemented the ability to open the form to make it easier to fill out. Now we will wait even more for your feedback!
 Mathematical Computing environment
Mathematical Computing environment
 Important new features in cell masks
Important new features in cell masks
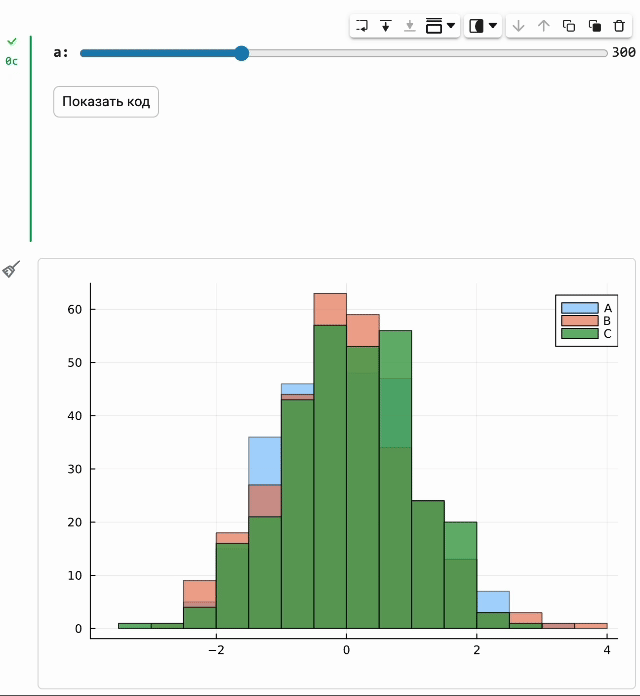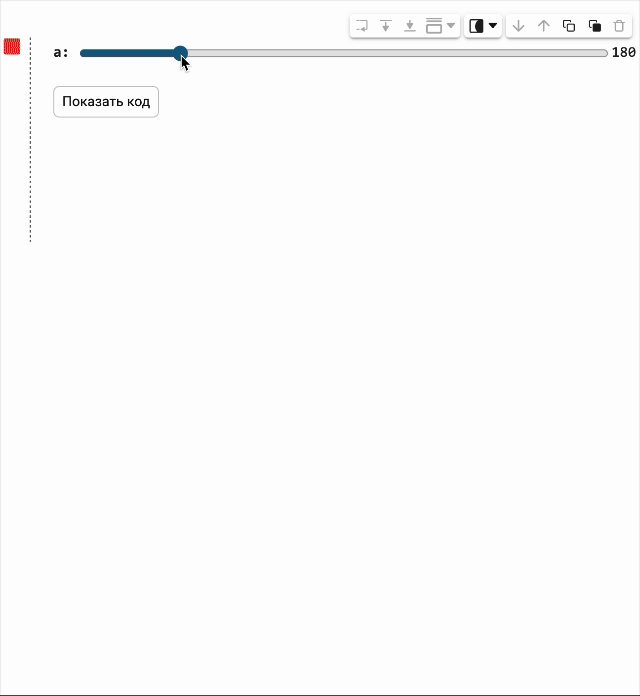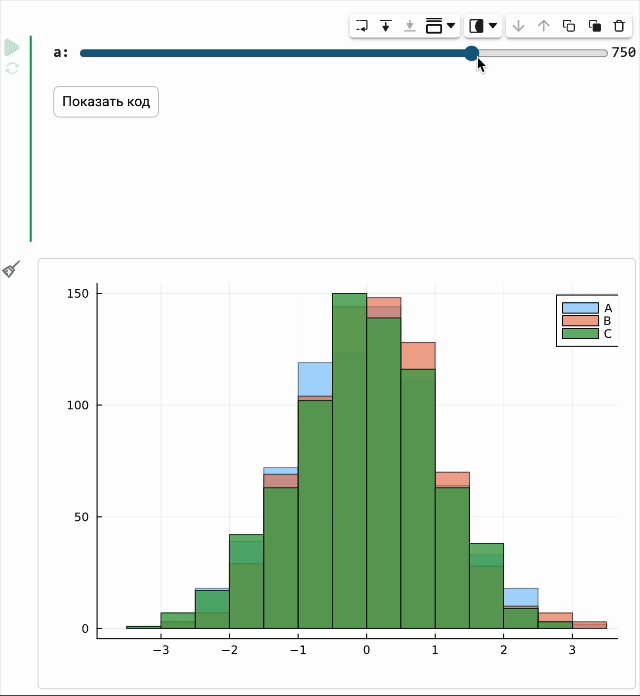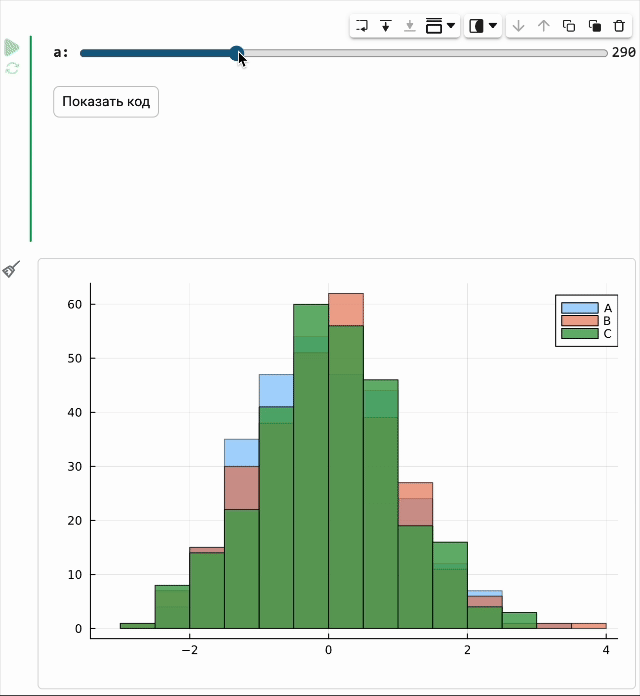
We have seriously improved the cell masks and now:
-
The code in the masked cell can be updated automatically on the fly when its parameters change. So now you just need to move the slider, and a new graph will be created immediately.
-
Also, from now on, you can hide the cell code, and this state will be preserved. Now your scripts will look like real interactive engineering applications!
 The modeling environment
The modeling environment
 Improving the performance and stability of the Engee computing core
Improving the performance and stability of the Engee computing core
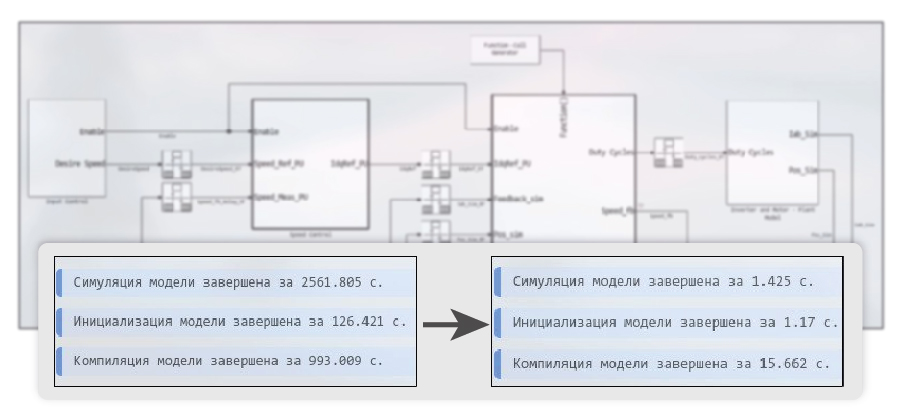
Working with large models in Engee allowed us to find bottlenecks in the internal representation of models. After the optimizations were performed, really large models (from 400 blocks) began to work orders of magnitude faster, some accelerated up to 200 times (compared to version 24.06)!
Another important area of optimization of the computing core has recently been the work of continuous integrators. We managed to speed them up to 10 times. In addition, we have improved the infrastructure for storing model calculation results, which also allowed us to speed up the simulation. As a result of our efforts, some simple models have become almost six times faster.
We also worked on a mechanism for detecting events in physical models and accelerated their simulation by up to 50% in discrete synchronization mode, which is used, for example, for real-time calculations, and up to 30% in continuous synchronization mode. In addition to speeding up the simulation, the changes had a positive impact on the stability and quality of calculations.
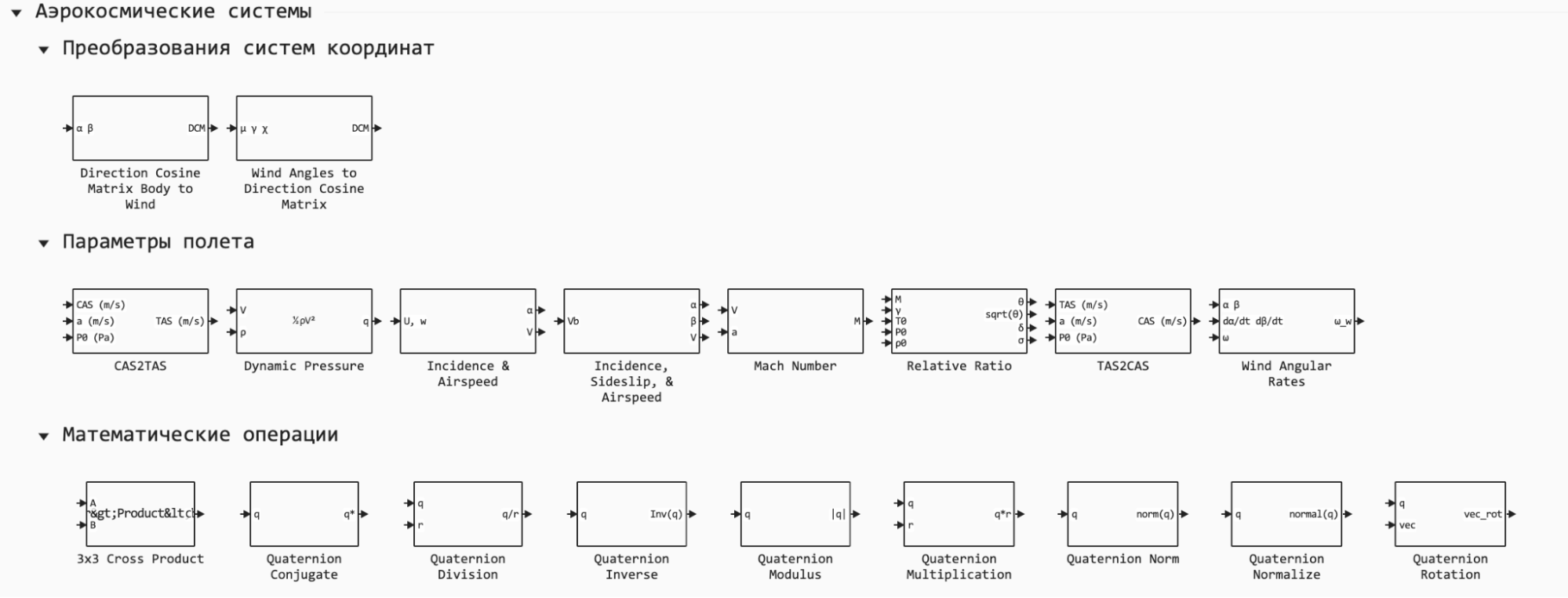
 New library of blocks: Aerospace Systems
New library of blocks: Aerospace Systems
The new built-in component library will allow simulating the dynamics of motion of aircraft, actuators and propulsion systems, as well as developing guidance, navigation and control algorithms.
With the help of specialized blocks, you will be able to develop a complete model of the movement of various types of aircraft as a material point or body with three (3DOF) and six (6DOF) degrees of freedom. To do this, you will have at your disposal a wide range of blocks for calculating equations of motion and flight parameters, such as flow angles, various speeds and the Mach number.
You can also find proven models of environments such as atmosphere, gravity, wind, geoid and gravity models. These models help to present flight conditions and improve simulation accuracy.
In addition, the library contains a large number of auxiliary blocks: you do not need to independently implement transformations of coordinate systems, recalculating units of measurement, or operations with quaternions.
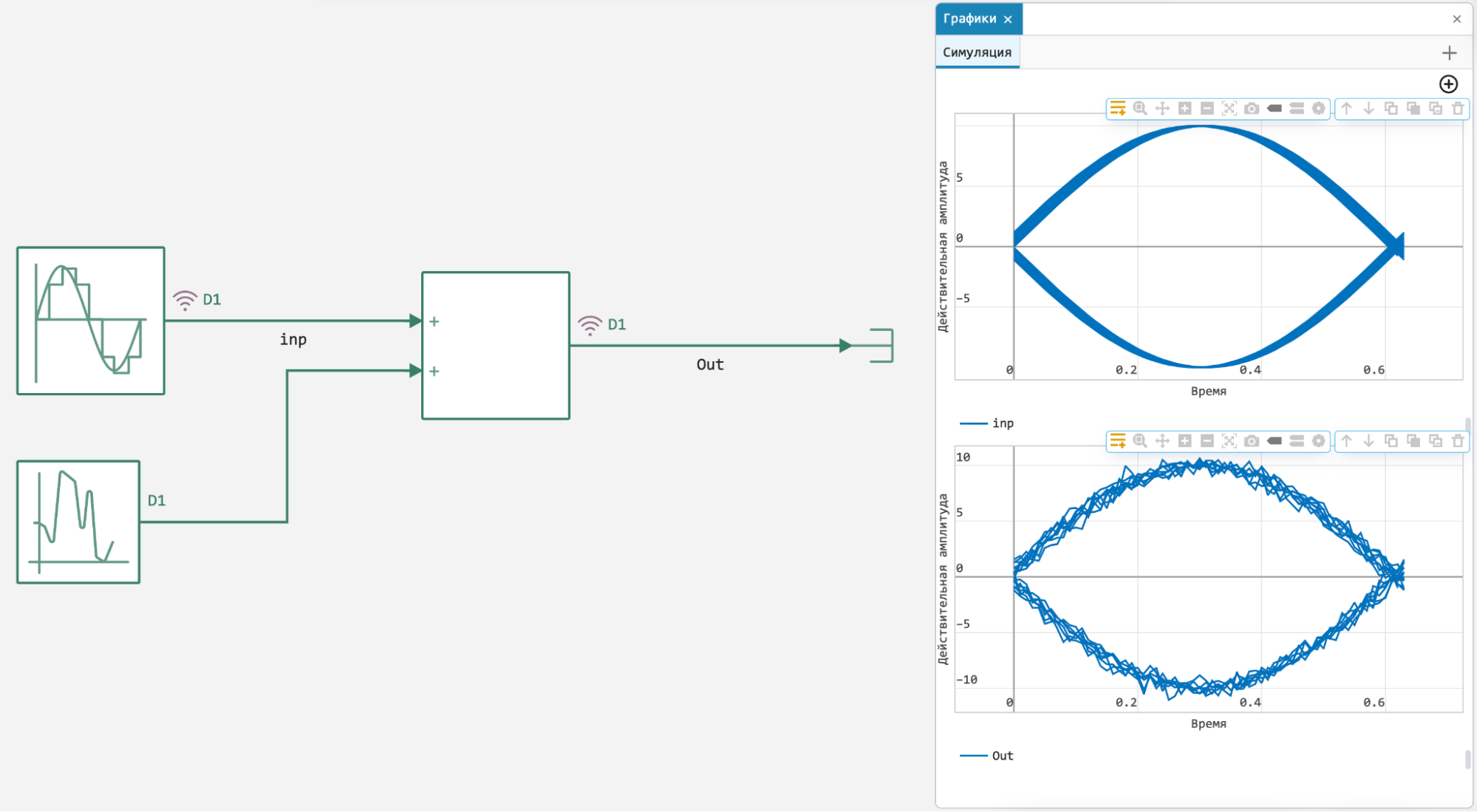
 New graph type: Eye Chart
New graph type: Eye Chart
An eye diagram of a signal is a summary view of all the bit periods of the measured signal superimposed on each other.
The eye diagram provides a lot of information about the jitter (phase noise) of the signal and about many other parameters of it. For example, many separate fronts and recessions indicate the likely presence of data-dependent jitter. The eye diagram is convenient for ease of use, including in any circuit with real data. It also allows you to determine the quality of the input signal by the level of "eye openness".
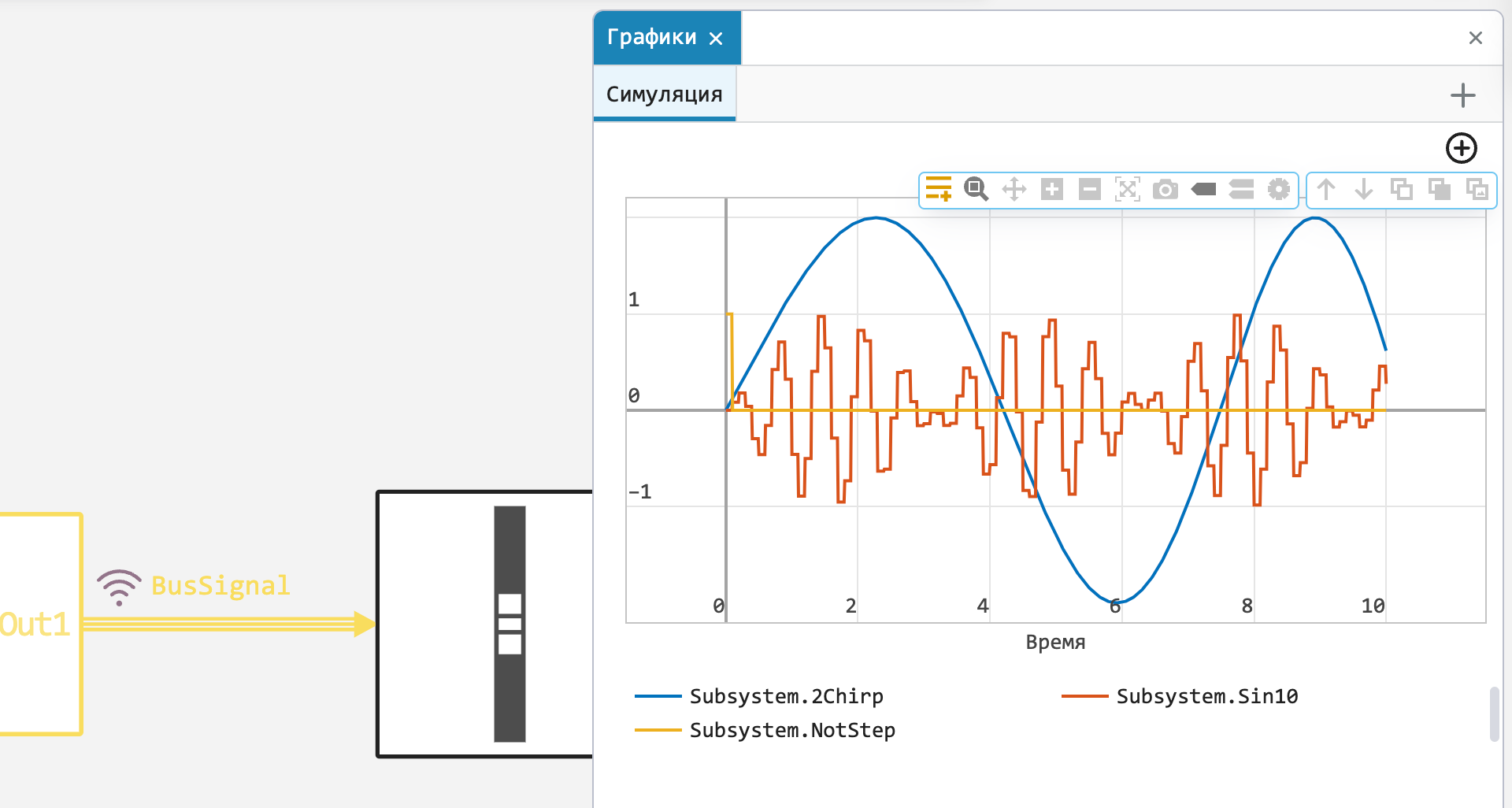
 Recording of bus signals
Recording of bus signals
Now you can mark the bus line for recording, select the signals you are interested in and display them on a graph.
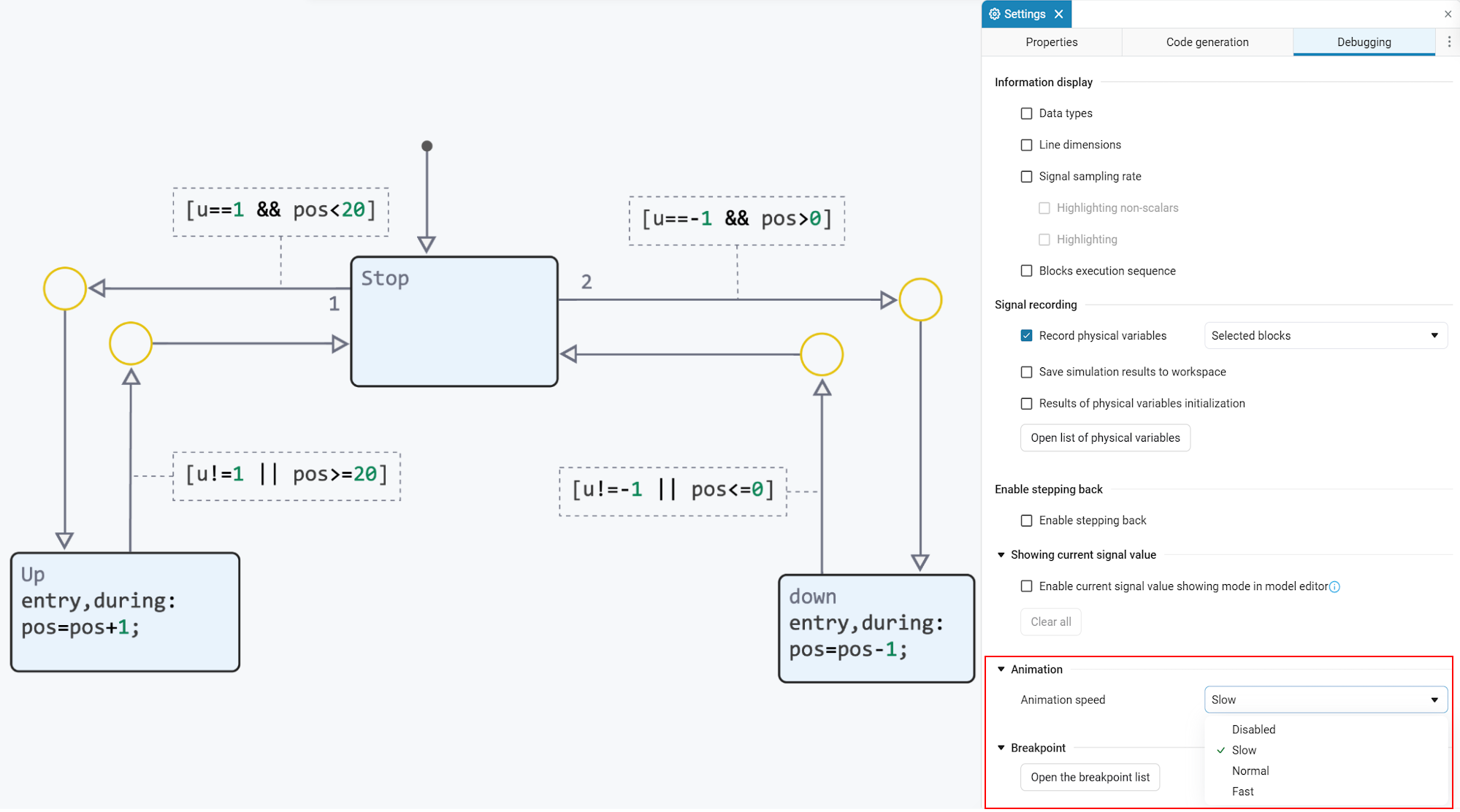
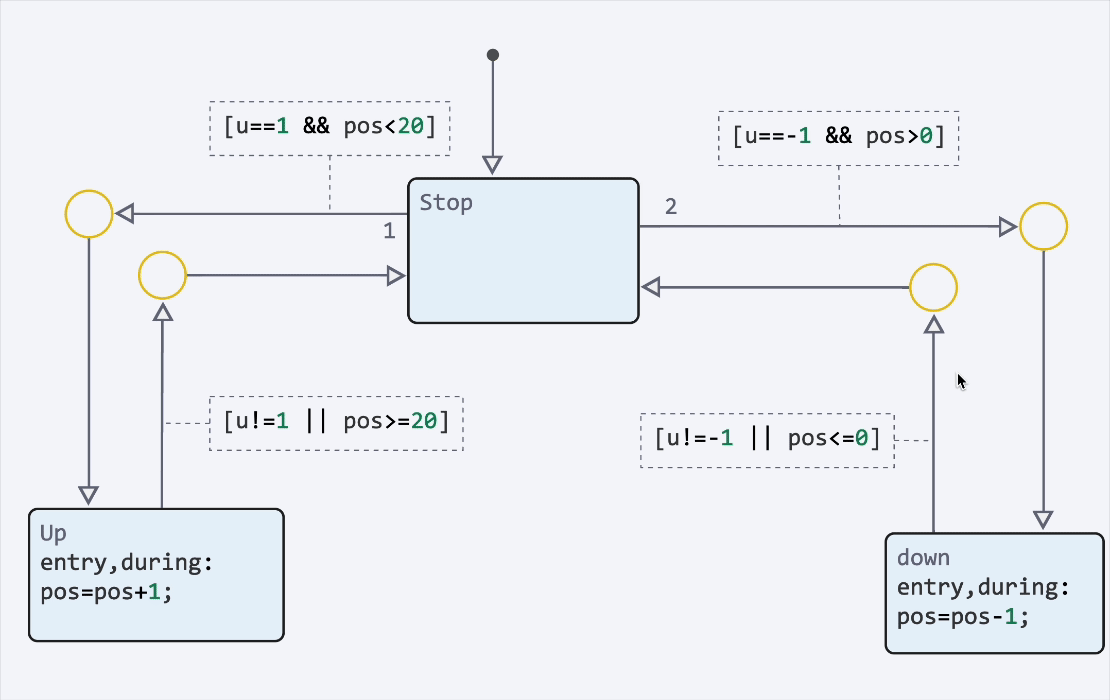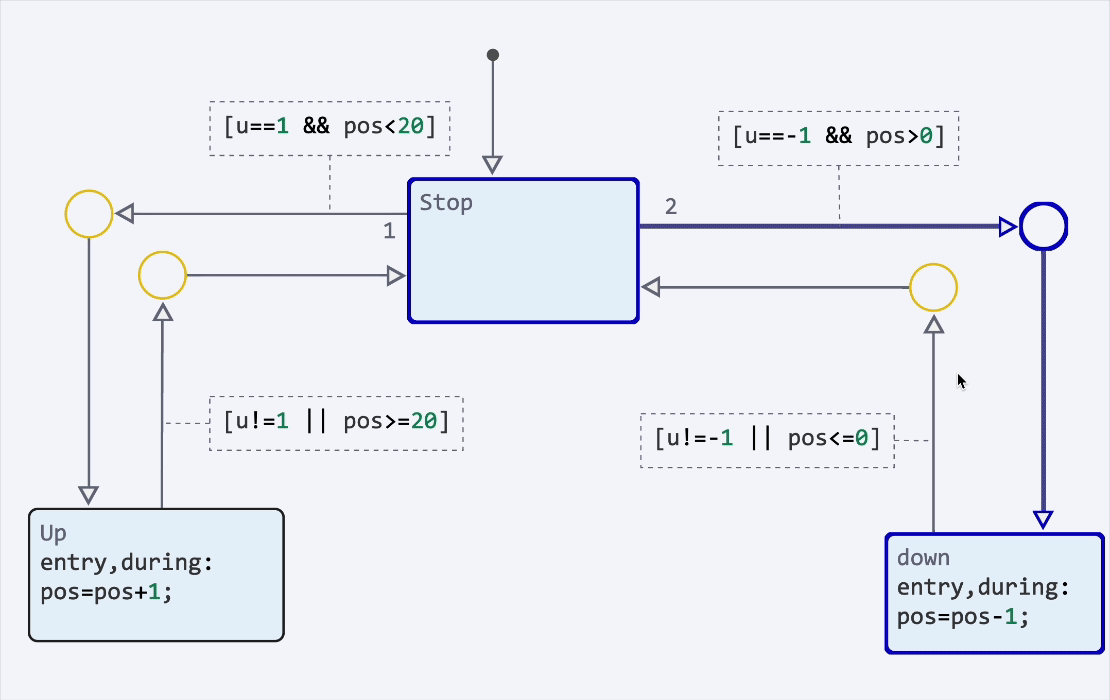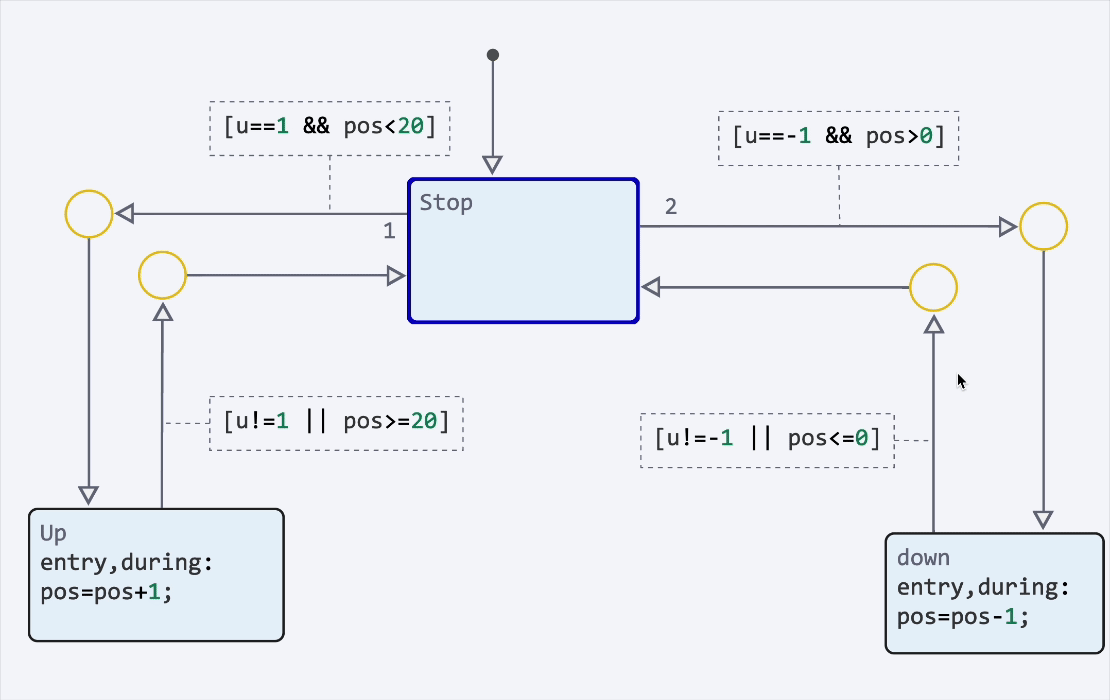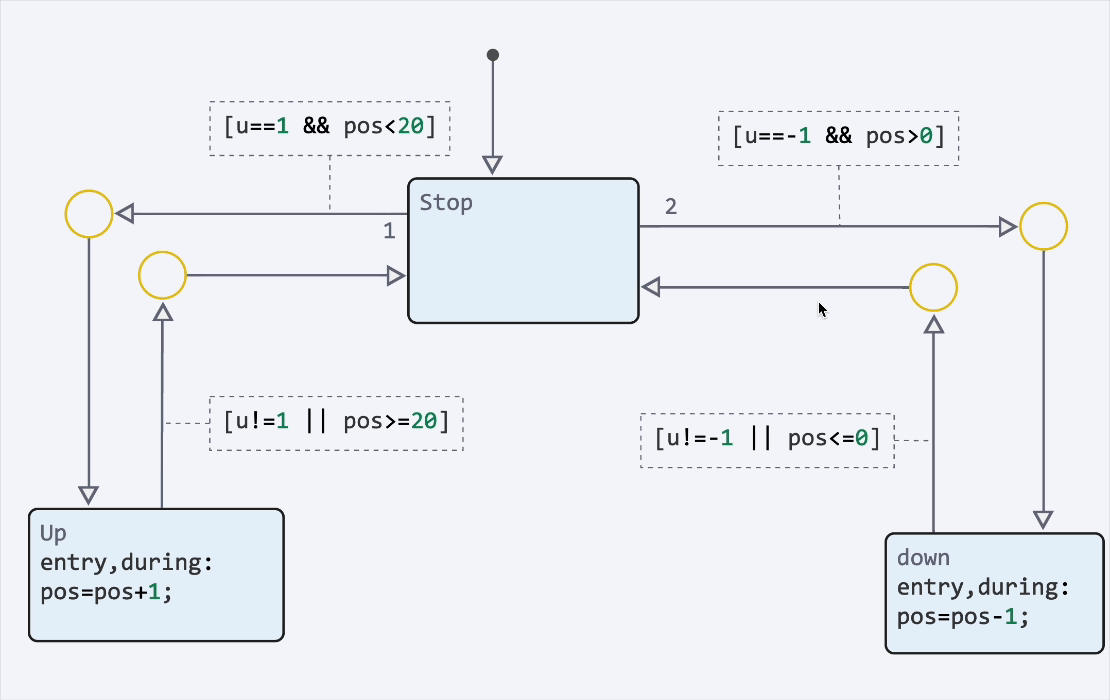
 Finite automata: highlighting transitions and syntax
Finite automata: highlighting transitions and syntax
We have implemented syntax highlighting of transitions, as well as animation of transitions during the modeling process. It has now become much more convenient to debug finite state machines. You can enable animation and adjust its speed in the model debugging menu.
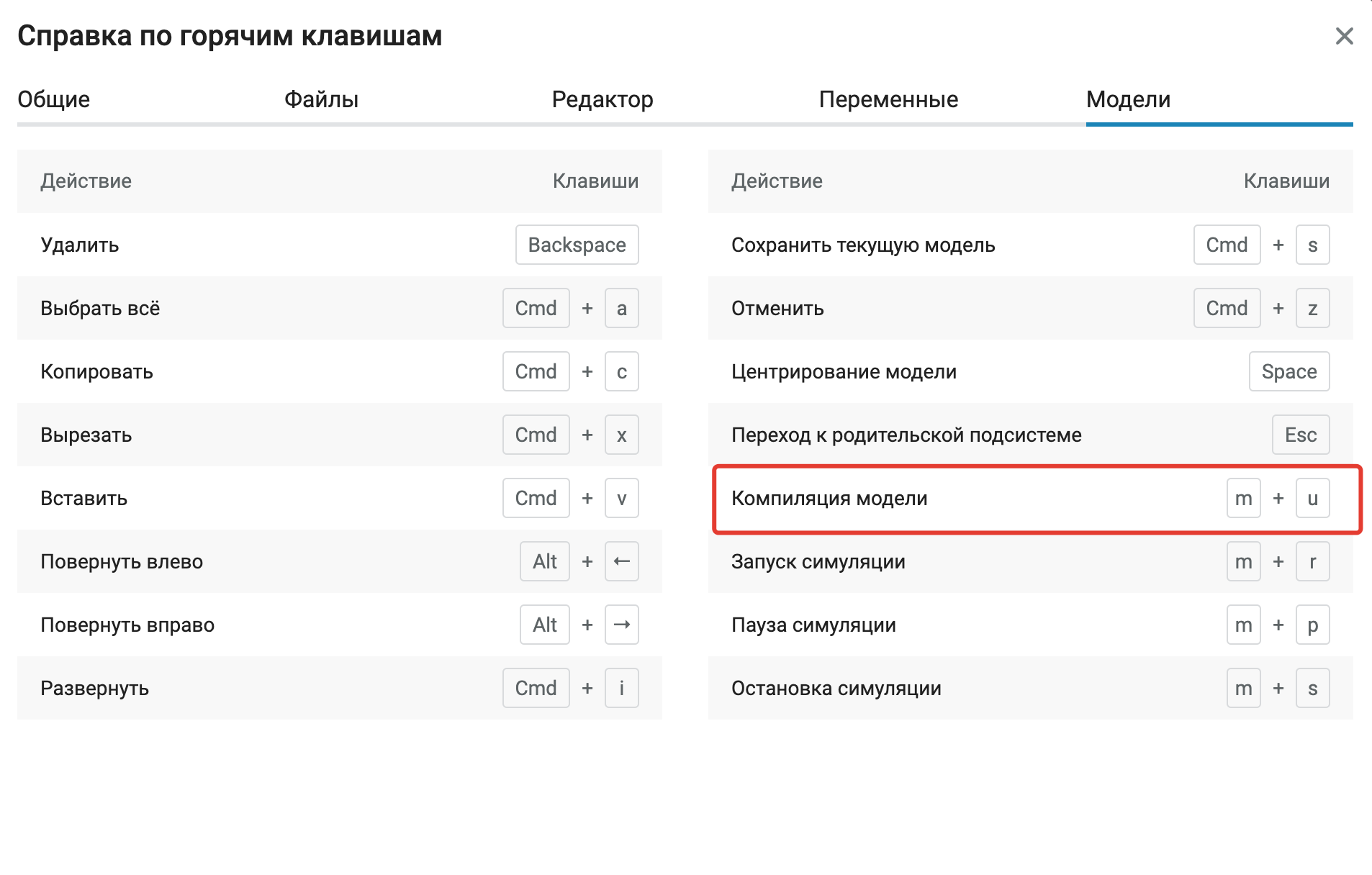
 Help with hotkeys in modeling
Help with hotkeys in modeling
We have added a section for the simulation environment in the hotkey menu. Recall that it causes a combination of Shift+?. And we also added the long-awaited combination for compiling the model (m+u).
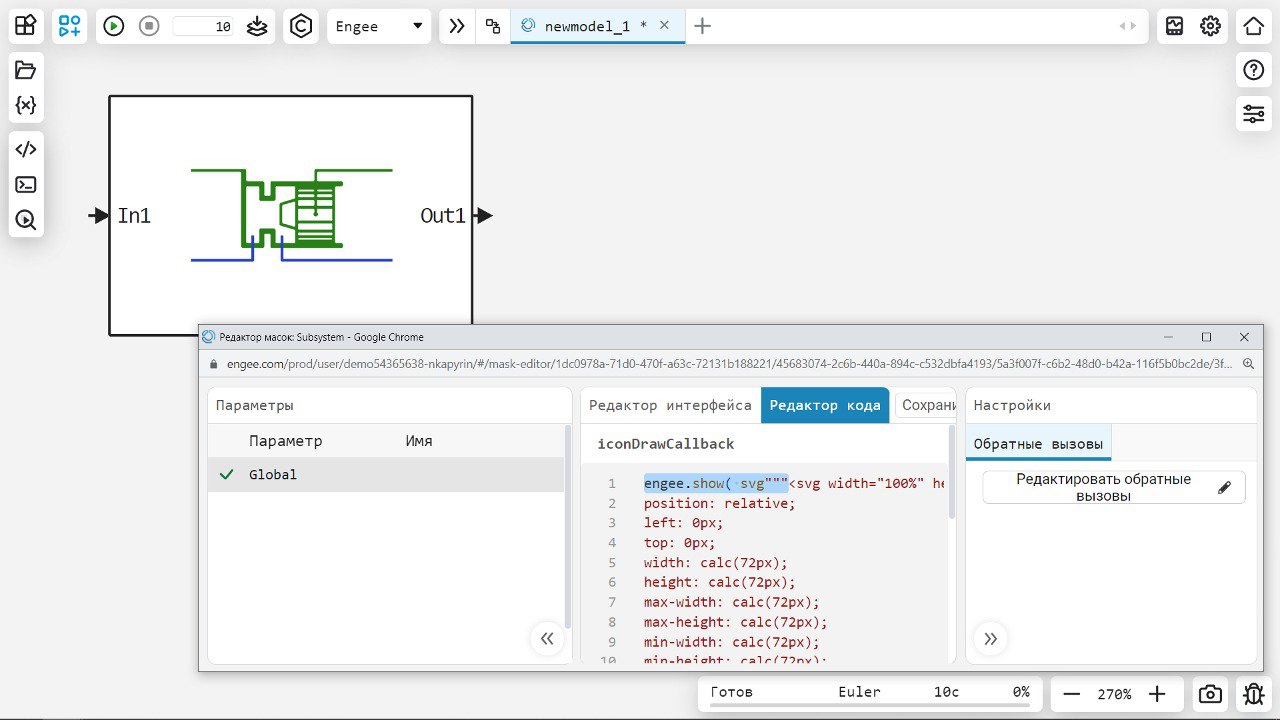
 Allowed to display SVG on the block mask
Allowed to display SVG on the block mask
Now you can display an image in SVG format on the mask. Your blocks will be beautiful and custom not only inside, but also outside! 🙂
 New blocks and updates
New blocks and updates
Library of Electrical Elements
Phased array antennas
Isothermal liquid
Signal processing
Aerospace systems
Communication systems
 Library updates and fixes
Library updates and fixes
Phased array antennas
System objects:
-
EngeePhased.DPCACanceller -
EngeePhased.SumDifferenceMonopulseTracker2D -
EngeePhased.SumDifferenceMonopulseTracker -
EngeePhased.ESPRITEstimator -
EngeePhased.AngleDopplerResponse -
EngeePhased.MVDRBeamformer -
EngeePhased.LCMVBeamformer -
EngeePhased.BeamscanEstimator -
EngeePhased.MVDREstimator -
EngeePhased.BeamscanEstimator2D -
EngeePhased.MVDREstimator2D -
EngeePhased.TimeDelayBeamformer -
EngeePhased.TimeDelayLCMVBeamformer -
EngeePhased.SubbandPhaseShiftBeamformer
Functions:
-
azelaxes -
cart2sphvec -
global2localcoord -
lcmvweights -
local2globalcoord -
mvdrweights -
radialspeed -
rotx -
roty -
rotz -
sensorcov -
sph2cartvec -
spsmooth
 Code generation
Code generation
 Managing signal names in the generated code
Managing signal names in the generated code
The code generator now takes into account the custom names of the signals in the model when generating the code. This allows you to make the code more readable and traceable to the model.
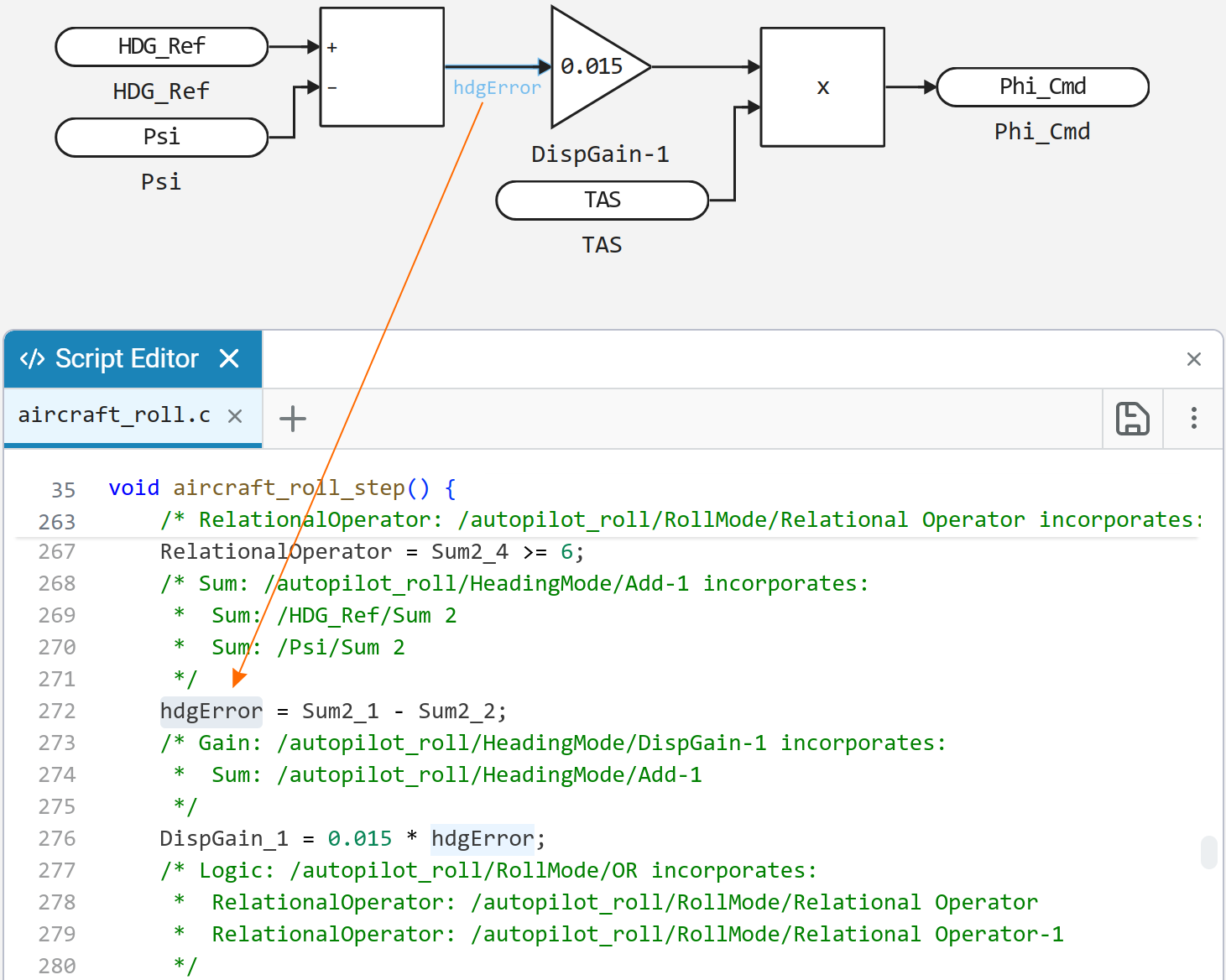
If the signal (block output) is signed, then the generated code for this signal will have the same variable name (if possible, that is, the signal has not been optimized and does not contain characters unsupported in the C code).