Integrating C code into Engee models using the C Function block
This example shows various ways to integrate C code into Engee models using the C Function block.
Before starting work, we will connect the library for comparison with MATLAB.:
using MATLAB
Using a macro @__DIR__ in order to find out the folder where the interactive script is located:
demoroot = @__DIR__
Basics of using the C Function block
Let's look at simple examples of using the C Function block, illustrating the basics of integrating C code into the Engee model.
1. Working with multidimensional signals, passing parameters and using the #define directive
Into the model cCodeIntegration_basics.engee The C Function block has been added, which receives a sinusoidal signal at its input. in:
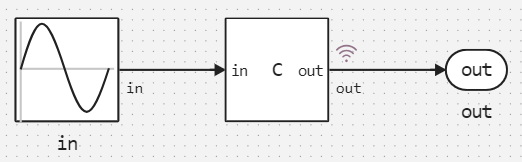
Suppose we want to increase the amplitude of the sine wave in in gain once and shift it by an amount bias. That is, the output signal should be determined by the formula out = gain * in + bias.
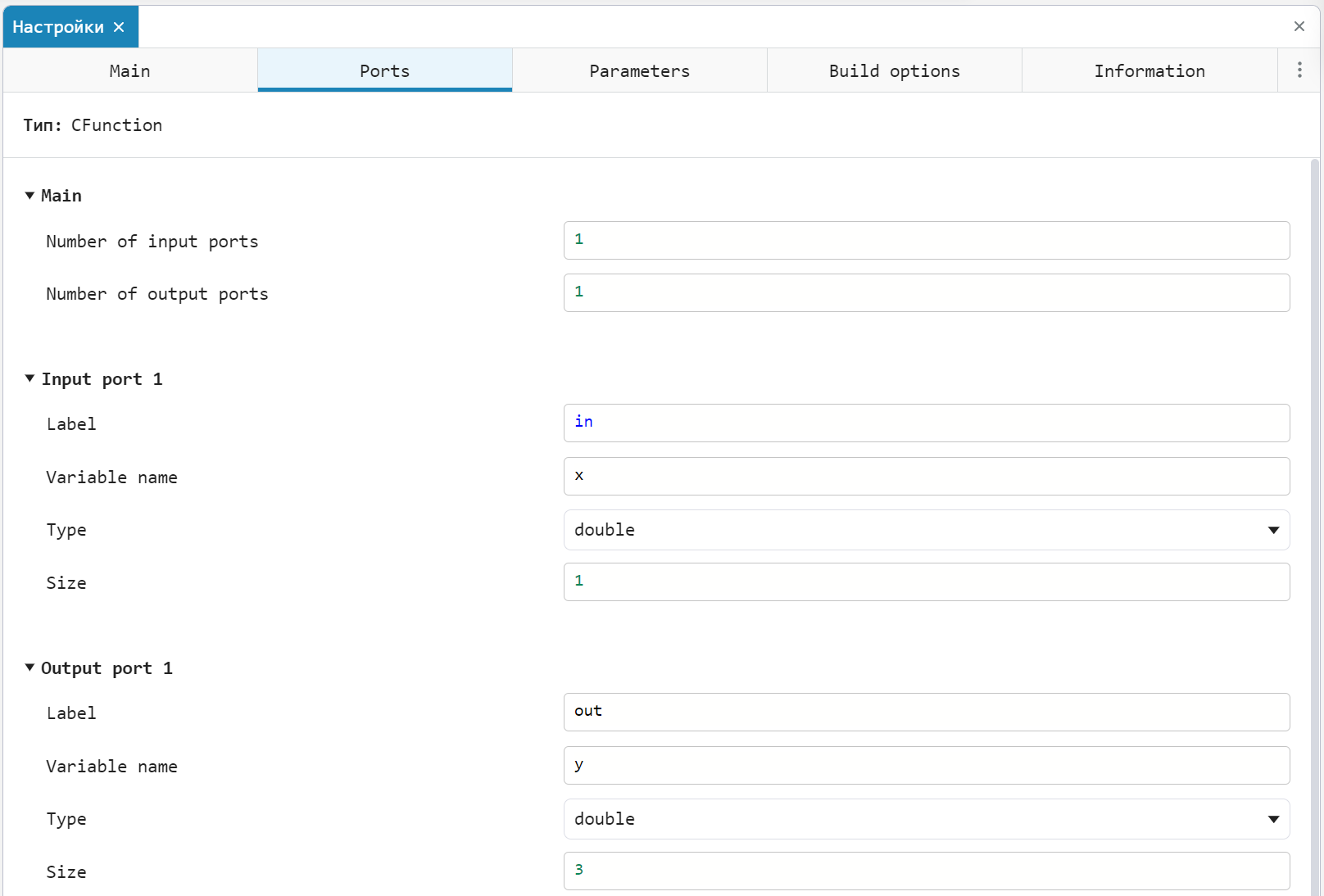
Let's go to the settings of the C Function block, where in the tab Ports we will get acquainted with the definition of the input and output of the block. This is where the source code variables are associated with the ports of the C Function block.:
- Scalar variable
xlikedoublecommunicates with the first input portin; - Vector (3 elements) variable
ylikedoublecommunicates with the first output portout.
Array gain it is also defined in the settings of the C Function block (tab Parameters):
It is worth noting that after passing a variable as a parameter, it becomes:
- Global - to
gainYou can access it from any tab of the source code editor.; - With a qualifier
const- when trying to change the valuegainan error will be received.
The amount of displacement bias determined by the identifier #define bias, which is set in the tab Build options:
.png)
In this example, the offset is 5.
Let's go to vladka Main set up the C Function block and click the "Edit source code" button. In the source code editor that opens, on the tab OutputCode the code executed at each step of the model calculation is given.:
.png)
In the loop for (for each of the three output signals) at each step of the model calculation, the value of the variable is determined y.
Let's model the system:
cCodeIntegration_basics = engee.load("$demoroot/models/cCodeIntegration_basics.engee", force = true)
simulationResults_basics = engee.run(cCodeIntegration_basics)
Closing the model:
engee.close(cCodeIntegration_basics, force = true);
Importing the simulation results:
cCodeIntegration_basics_t = simulationResults_basics["out"].time;
cCodeIntegration_basics_y1 = [y[1] for y in simulationResults_basics["out"].value];
cCodeIntegration_basics_y2 = [y[2] for y in simulationResults_basics["out"].value];
cCodeIntegration_basics_y3 = [y[3] for y in simulationResults_basics["out"].value];
Let's build a graph:
plot(cCodeIntegration_basics_t, cCodeIntegration_basics_y1)
plot!(cCodeIntegration_basics_t, cCodeIntegration_basics_y2)
plot!(cCodeIntegration_basics_t, cCodeIntegration_basics_y3)
title!("The output signal of the C Function block <br> (Multidimensional signals, parameters, and #define)")
xlabel!("Time, [s]")
ylabel!("The amplitude")
2. Using integer data types and static variables
In the model cCodeIntegration_integers.engee using the C Function block, we implement a simple counter, the output of which will be a positive integer indicating the number of the current iteration.:
Let's analyze the contents of the tabs Ports and Build Options in the C Function block settings:
.png)
.png)
The names of integer data types in the C Function block are set according to the header file <stdint.h> the standard library of the C language. This file is attached in the line Headers tabs Build options.
In the tab Ports an unsigned 64-bit variable is bound. out (the type is set as uint64_t rather than long, see the previous paragraph about <stdint.h>) of the source code with the first output port of the C Function block.
In the tab Output code the editor of the source code of the C Function block shows the code executed at each step of the simulation.:
.png)
Static variable counter it is initialized to 0 at the first step of the simulation, after which, at each iteration, its value increases by 1 and is assigned to a variable out.
Let's model the system:
cCodeIntegration_integers = engee.load("$demoroot/models/cCodeIntegration_integers.engee", force = true)
simulationResults_integers = engee.run(cCodeIntegration_integers)
Closing the model:
engee.close(cCodeIntegration_integers, force = true);
Importing the simulation results:
cCodeIntegration_integers_t = simulationResults_integers["counter"].time;
cCodeIntegration_integers_y = simulationResults_integers["counter"].value;
Let's build a graph:
plot(cCodeIntegration_integers_t, cCodeIntegration_integers_y, legend = false)
title!("The output signal of the C Function block <br> (Integer types and static variables)")
xlabel!("Time, [s]")
ylabel!("Iteration number")
More detailed information about the purpose of the source code editor tabs, building capabilities, and available data types is provided [in the documentation] (https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/base-lib-user-defined-function/c-function.html ) Engee.
Integration of external source code
Setting the task
Let's consider a more interesting engineering problem.
Let's assume that, taking into account the measurement noise, we need to control a stable object of the second order, which is affected by external disturbances. Therefore, we will need to solve the problem of filtering the output signal of the control object, and fortunately, Engee has a tool that is great for this!
In the files alphabetafilter.c and alphabetafilter.h the implementation of the [alpha-beta filter] is proposed (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_beta_filter ) in the C language.
File Contents alphabetafilter.c:
#include "alphabetafilter.h"
#include <math.h>
double dt = 0.01;
static double xk_1, vk_1;
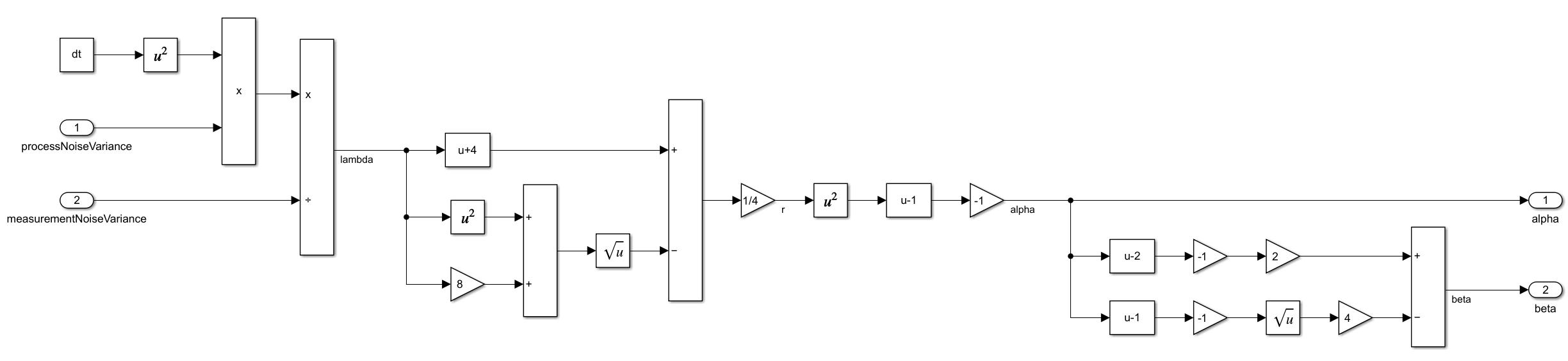
Parameters determineAlphaBeta(double processNoiseVariance, double measurementNoiseVariance)
{
double lambda, r;
Parameters p;
lambda = (processNoiseVariance * pow(dt, 2)) / measurementNoiseVariance;
r = (4 + lambda - sqrt(8 * lambda + pow(lambda, 2))) / 4;
p.alpha = 1 - pow(r, 2);
p.beta = 2 * (2 - p.alpha) - 4 * sqrt(1 - p.alpha);
return p;
}
double alphaBetaFilter(double value, Parameters p)
{
double xk, vk, rk;
xk = xk_1 + (vk_1 * dt);
vk = vk_1;
rk = value - xk;
xk += p.alpha * rk;
vk += (p.beta * rk) / dt;
xk_1 = xk;
vk_1 = vk;
return xk;
}
void initializeStaticVariables()
{
xk_1 = 0;
vk_1 = 0;
}
File Contents alphabetafilter.h:
typedef struct {
double alpha;
double beta;
} Parameters;
Parameters determineAlphaBeta(double, double);
double alphaBetaFilter(double, Parameters);
void initializeStaticVariables();
We integrate this source code into our Engee model.
Model analysis
Model cCodeIntegration_source.engee:
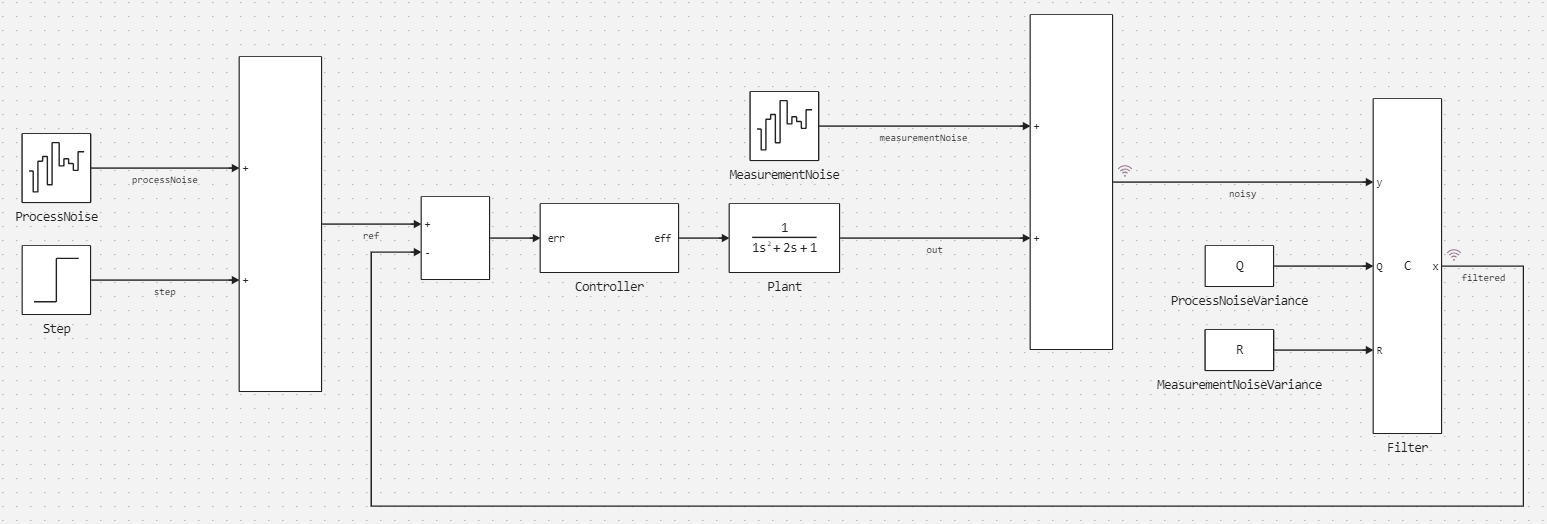
This model consists of:
- The management object
Plant - Subsystems implementing a second-order PID controller
Controller; - Blocks Band-Limited White Noise
ProcessNoiseandMeasurementNoisesimulating the external impact and measurement noise; - The C Function block
Filter, which implements the alpha-beta filter.
Parameter Sample Time the block Filter is equal to the step of the model solver Ts:
.png)
Let's analyze the contents of the tab Build options block settings Filter:
.png)
In the lines of this tab:
Source files- the source code file is connectedalphabetafilter.c;Iinclude directories- the path to the folder containing the header file is set.;Headers- the header file is connectedalphabetafilter.h.
In the tab Ports The source code variables are associated with the input and output ports of the block. Filter.
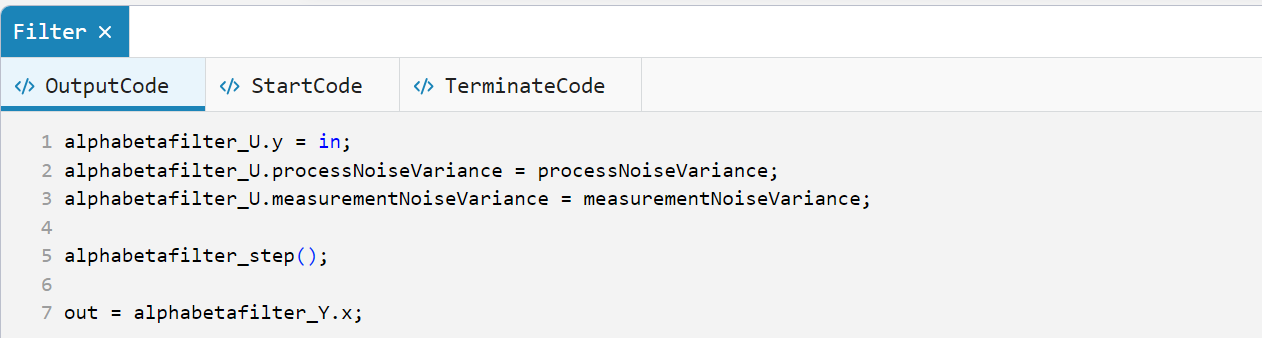
In the source code of the block Filter on the tab OutputCode the cyclically executed code is given:
.png)
At each step of the model calculation, the functions are called sequentially determineAlphaBeta() and alphabetafilter(), after which the filtered value is saved to a variable out corresponding to the output port x the block Filter.
Running the simulation
Let's model the system:
cCodeIntegration_source = engee.load("$demoroot/models/cCodeIntegration_source.engee", force = true)
simulationResults_source = engee.run(cCodeIntegration_source)
Closing the model:
engee.close(cCodeIntegration_source, force = true);
Simulation results
Importing the simulation results:
cCodeIntegration_source_noisy_t = simulationResults_source["noisy"].time;
cCodeIntegration_source_noisy_y = simulationResults_source["noisy"].value;
cCodeIntegration_source_filtered_t = simulationResults_source["filtered"].time;
cCodeIntegration_source_filtered_y = simulationResults_source["filtered"].value;
Let's build a graph:
plot(cCodeIntegration_source_noisy_t, cCodeIntegration_source_noisy_y, label = "The original signal")
plot!(cCodeIntegration_source_filtered_t, cCodeIntegration_source_filtered_y, label = "Filtered signal")
plot!(legend = :bottomright)
title!("Alpha-beta filter <br> (Integration of external source code)")
xlabel!("Time, [s]")
ylabel!("The amplitude")
Integration of static and dynamic libraries
Setting the task
The source code is often supplied not explicitly, but as part of static or dynamic libraries. Libraries with the C API interface are integrated into Engee models as easily as external source code!
Compile a static (alphabetafilter.a) and dynamic (alphabetafilter.so) a library of files alphabetafilter.c and alphabetafilter.h using MakeFile.
File Contents Makefile:
all: alphabetafilter.a alphabetafilter.so
alphabetafilter.o: alphabetafilter.c
$(CC) -c -fPIC $^ -o $@
alphabetafilter.a: alphabetafilter.o
ar rcs $@ $^
alphabetafilter.so: alphabetafilter.o
$(CC) -shared $^ -o $@
clean:
rm -f *.o *.a *.so
Let's start compiling libraries:
run(`make -C $demoroot/source`)
Integrating the static and dynamic library into our Engee model.
Static Library: Model analysis
By its structure, the model cCodeIntegration_library_static.engee it does not differ from the one discussed earlier cCodeIntegration_source.engee; only the directives on the tab differ Build options block settings Filter. Let's analyze its contents:
.png)
The following construction options are defined here:
Include directories- the path to the folder containing the header file is set.;Library directories- the path to the folder containing the static library is set.;Headers- the header file is connectedalphabetafilter.h;Libraries- the static library is connectedalphabetafilter.a.
Static Library: Running a simulation
Let's model the system:
cCodeIntegration_library_static = engee.load("$demoroot/models/cCodeIntegration_library_static.engee", force = true)
simulationResults_library_static = engee.run(cCodeIntegration_library_static)
Closing the model:
engee.close(cCodeIntegration_library_static, force = true);
Static Library: Simulation results
Importing the simulation results:
cCodeIntegration_library_static_noisy_t = simulationResults_library_static["noisy"].time;
cCodeIntegration_library_static_noisy_y = simulationResults_library_static["noisy"].value;
cCodeIntegration_library_static_filtered_t = simulationResults_library_static["filtered"].time;
cCodeIntegration_library_static_filtered_y = simulationResults_library_static["filtered"].value;
Let's build a graph:
plot(cCodeIntegration_library_static_noisy_t, cCodeIntegration_library_static_noisy_y, label = "The original signal")
plot!(cCodeIntegration_library_static_filtered_t, cCodeIntegration_library_static_filtered_y, label = "Filtered signal")
plot!(legend = :bottomright)
title!("Alpha-beta filter <br> (Static Library integration)")
xlabel!("Time, [s]")
ylabel!("The amplitude")
Dynamic Library: Model Analysis
By its structure, the model cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic.engee it does not differ from the one discussed earlier cCodeIntegration_source.engee; only the directives on the tab differ Build options block settings Filter. Let's analyze its contents:
.png)
The following construction options are defined here:
Include directories- the path to the folder containing the header file is set.;Library directories- the path to the folder containing the dynamic library is set.;Headers- the header file is connectedalphabetafilter.h;Libraries- a dynamic library is enabledalphabetafilter.so.
In the Start code tab of the block source editor Filter the function is being called initializeStaticVariables():
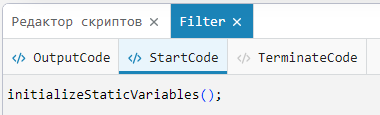
Function initializeStaticVariables() declared in the file alphabetafilter.h and it is intended for initialization of static variables. xk_1 and vk_1, used in the dynamic library. This is necessary so that when the simulation is restarted, the variables do not retain their last calculated value, but reset to their original value (in this case, in 0).
Dynamic Library: Running a simulation
Let's model the system:
cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic = engee.load("$demoroot/models/cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic.engee", force = true)
simulationResults_library_dynamic = engee.run(cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic)
Closing the model:
engee.close(cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic, force = true);
Dynamic Library: Simulation results
Importing the simulation results:
cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic_noisy_t = simulationResults_library_dynamic["noisy"].time;
cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic_noisy_y = simulationResults_library_dynamic["noisy"].value;
cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic_filtered_t = simulationResults_library_dynamic["filtered"].time;
cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic_filtered_y = simulationResults_library_dynamic["filtered"].value;
Let's build a graph:
plot(cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic_noisy_t, cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic_noisy_y, label = "The original signal")
plot!(cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic_filtered_t, cCodeIntegration_library_dynamic_filtered_y, label = "Filtered signal")
plot!(legend = :bottomright)
title!("Alpha-beta filter <br> (Dynamic Library integration)")
xlabel!("Time, [s]")
ylabel!("The amplitude")
Integration of the code generated from the Simulink model
Setting the task
Generate the C code from the Simulink model alphabetafilter.slx and integrate it into our Engee model. cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink.engee.
Model alphabetafilter.slx, which implements the alpha-beta filter, is assembled in Simulink from simple blocks and consists of subsystems determineAlphaBeta and filterInputSignal.
The upper level of the model:
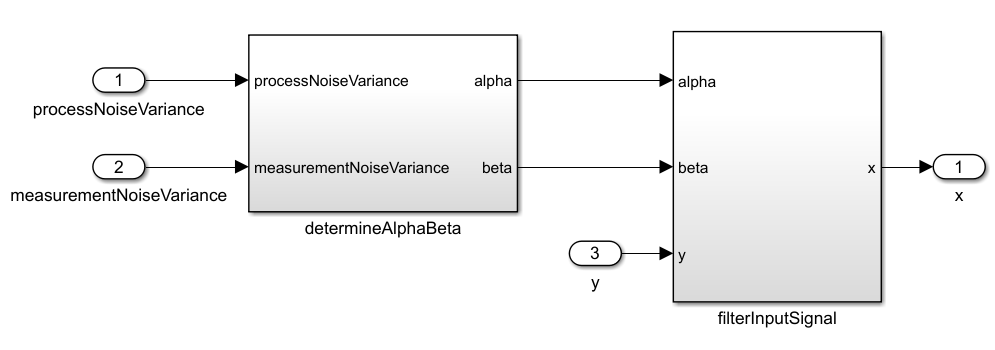
Subsystem determineAlphaBeta:
Subsystem filterInputSignal:
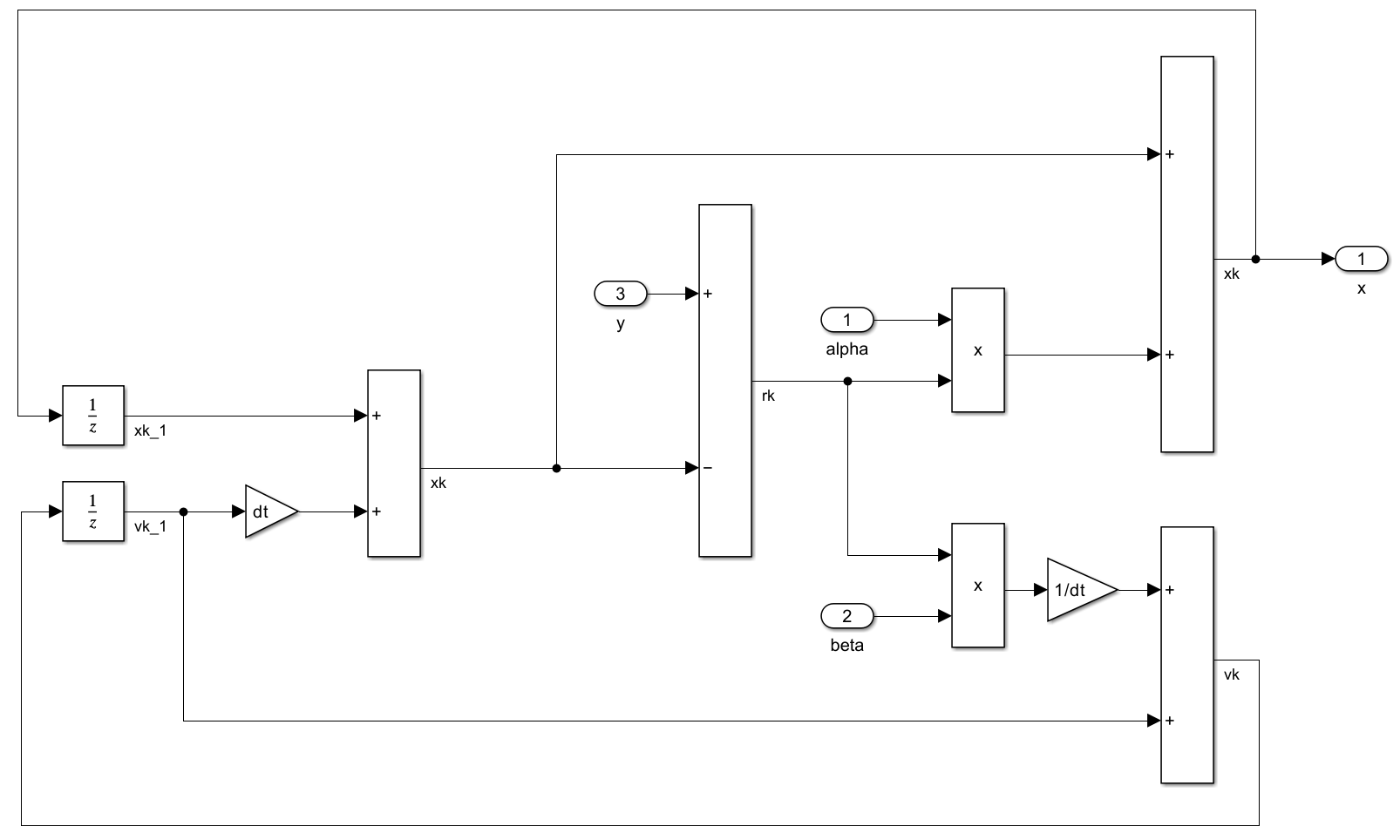
Generate the code using Simulink Embedded Coder:
cgPath = joinpath(demoroot,"cg/simulink")
cgModel = joinpath(demoroot,"cg/simulink/alphabetafilter")
mat"""
model = load_system($cgModel);
path = $cgPath;
set_param(0, 'CacheFolder', path)
set_param(0, 'CodeGenFolder', path)
slbuild(model)
set_param(0, 'CacheFolder', '')
set_param(0, 'CodeGenFolder', '')
"""
Model analysis
By its structure, the model cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink.engee it does not differ from the one discussed earlier cCodeIntegration_source.engee; only the directives on the tab differ Build options block settings Filter. Let's analyze its contents:
.png)
The following construction options are defined here:
Source files- the source code files are connectedalphabetafilter.candalphabetafilter_data.c;Include directories- the path to the folder containing the header files is set;Headers- header files are connectedalphabetafilter.h,alphabetafilter_types.handrtwtypes.h.
The cyclically executed code is shown on the tab Output code block source code editor Filter:
.png)
At each step of the model calculation, the following is performed:
-
Initialization of the structure
alphabetafilter_Uvariablesin,processNoiseVarianceandmeasurementNoiseVariance(input signals); -
Function call
alphabetafilter_step(); -
Assigning a variable
out(output signal) of the resultx, saved in the structurealphabetafilter_Y.
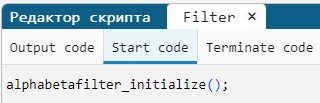
In the Start code tab of the block source editor Filter the function is being called alphabetafilter_initialize():
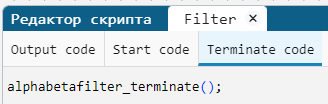
In the Terminate code tab of the block source code editor Filter the function is being called alphabetafilter_terminate():
Running the simulation
Let's model the system:
cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink = engee.load("$demoroot/models/cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink.engee", force = true)
simulationResults_cg_simulink = engee.run(cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink)
Closing the model:
engee.close(cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink, force = true);
Simulation results
Importing the simulation results:
cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink_noisy_t = simulationResults_cg_simulink["noisy"].time;
cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink_noisy_y = simulationResults_cg_simulink["noisy"].value;
cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink_filtered_t = simulationResults_cg_simulink["filtered"].time;
cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink_filtered_y = simulationResults_cg_simulink["filtered"].value;
Let's build a graph:
plot(cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink_noisy_t, cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink_noisy_y, label = "The original signal")
plot!(cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink_filtered_t, cCodeIntegration_cg_simulink_filtered_y, label = "Filtered signal")
plot!(legend = :bottomright)
title!("Alpha-beta filter <br> (Integration of the code generated from the Simulink model)")
xlabel!("Time, [s]")
ylabel!("The amplitude")
Integration of the code generated from the Engee model
Setting the task
Generate the C code from the Engee model alphabetafilter.engee, assembled from simple blocks and implementing an alpha-beta filter, and integrating it into our Engee model cCodeIntegration_cg_engee.engee.
The upper level of the model:
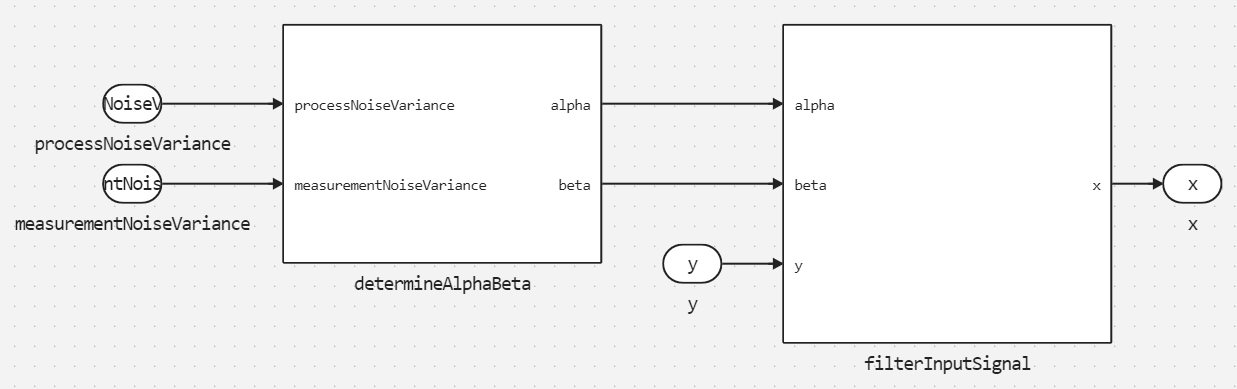
Subsystem determineAlphaBeta:
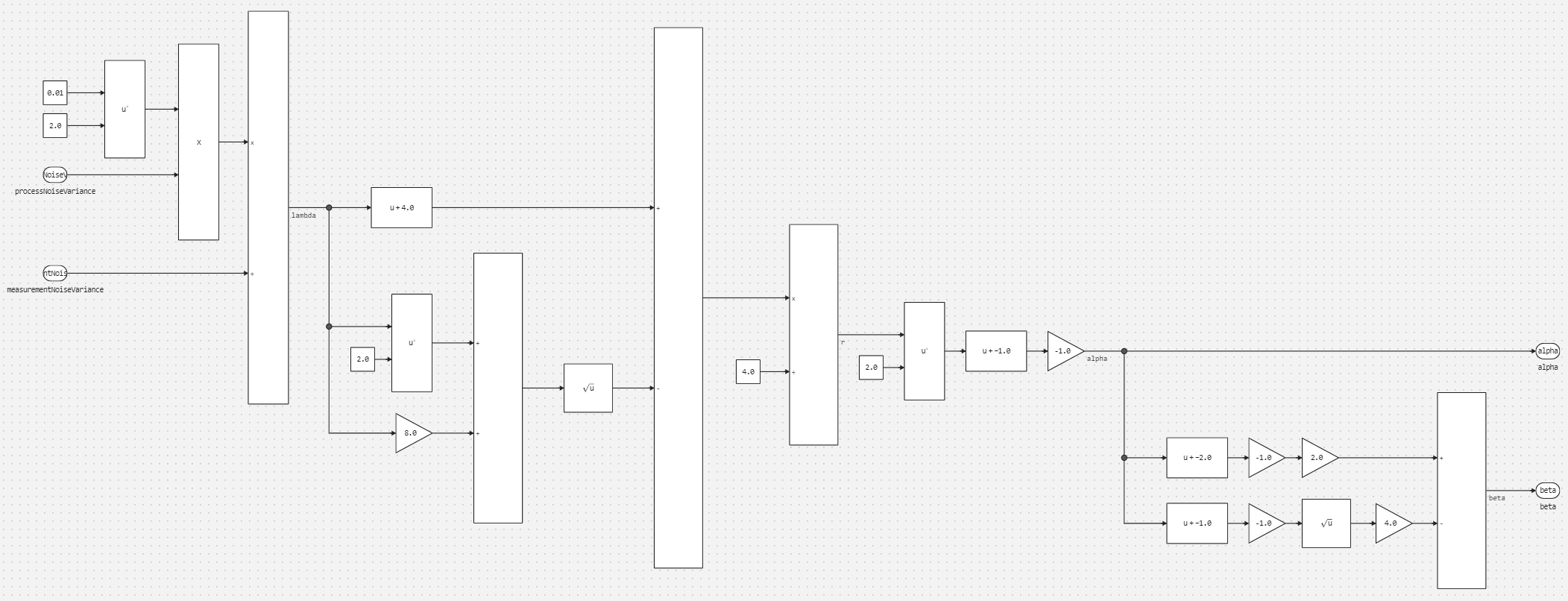
Subsystem filterInputSignal:
Generate the code using the Engee code generator:
engee.generate_code("$demoroot/cg/engee/alphabetafilter.engee", "$demoroot/cg/engee/alphabetafilter_cg")
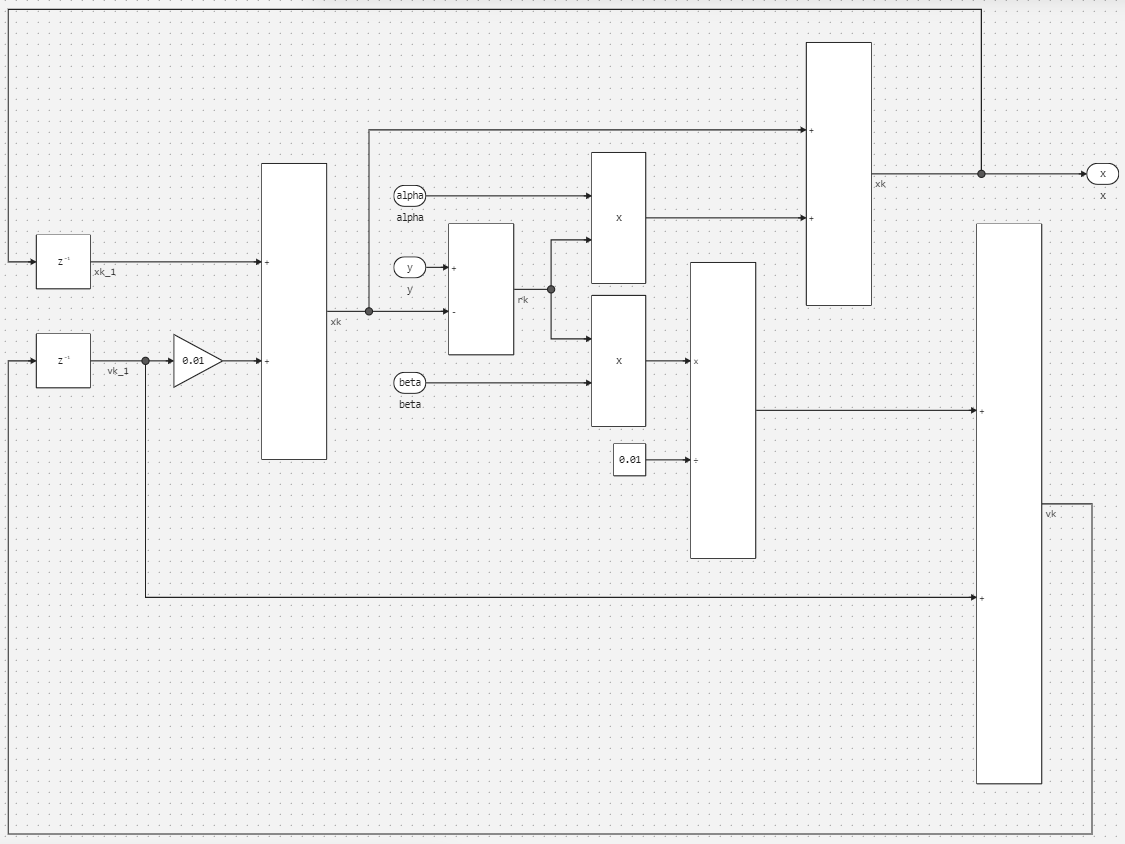
Model analysis
By its structure, the model cCodeIntegration_cg_engee.engee it does not differ from the one discussed earlier cCodeIntegration_source.engee; only the directives on the tab differ Build options block settings Filter. Let's analyze its contents:
.png)
The following construction options are defined here:
Source files- the source code file is connectedalphabetafilter.c;Include directories- the path to the folder containing the header files has been set;Headers- the header file is connectedalphabetafilter.h.
The cyclically executed code is shown on the tab Output code block source code editor Filter:
.png)
At each step of the model calculation, the following is performed:
-
Initialization of the structure
alphabetafilter_Uvariablesin,processNoiseVarianceandmeasurementNoiseVariance(input signals); -
Function call
alphabetafilter_step(); -
Assigning a variable
out(output signal) of the resultx, saved in the structurealphabetafilter_Y.
In the Start code tab of the block source editor Filter the function is being called alphabetafilter_init():
In the Terminate code tab of the block source code editor Filter the function is being called alphabetafilter_term():
Running the simulation
Let's model the system:
cCodeIntegration_cg_engee = engee.load("$demoroot/models/cCodeIntegration_cg_engee.engee", force = true)
simulationResults_cg_engee = engee.run(cCodeIntegration_cg_engee)
Closing the model:
engee.close(cCodeIntegration_cg_engee, force = true);
Simulation results
Importing the simulation results:
cCodeIntegration_cg_engee_noisy_t = simulationResults_cg_engee["noisy"].time;
cCodeIntegration_cg_engee_noisy_y = simulationResults_cg_engee["noisy"].value;
cCodeIntegration_cg_engee_filtered_t = simulationResults_cg_engee["filtered"].time;
cCodeIntegration_cg_engee_filtered_y = simulationResults_cg_engee["filtered"].value;
Let's build a graph:
plot(cCodeIntegration_cg_engee_noisy_t, cCodeIntegration_cg_engee_noisy_y, label = "The original signal")
plot!(cCodeIntegration_cg_engee_filtered_t, cCodeIntegration_cg_engee_filtered_y, label = "Filtered signal")
plot!(legend = :bottomright)
title!("Alpha-beta filter <br> (Integration of the code generated from the Engee model)")
xlabel!("Time, [s]")
ylabel!("The amplitude")
Conclusions
This example demonstrates the features of using the C Function block and various ways to integrate C code into Engee models.:
- Integration of external source code;
- Integration of static and dynamic libraries;
- Integration of the code generated from the Simulink model;
- Integration of the code generated from the Engee model.