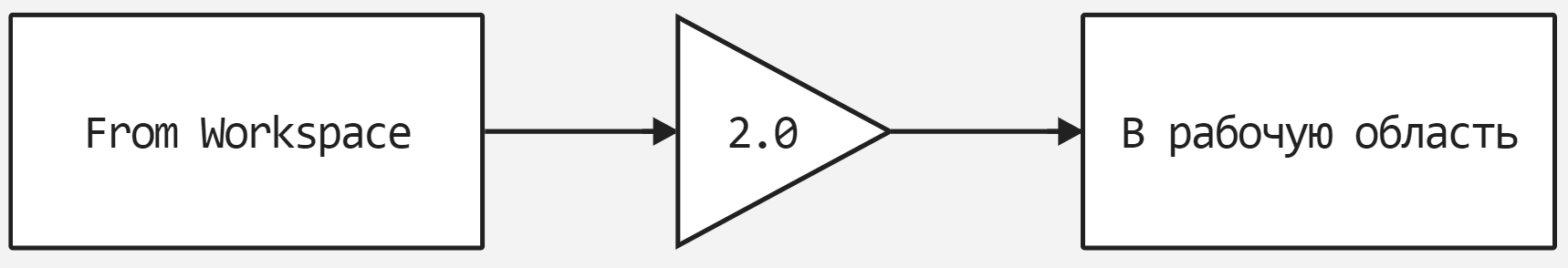
From Workspace and To Workspace
In this demo, we will describe the features of using the From Workspace and To Workspace blocks. Our goal is to show how we can feed data into the model or read it from it. To do this, a simple model is implemented, shown in the figure below.
Next, we will connect the library necessary to form the WorkspaceArray data structure.
First, let's create a DataFrame structure with columns of timestamps and data.
After that, we create a WorkspaceArray object, the first parameter of which is the internal database name, and the second is data from the DataFrame structure.
using DataFrames
# Setting the data:
t = [1.0, 2.0, 4.0];
d = rand(Float64, size(t));
df = DataFrame(time=t, value=d)
wa = WorkspaceArray(string(rand()), df)
Let's move on to launching our model.
function run_model( name_model, path_to_folder )
Path = path_to_folder * "/" * name_model * ".engee"
if name_model in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] # Checking the condition for loading a model into the kernel
model = engee.open( name_model ) # Open the model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
else
model = engee.load( Path, force=true ) # Upload a model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
engee.close( name_model, force=true ); # Close the model
end
return model_output
end
run_model("from_to_workspace", @__DIR__)
At the output, we will also get the WorkspaceArray structure. Let's view its fields and compare them with the input data.
dump(out)
data = collect(out)
using Plots
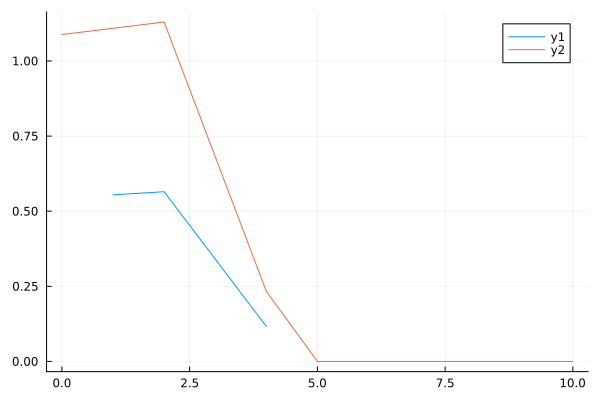
plot(df.time,df.value) # Input data
plot!(data.time,data.value) # Output data
As we can see from the comparison, as a result, the data that we submitted to the model was doubled.
Conclusion
We have demonstrated the options for transferring data from the workspace to the model and back. These features of the environment greatly simplify your interaction with the models.