Imitation of the parachute opening algorithm
In this demonstration, we will build a parachute model for the Curiosity rover. This is a third-generation rover
designed to explore Gale Crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission.
The rover is an autonomous chemical
laboratory several times larger and heavier than the previous
Spirit and Opportunity rovers. The parachute under it, as well as under many other devices, was used with
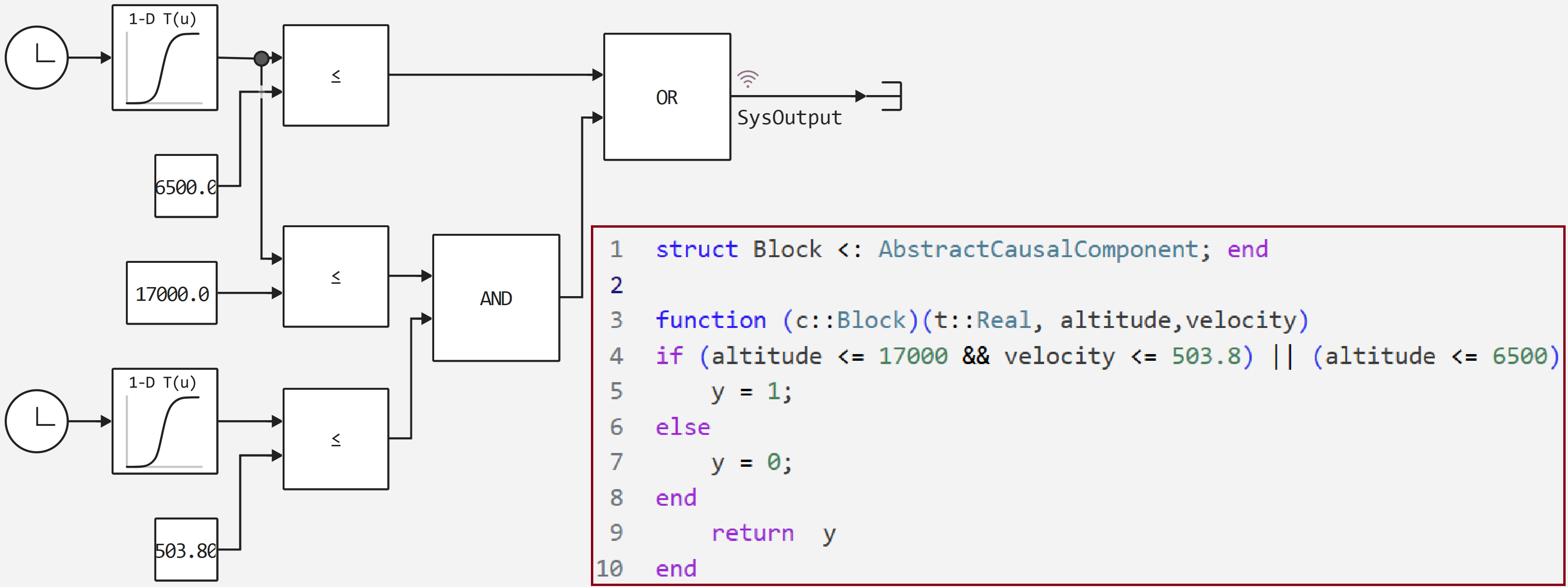
the following algorithms, which open automatically based on height,
as well as determine its speed.
The parachute is deployed in the altitude range from 6500 to
17,000 m .
In this example, two variants of the implementation
of this algorithm are analyzed. In the first case, we use blocks from
the basic block library, and in the second case, we use the engee function.
The implementation of these two algorithms is presented below.
Auxiliary function Declarations
# Enabling the auxiliary model launch function.
function run_model( name_model)
Path = (@__DIR__) * "/" * name_model * ".engee"
if name_model in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] # Checking the condition for loading a model into the kernel
model = engee.open( name_model ) # Open the model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
else
model = engee.load( Path, force=true ) # Upload a model
model_output = engee.run( model, verbose=true ); # Launch the model
engee.close( name_model, force=true ); # Close the model
end
sleep(5)
return model_output
end
Comparison of the results of the models
run_model("mars_para_block")
run_model("mars_para_julia")
out_block = collect(out_block)
out_julia = collect(out_julia)
out_time = out_block.time
out_block = out_block.value
out_julia = out_julia.value
A = plot(out_time, out_block)
plot!(out_time, out_julia)
xlabel!("Time")
ylabel!("State")
B = plot(out_block-out_julia, label="error")
plot(A,B)
Conclusion
As we can see in the graphs, the systems work the same way, and the moment
of parachute opening coincided for both implementations of the algorithm,
which indicates the identity of the implemented logic.