What’s new in 25.7
_ Release Date: July 2025_
 Overall user experience
Overall user experience
 A separate module for graphs of the computing environment
A separate module for graphs of the computing environment
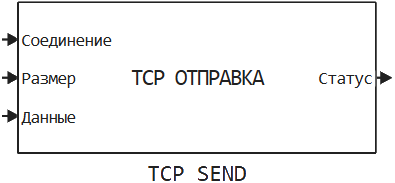
For the convenience of working in the main tools of Engee, an environment for technical computing and an editor for building models, we have created a separate module for charts ![]() and visualizations from command line
and visualizations from command line  . Now the graphs of different tools will not "mix" and it will be easier and clearer to work with them.
. Now the graphs of different tools will not "mix" and it will be easier and clearer to work with them.
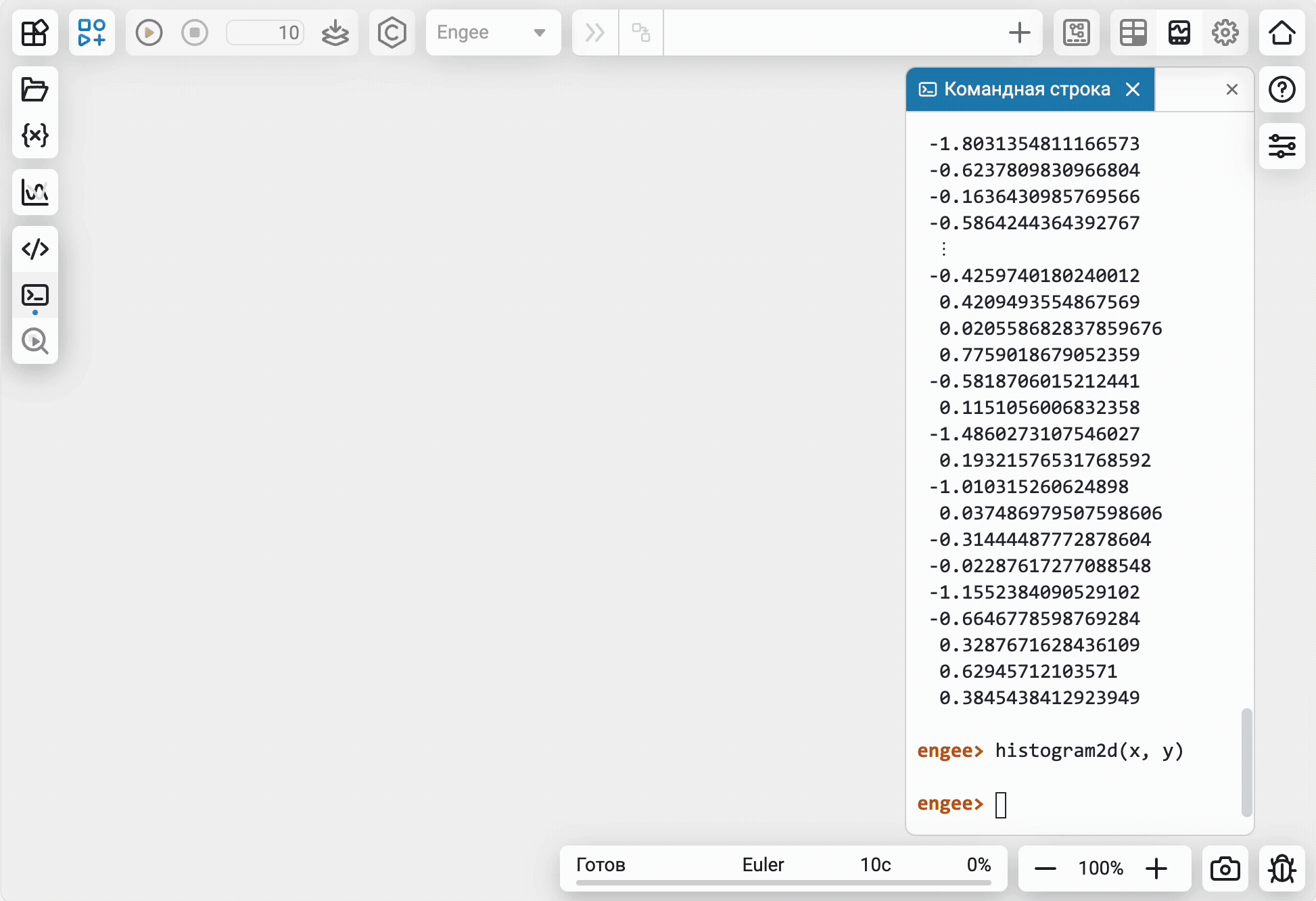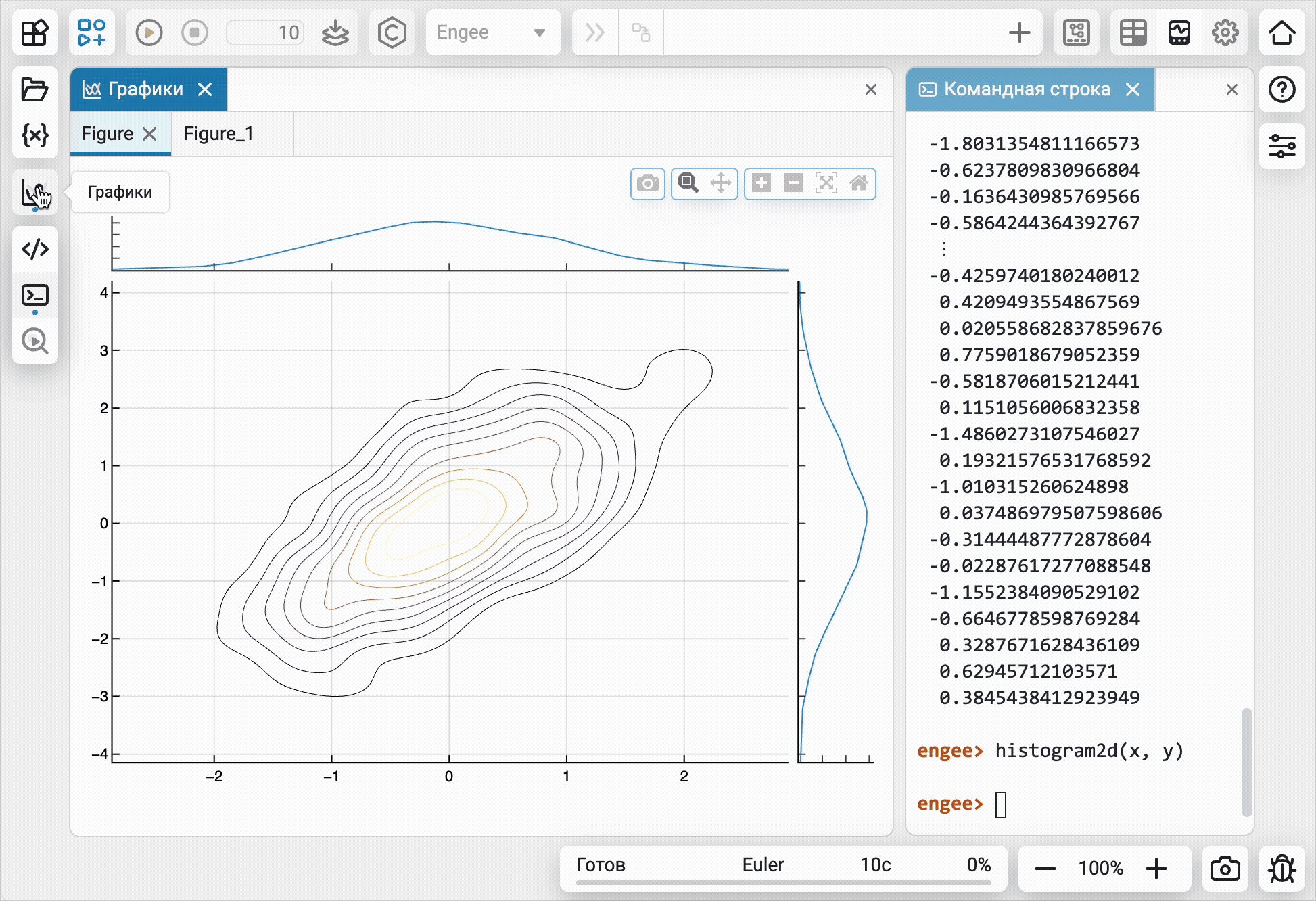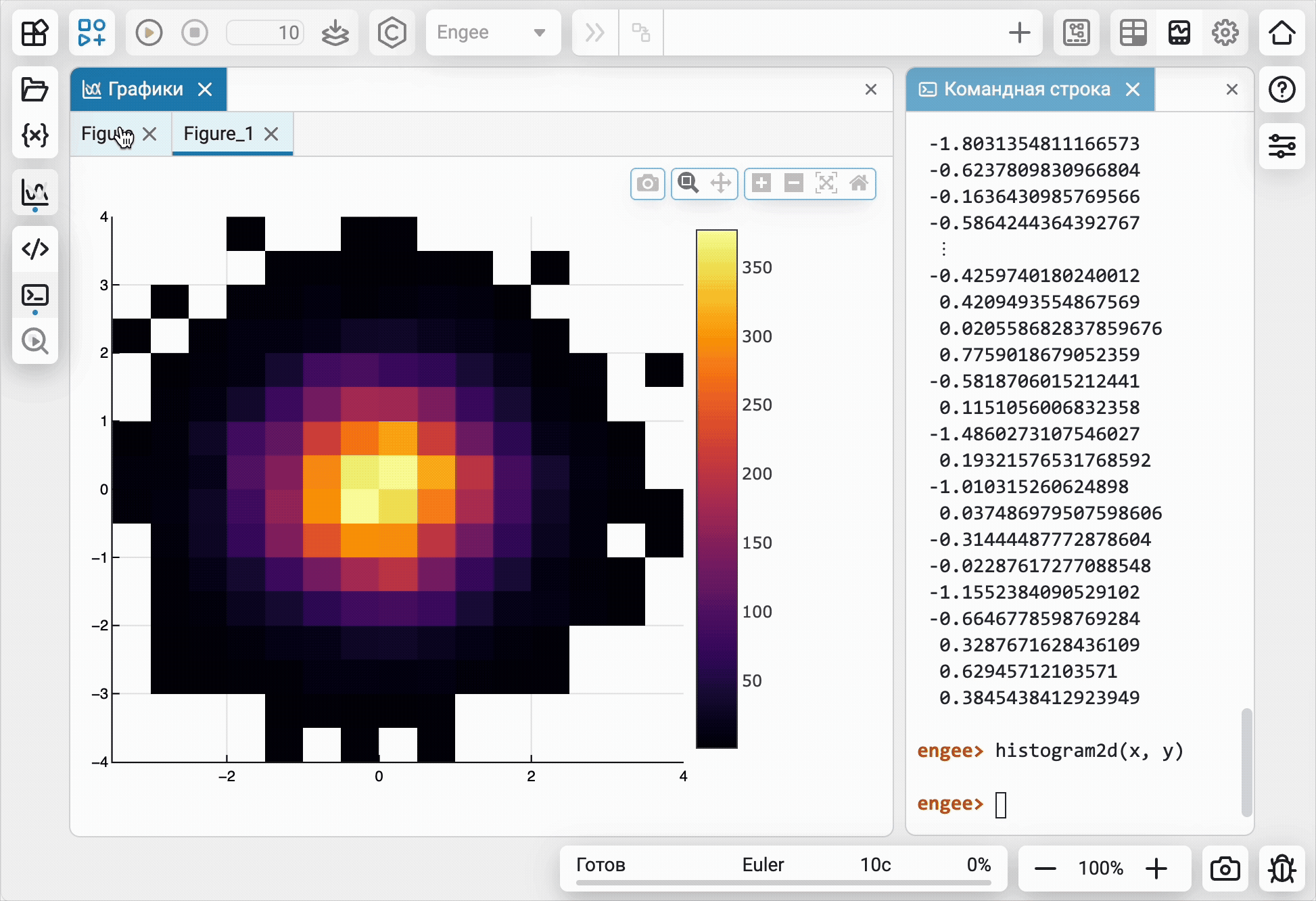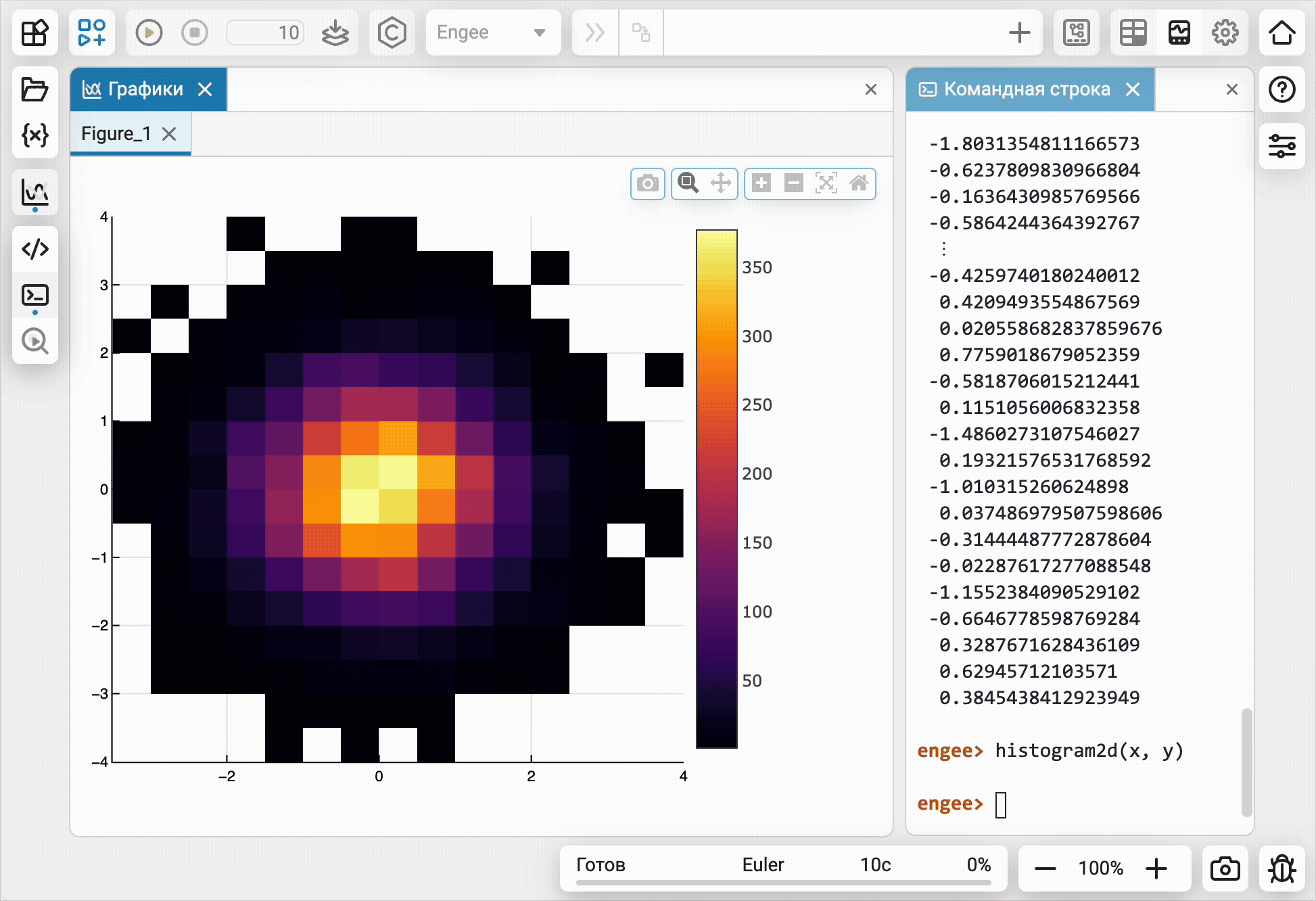
 Mathematical Computing environment
Mathematical Computing environment
 Support for an advanced text cell editor in the Community and script export
Support for an advanced text cell editor in the Community and script export
In May release we have completely replaced the text cell editor in interactive scripts ![]() . It has become much more functional and friendly. Now we have implemented support for all new types of elements for a cell when exporting an interactive script to PDF and html. The same applies to the formation of posts in Community. These beautiful elements will decorate not only Engee scripts, but also your automated reports and posts for colleagues and the Community!
. It has become much more functional and friendly. Now we have implemented support for all new types of elements for a cell when exporting an interactive script to PDF and html. The same applies to the formation of posts in Community. These beautiful elements will decorate not only Engee scripts, but also your automated reports and posts for colleagues and the Community!
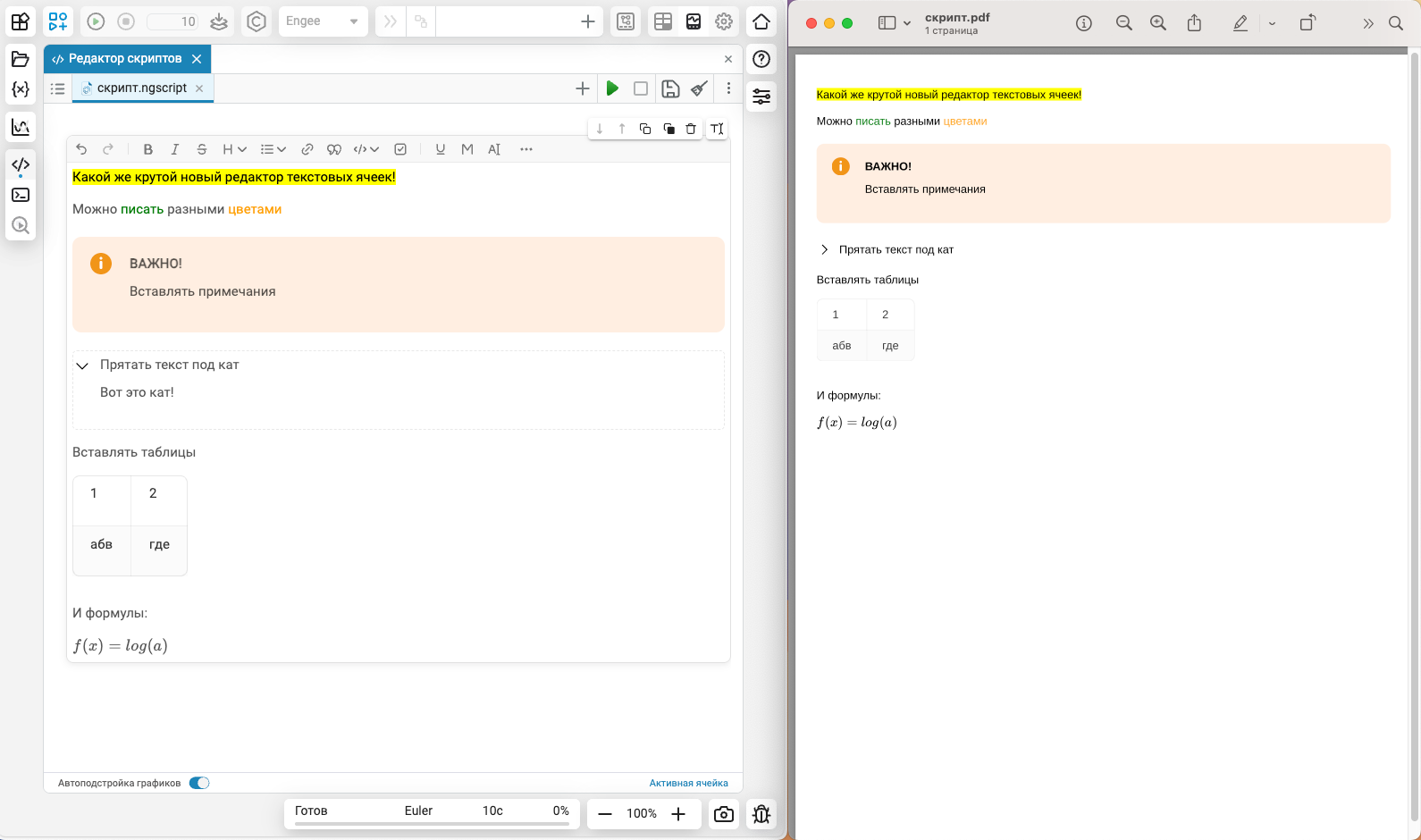
 Constants in variables
Constants in variables
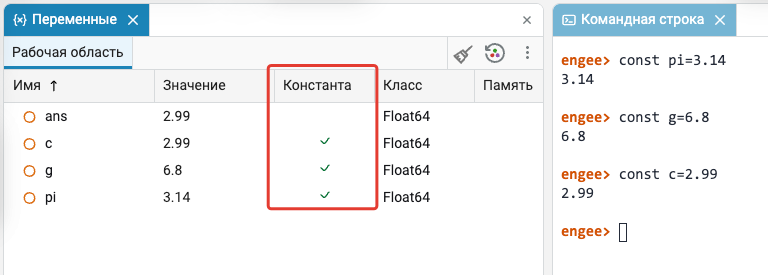
If you set a variable using the const function, then such a variable will become a global constant and its value will not change or be cleared in the module. Variables  using a "broom"
using a "broom"  . It can only be cleared by restarting the Julia kernel. We have added a special field to the corresponding menu, in which constants will be marked, in order to understand which method it is necessary to clear certain values.
. It can only be cleared by restarting the Julia kernel. We have added a special field to the corresponding menu, in which constants will be marked, in order to understand which method it is necessary to clear certain values.
 New objects for configuring Control Systems: Pid, PidStd and the Pidtune function
New objects for configuring Control Systems: Pid, PidStd and the Pidtune function
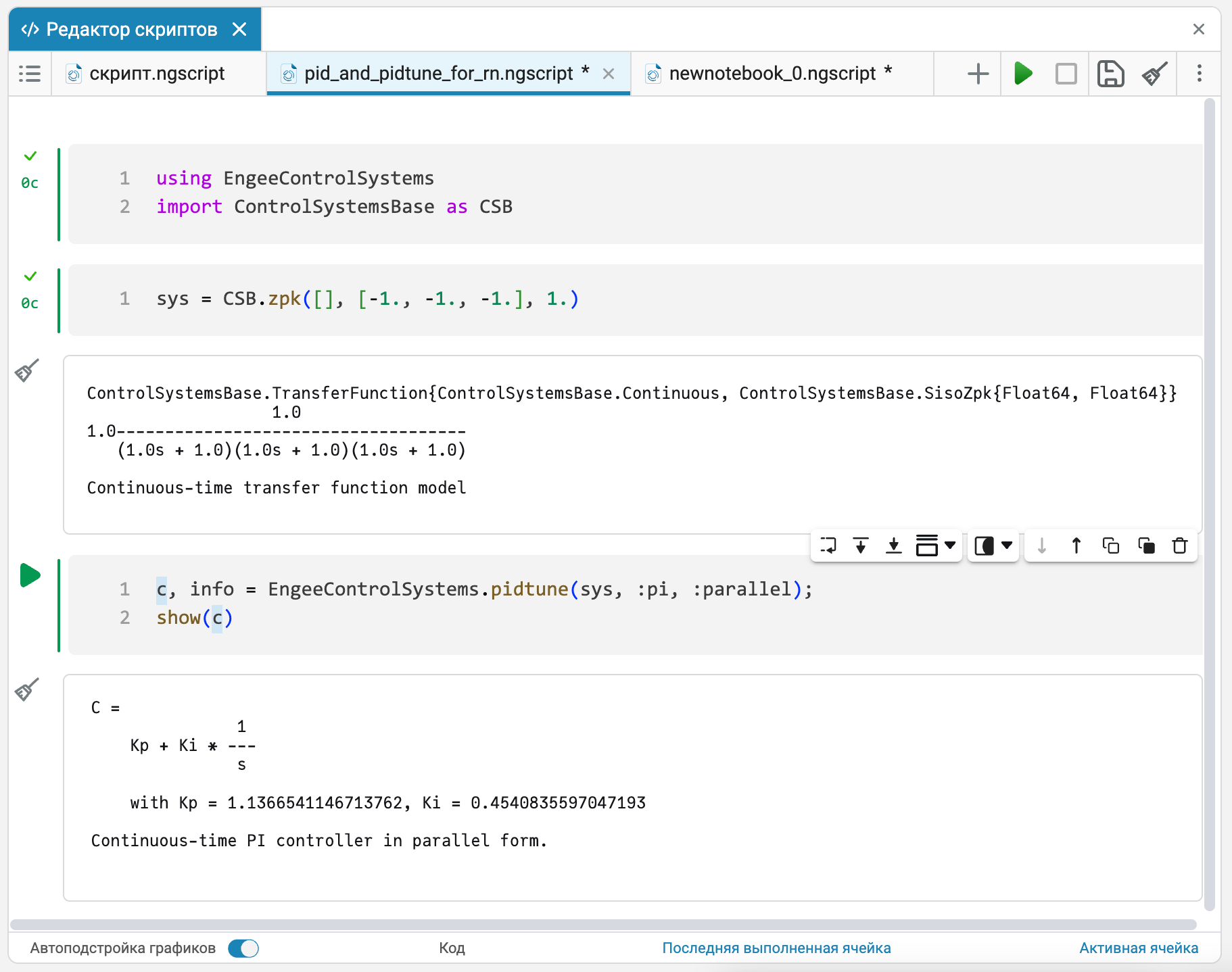
We have added new object models — PID controllers in parallel Pid form and in standard PidStd form, as well as a new pidtune function. PID controllers can be either continuous or discrete. Now it has become even easier to study the dynamic characteristics of control systems.
The pidtune function allows you to configure PID controllers in parallel and standard forms of linear system models. For better tuning, you can specify the desired cutoff frequency, as well as a strategy for selecting controller parameters based on performance requirements.
 The modeling environment
The modeling environment
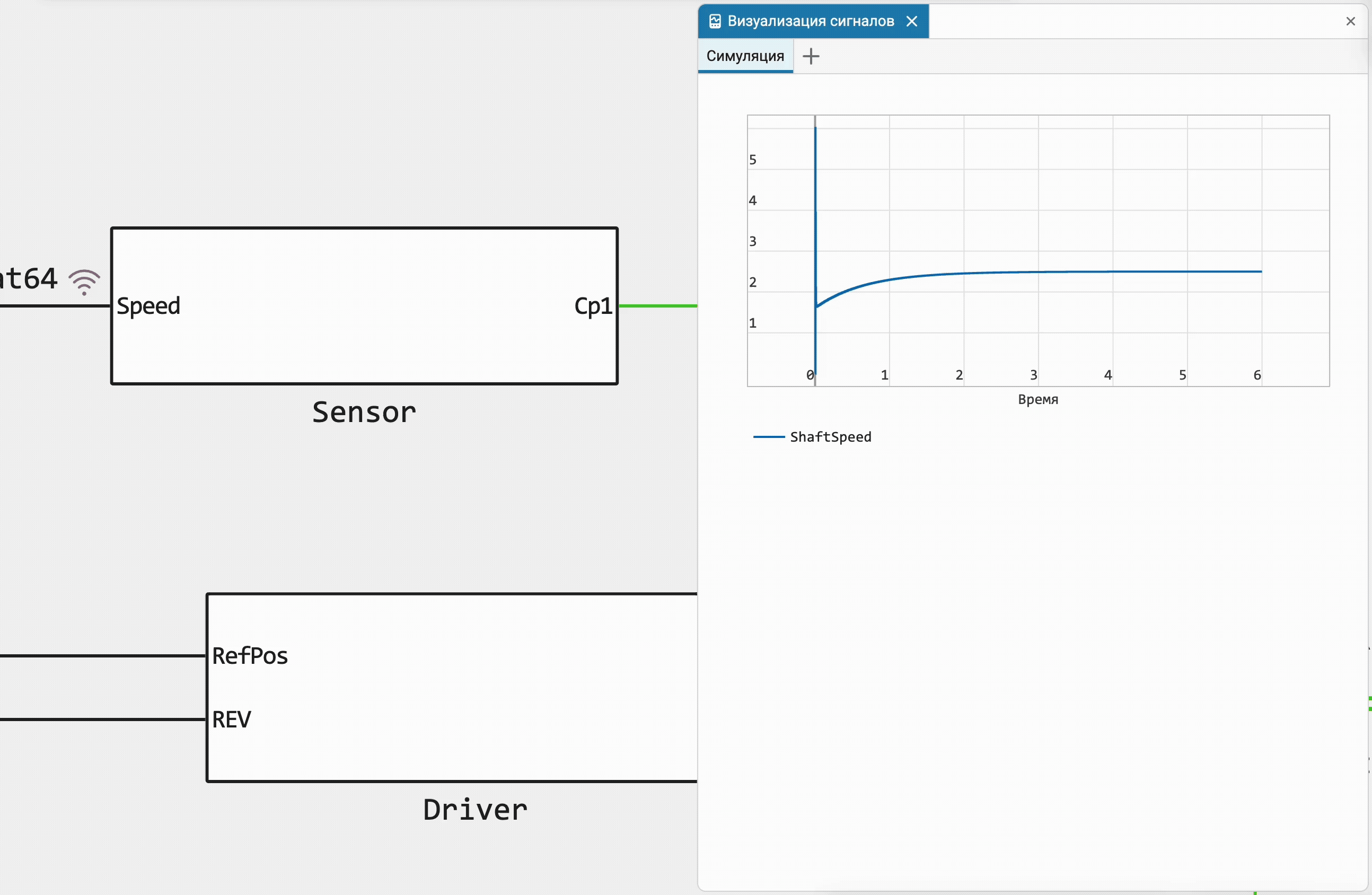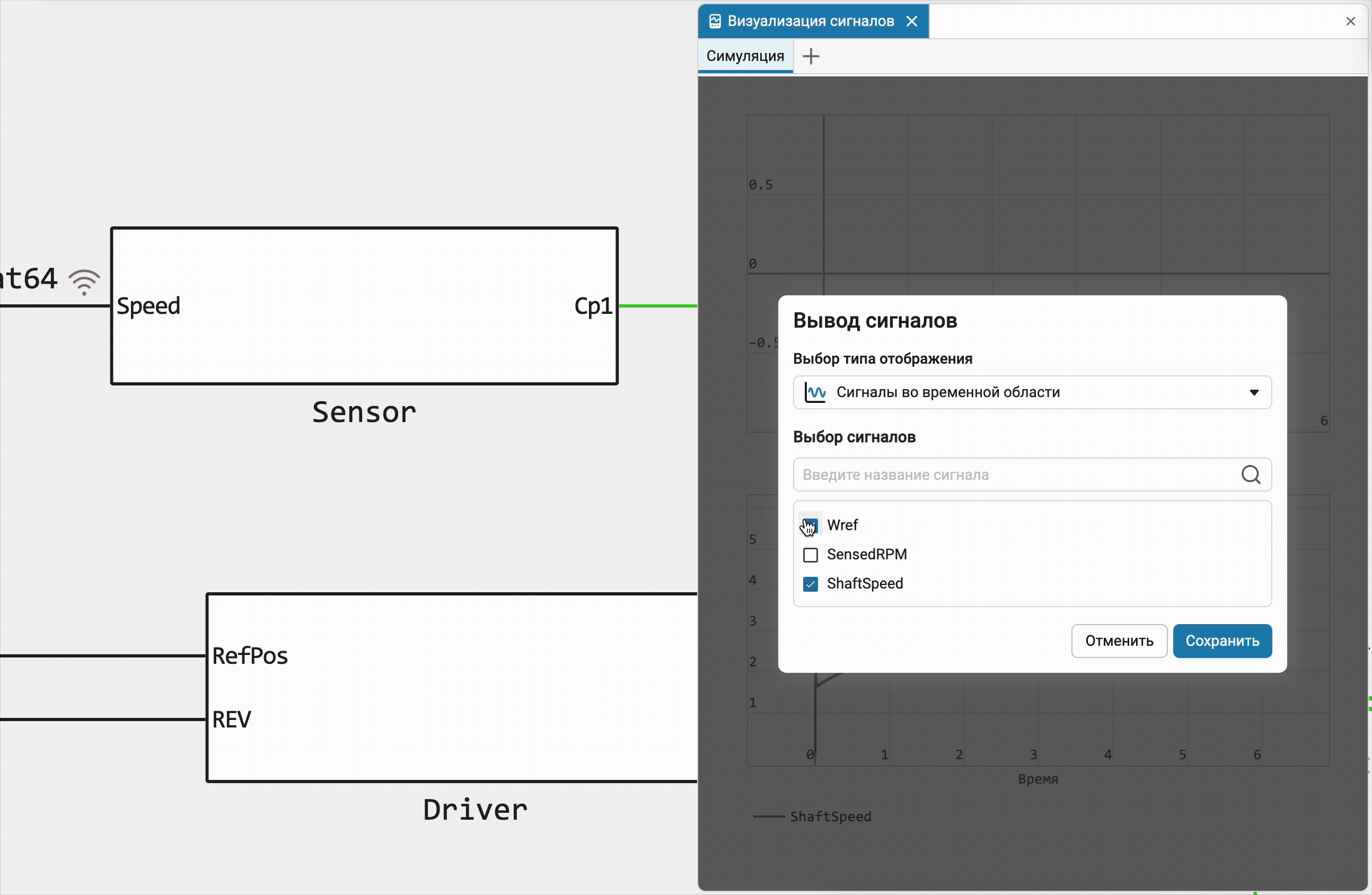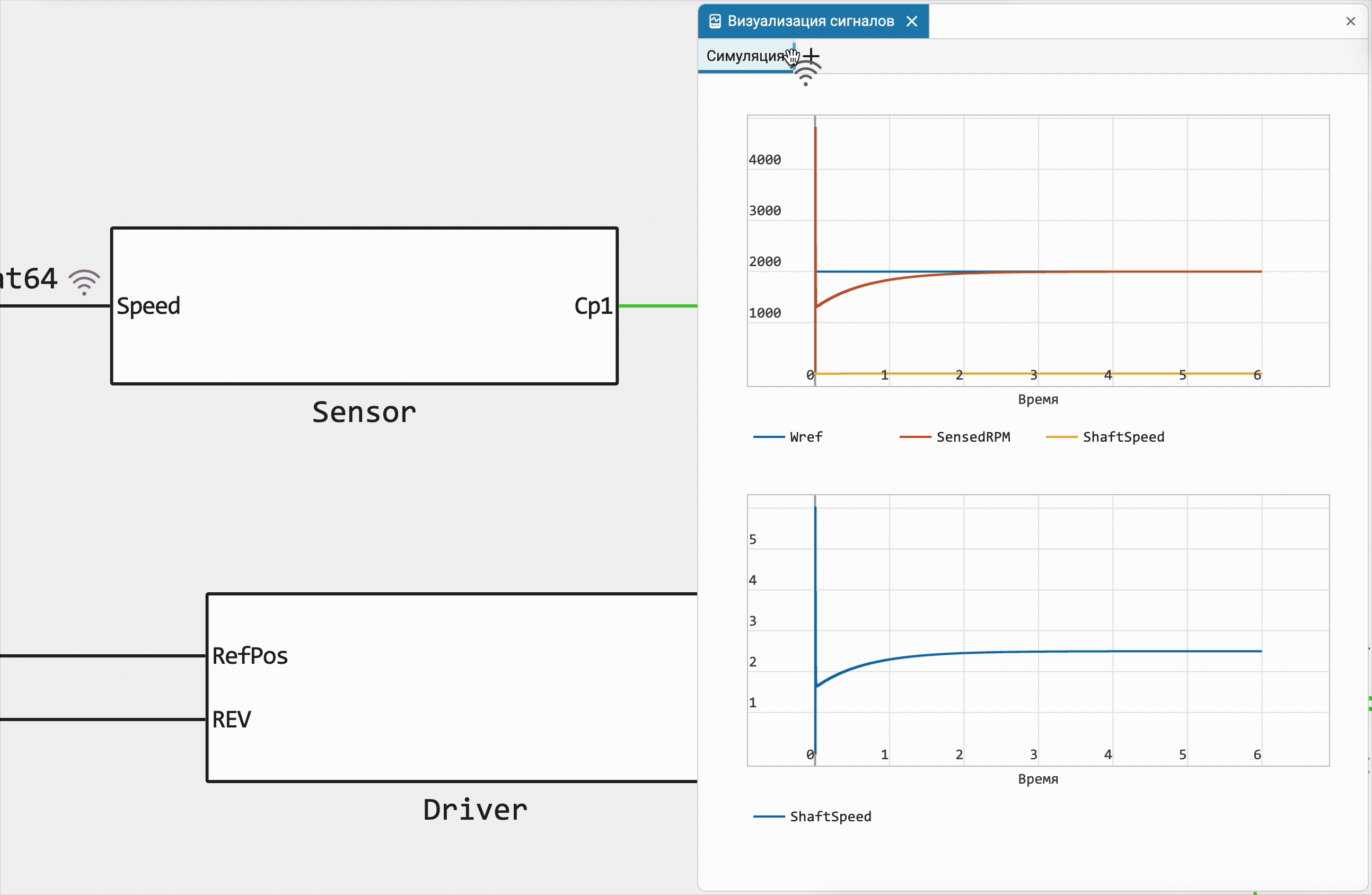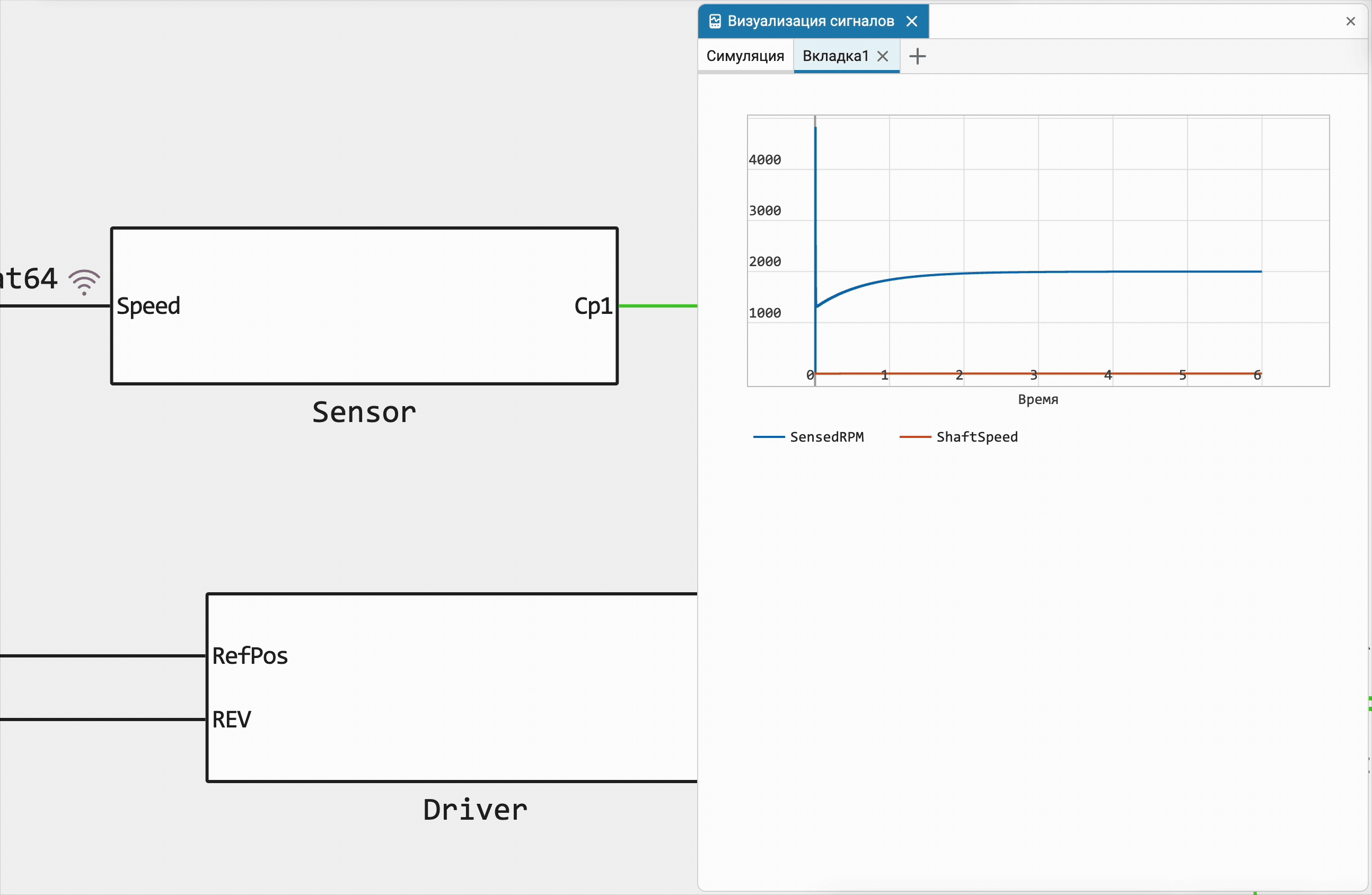
 Quickly add a new chart for signals
Quickly add a new chart for signals
Previously, we implemented the ability to add a signal to the graph by simply dragging the recording icon from the model canvas, and now you can use this familiar action to create a new graph anywhere you like, or immediately create a new bookmark in the Signals field!
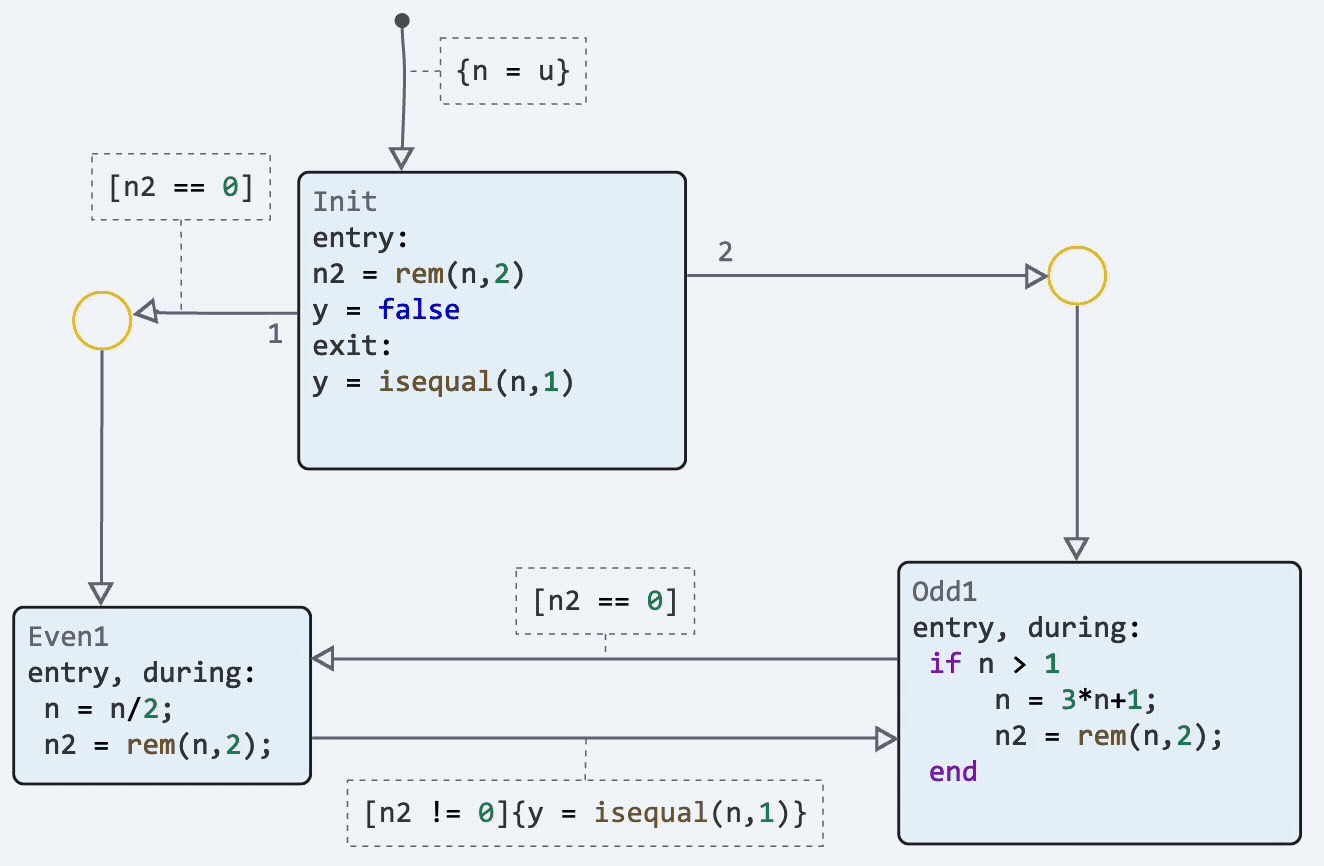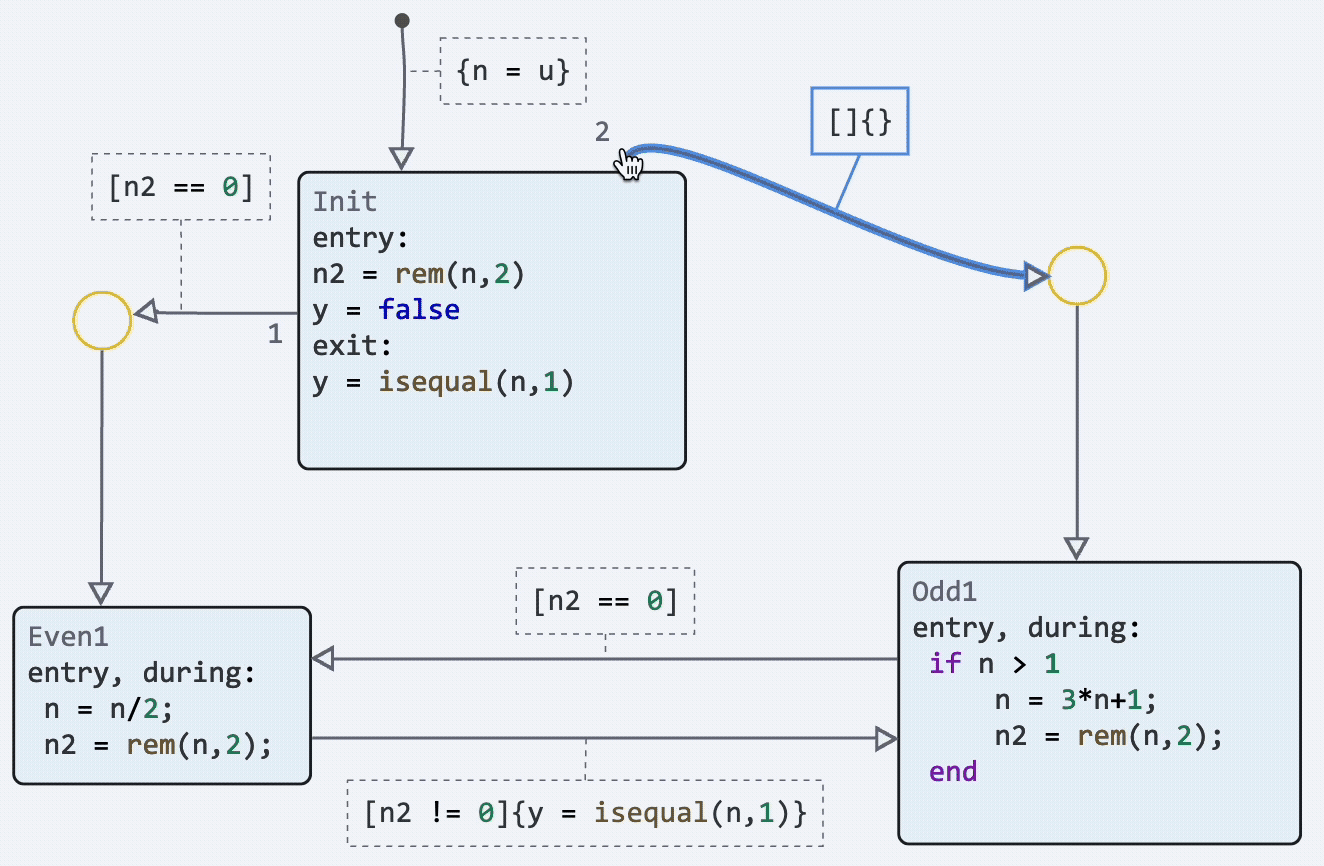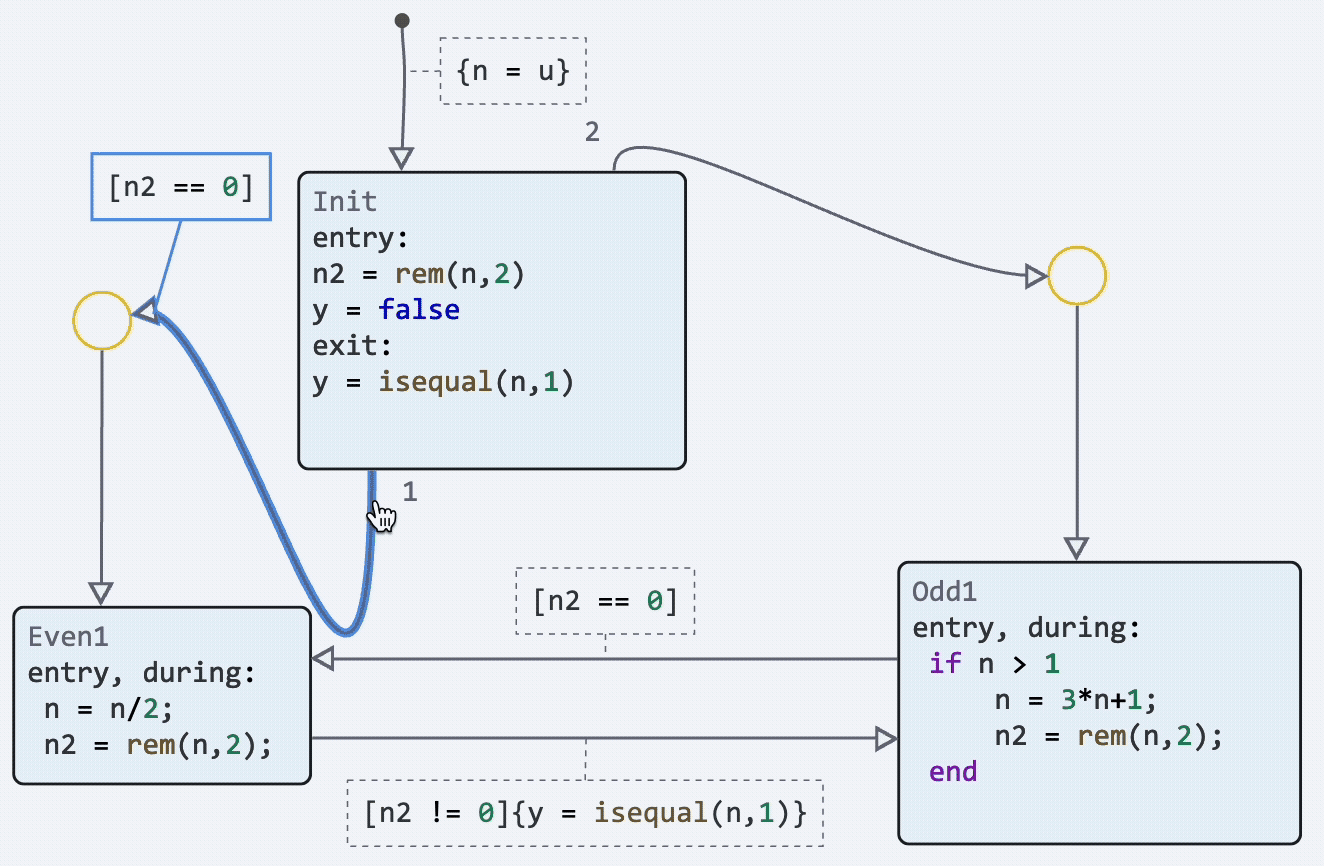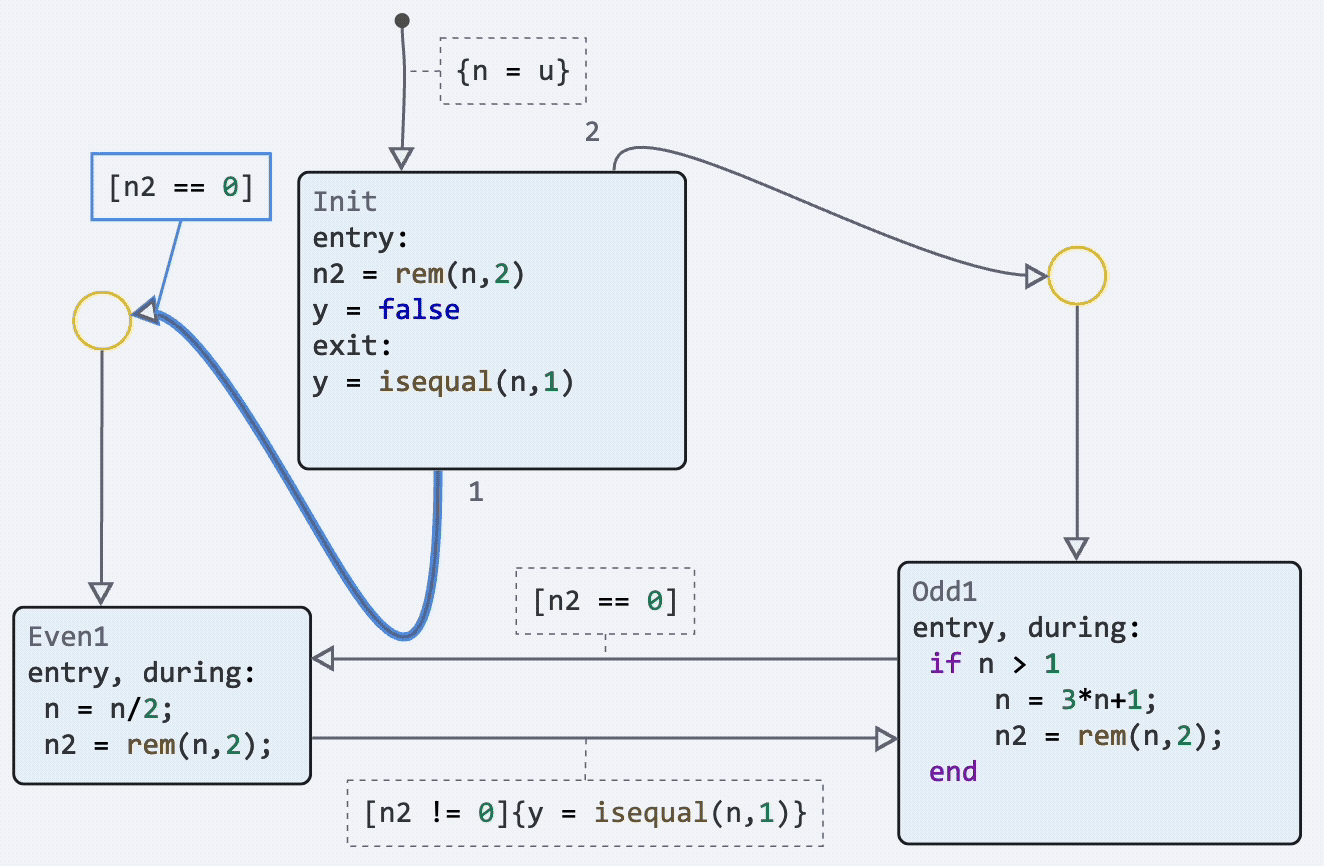
 Finite automata: dragging the initial transition point
Finite automata: dragging the initial transition point
We have implemented the possibility to change the location of not only the end point of the transition, but also the starting point. Now you can customize your state diagrams even more beautifully and make them more readable.
 Finite automata: viewing and editing variable values during debugging
Finite automata: viewing and editing variable values during debugging
To improve the efficiency of working with state diagrams, we have expanded the capabilities debugging for finite automata. Now you will be able to display the values of variables at each step of the debugger in the signal table, and the signals that have changed from the previous step will be highlighted. In addition, it is now possible to edit the values of output signals and local variables during a pause at the breakpoint.
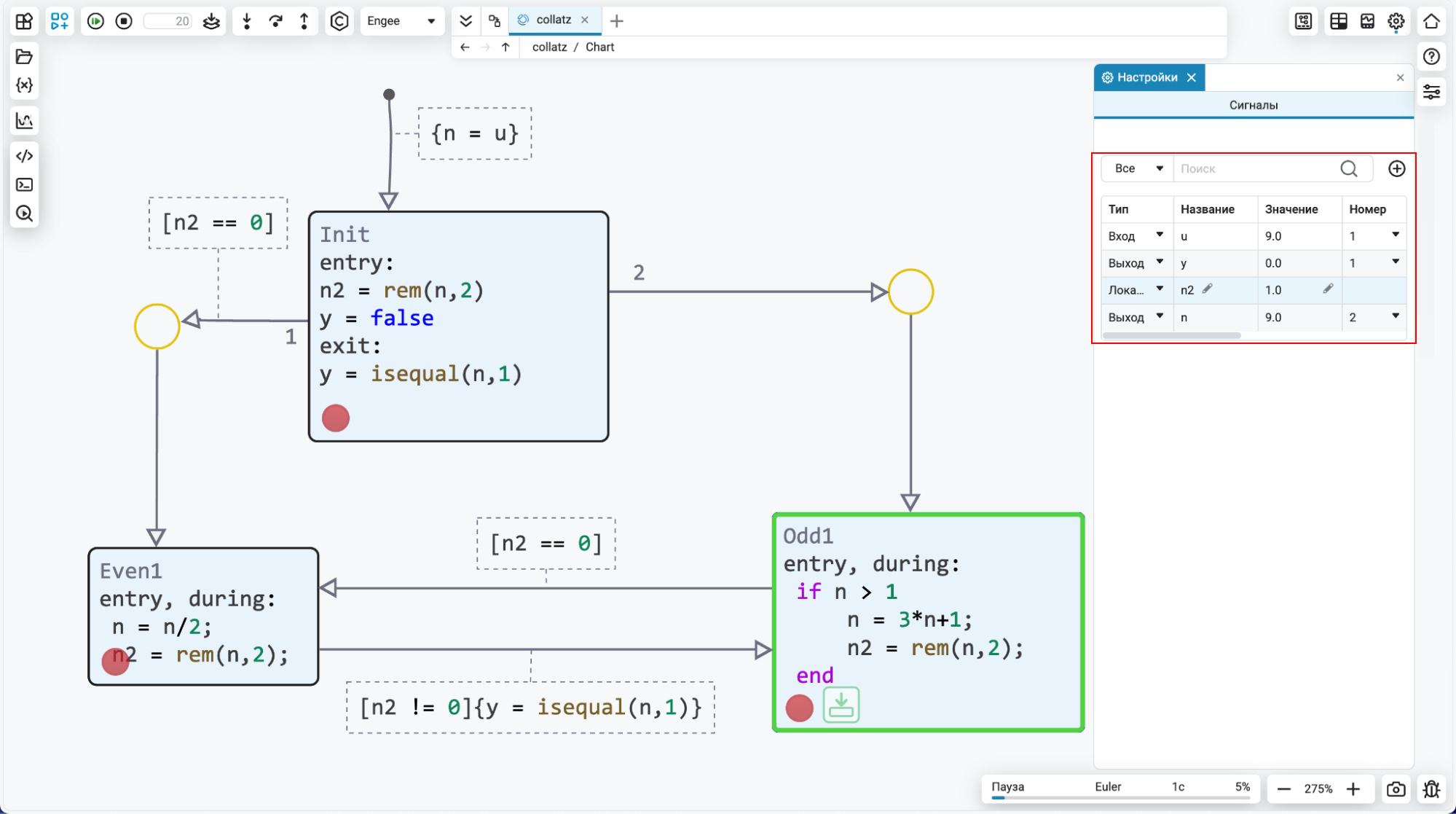
 Explicit tire support in reference models
Explicit tire support in reference models
Added explicit bus support at the entrances and exits link models. The type of signal is set in the settings of the output block of the link model (where it is also required to determine the types of bus signals) and all bus functions will be available to you — selecting the desired signal, etc.
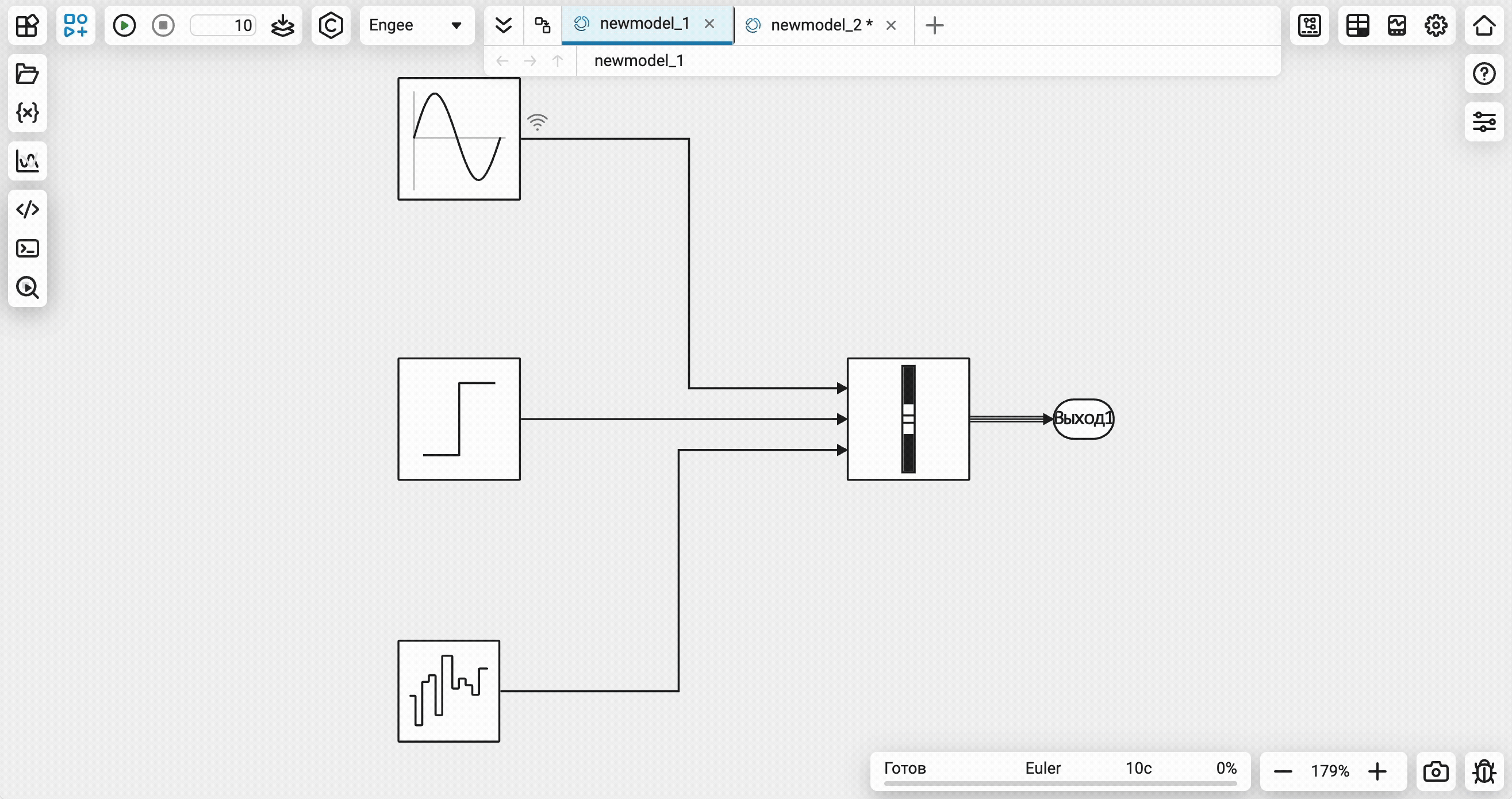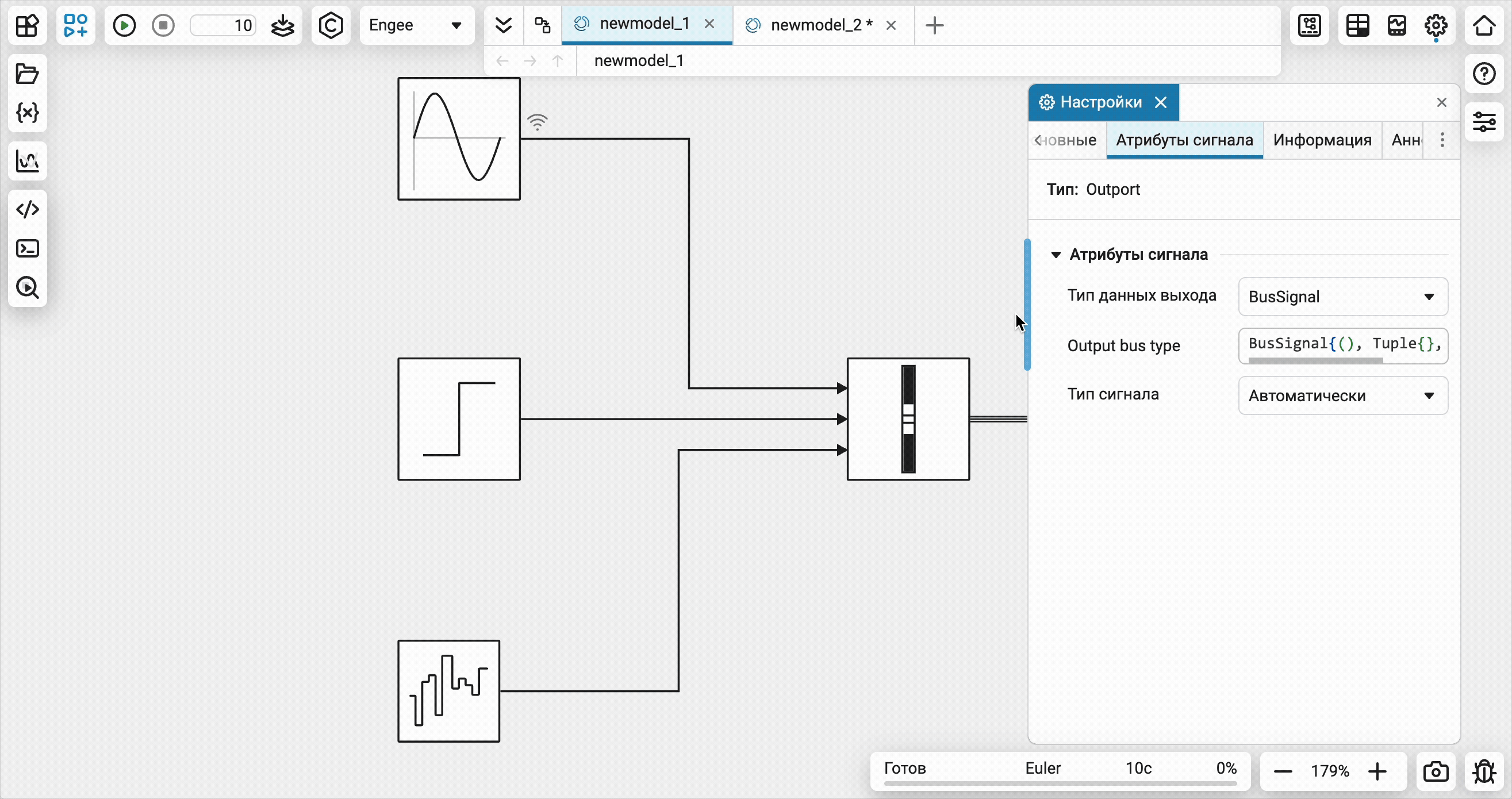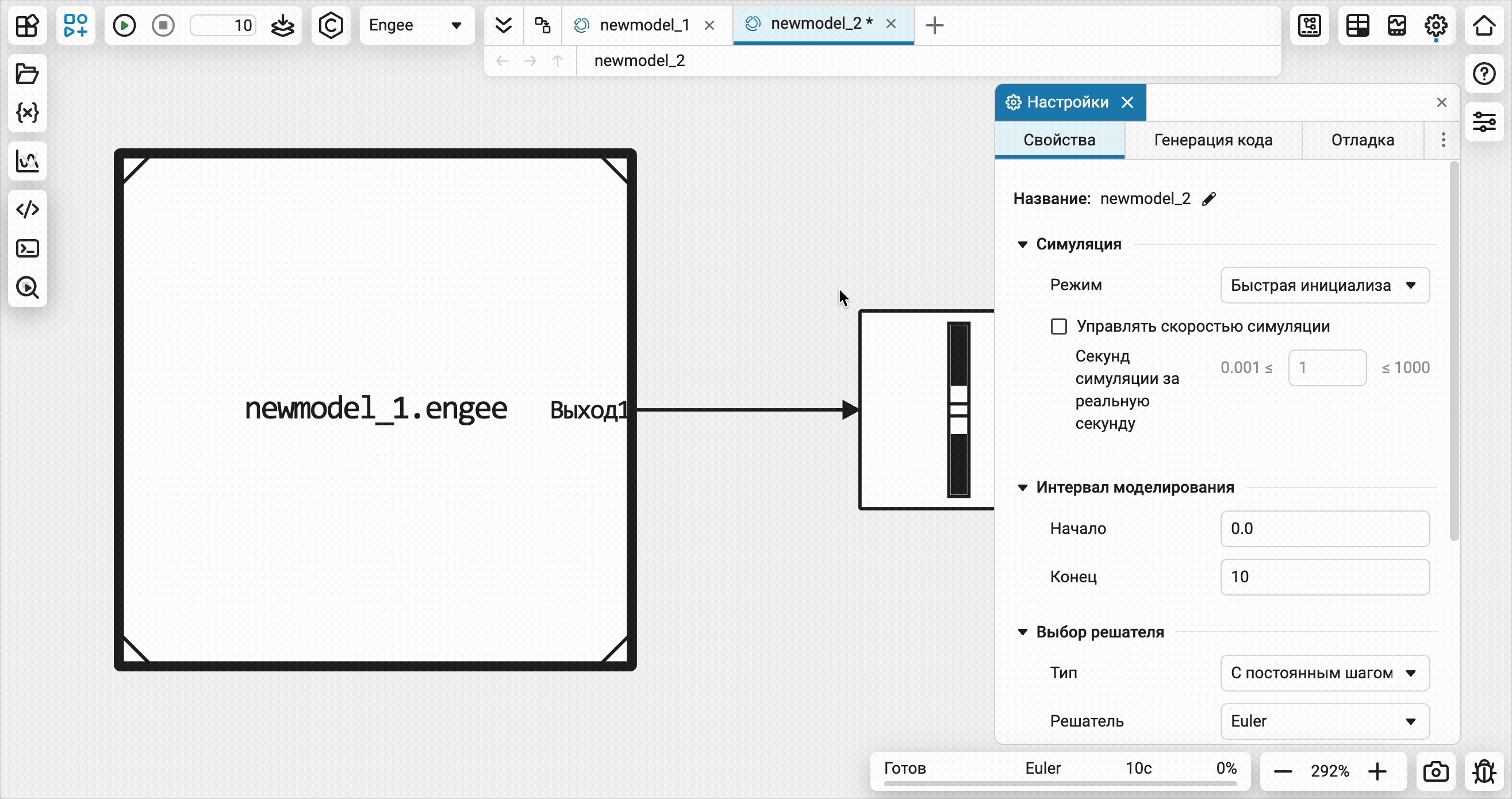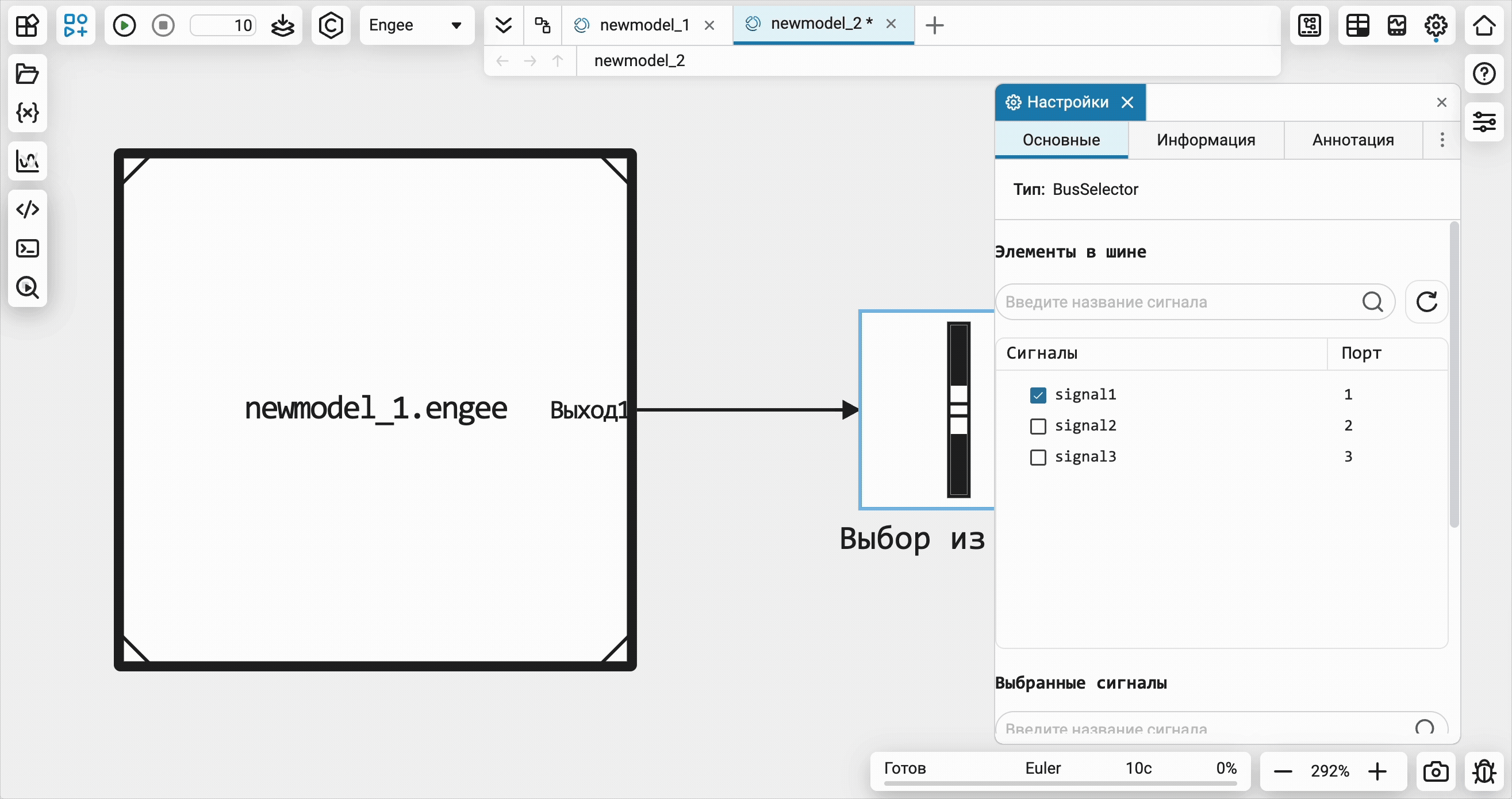
 Visualization of software control commands on an open model
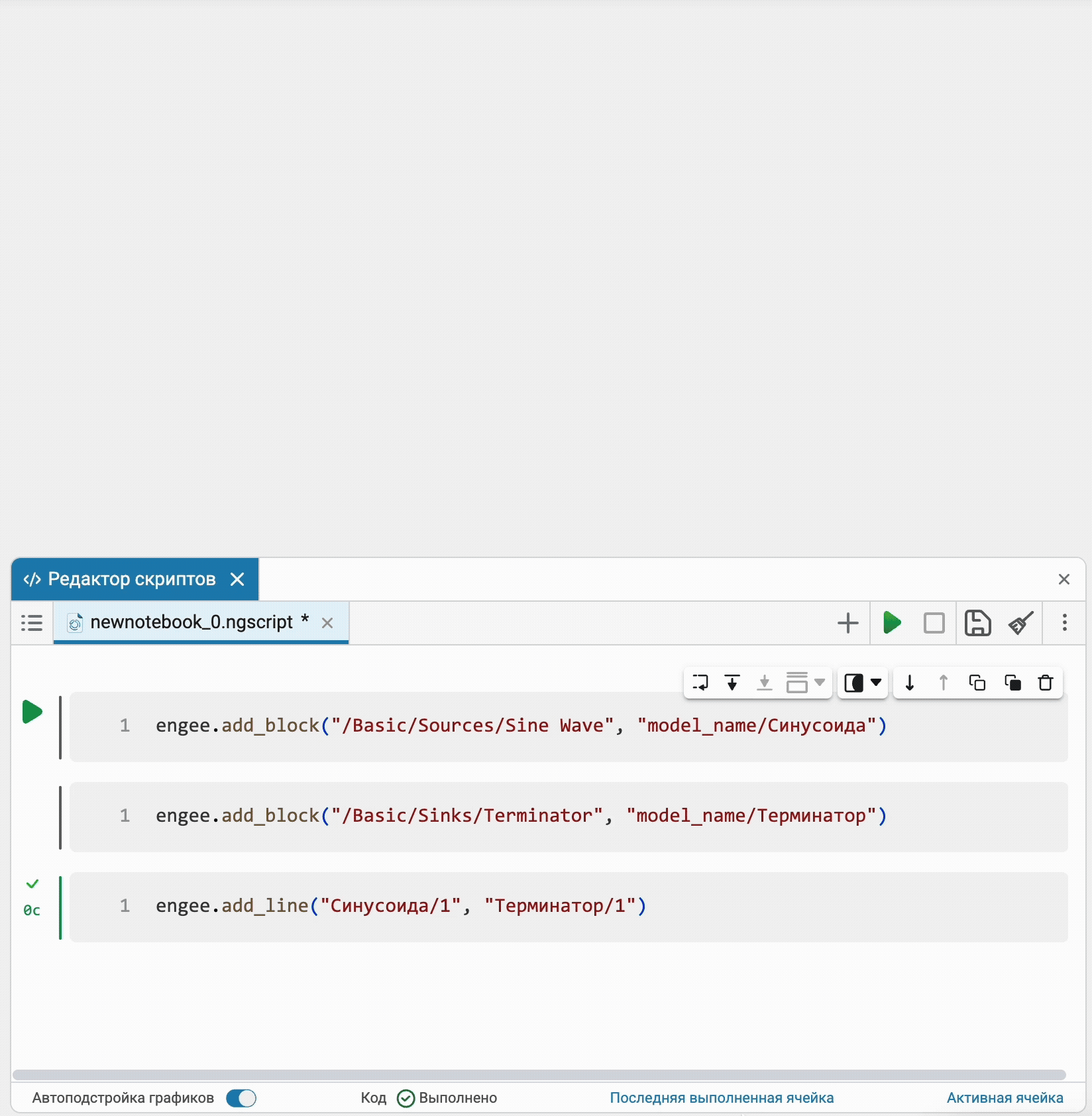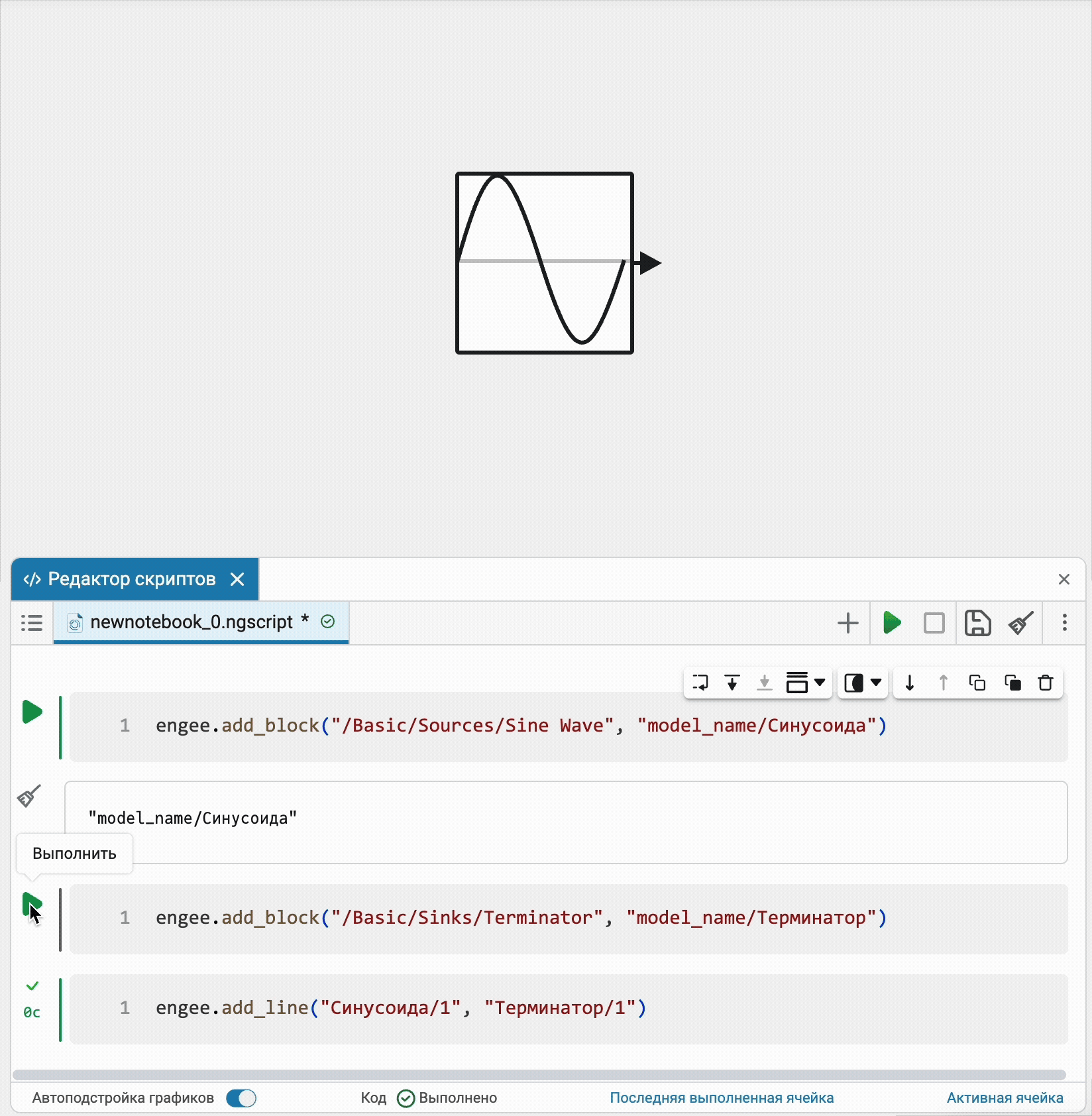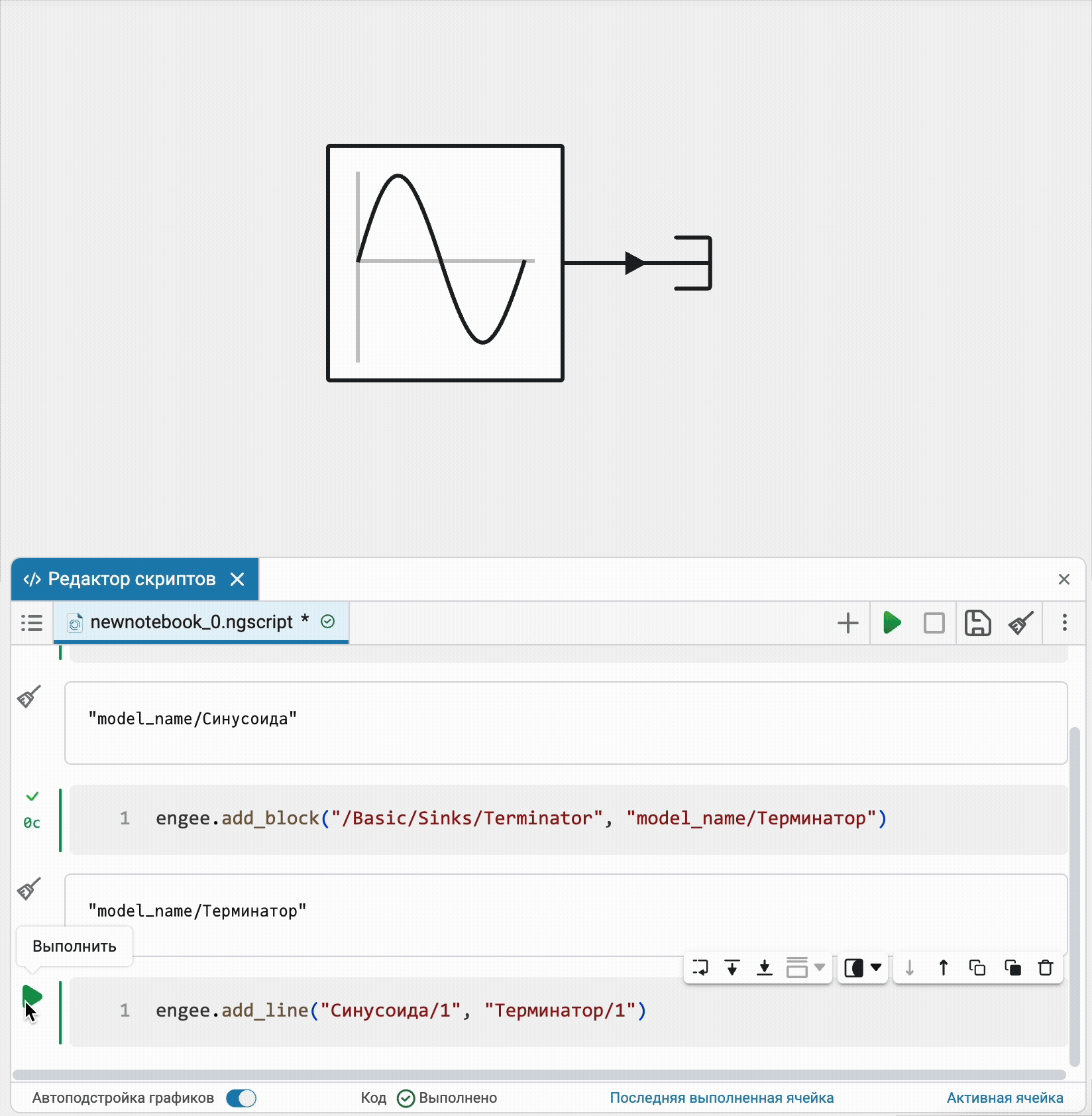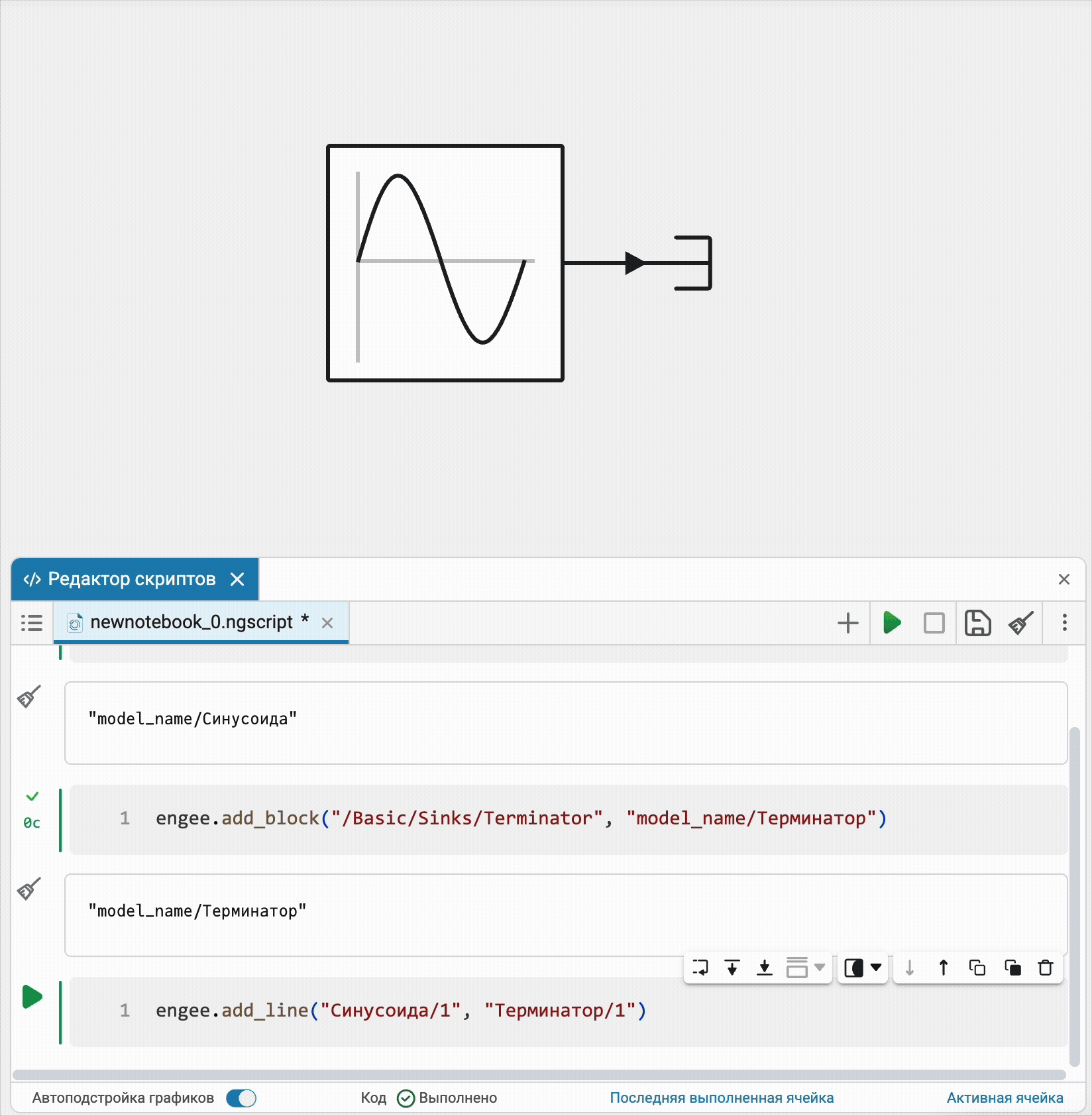
Visualization of software control commands on an open model
Now all software control commands for actions with the model open in the editor will immediately be reflected in the interface on the canvas. Additional synchronization settings are no longer required.
 Fix the block settings card in the interface
Fix the block settings card in the interface
Now you can display the block settings card in a separate window and lock it in the interface. This is done in the context menu by pressing the PCM. It will be open at any nesting level of the model, and you will be able to adjust the block parameters at the right time.
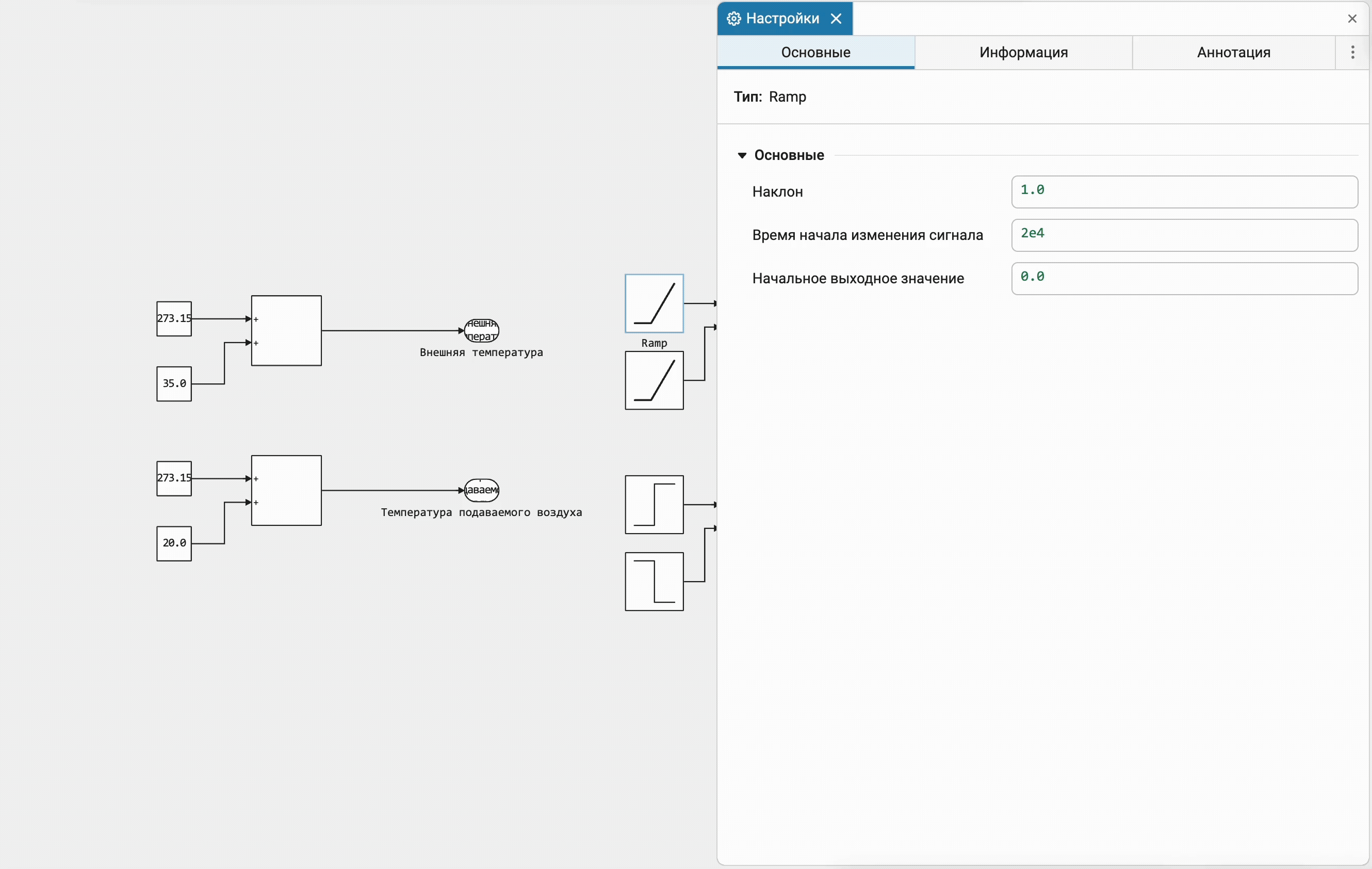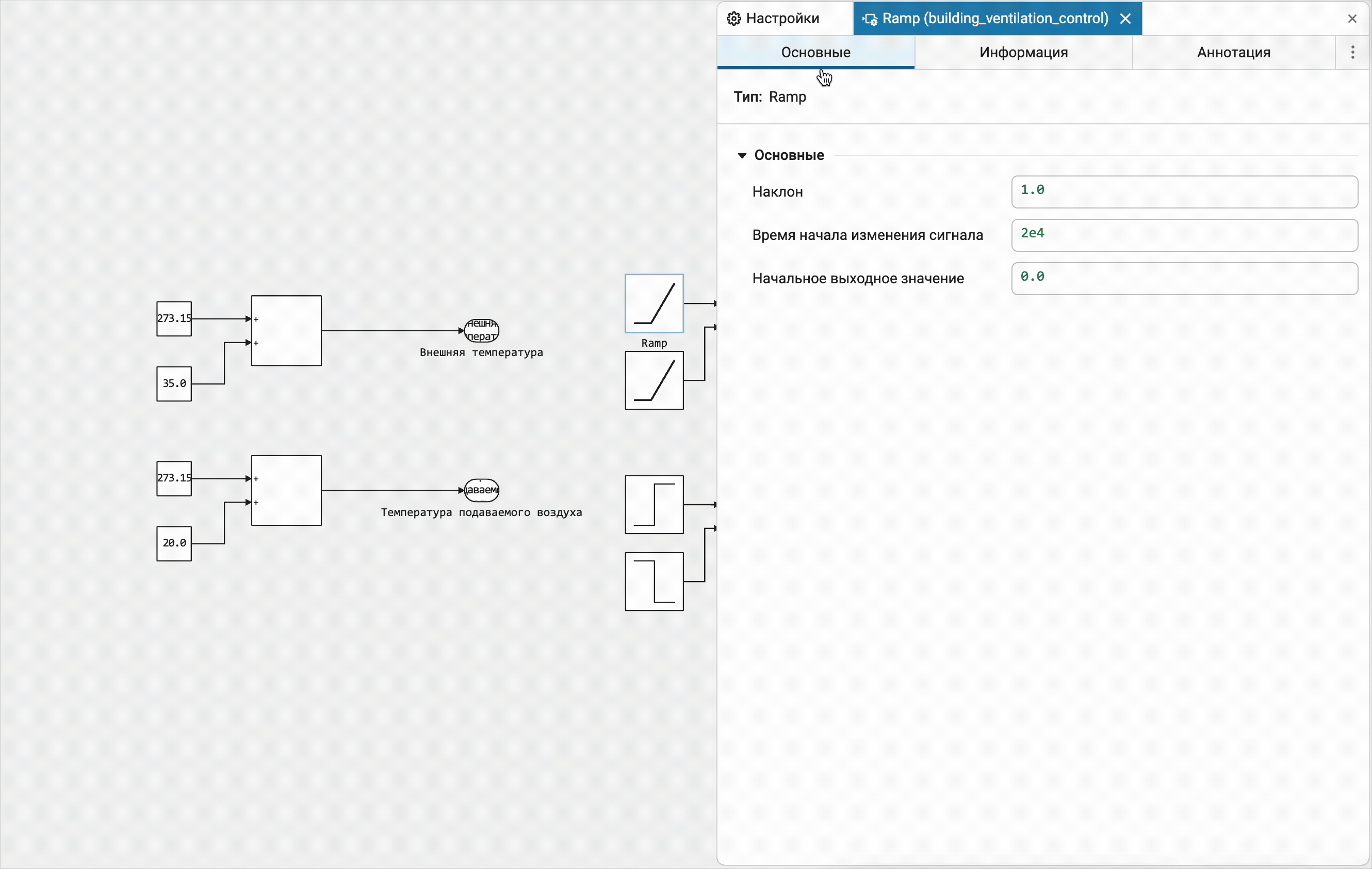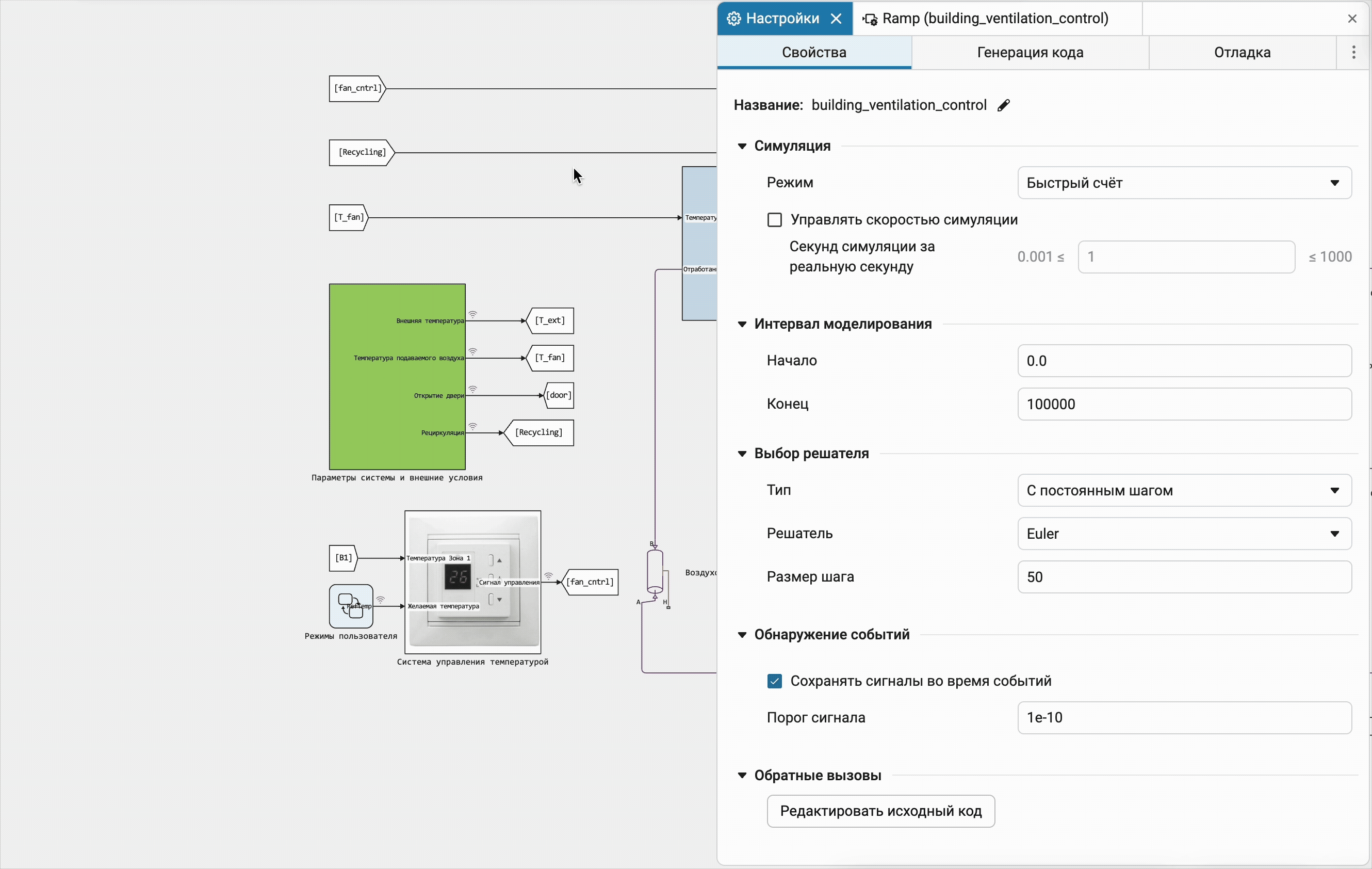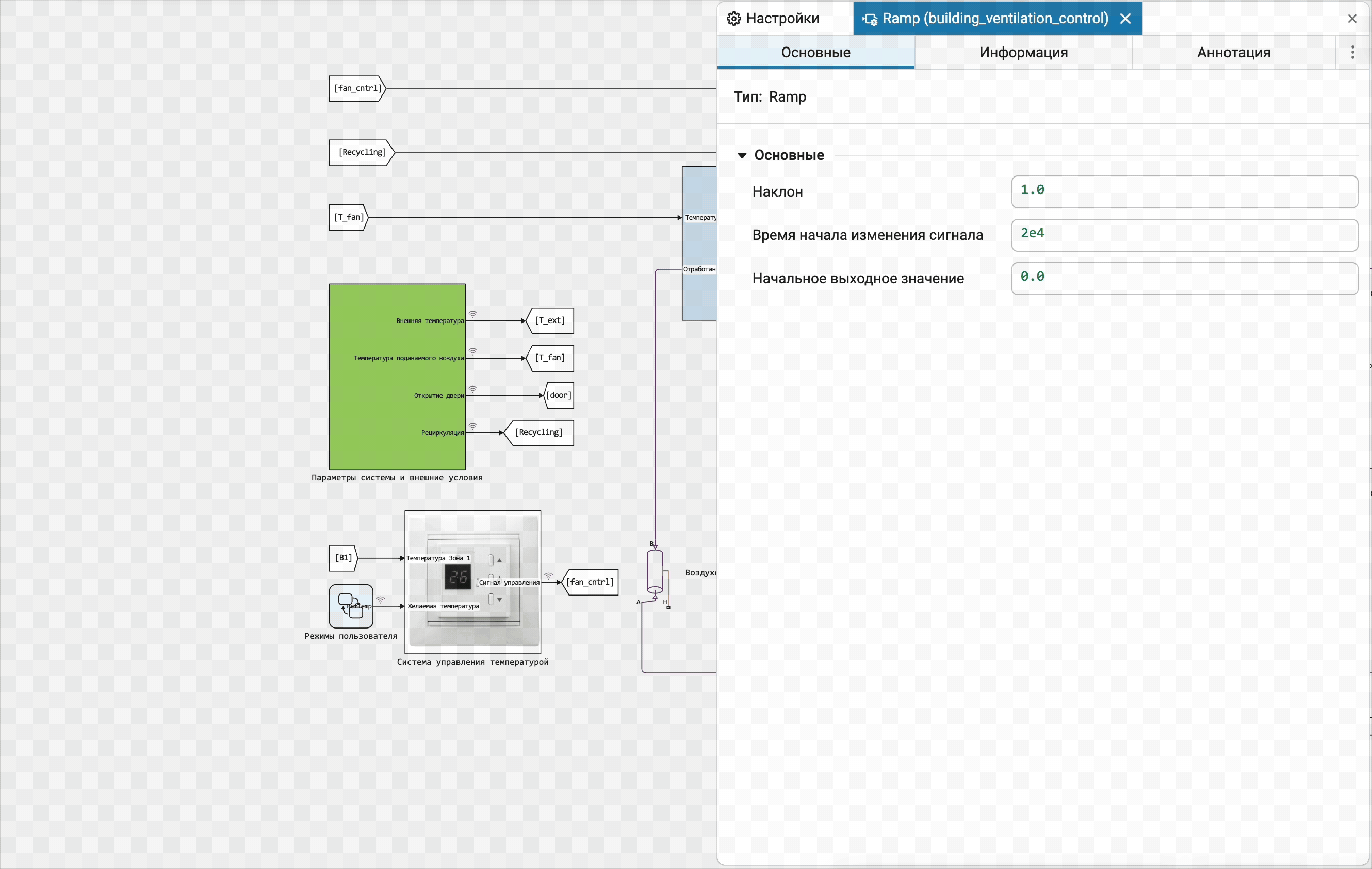
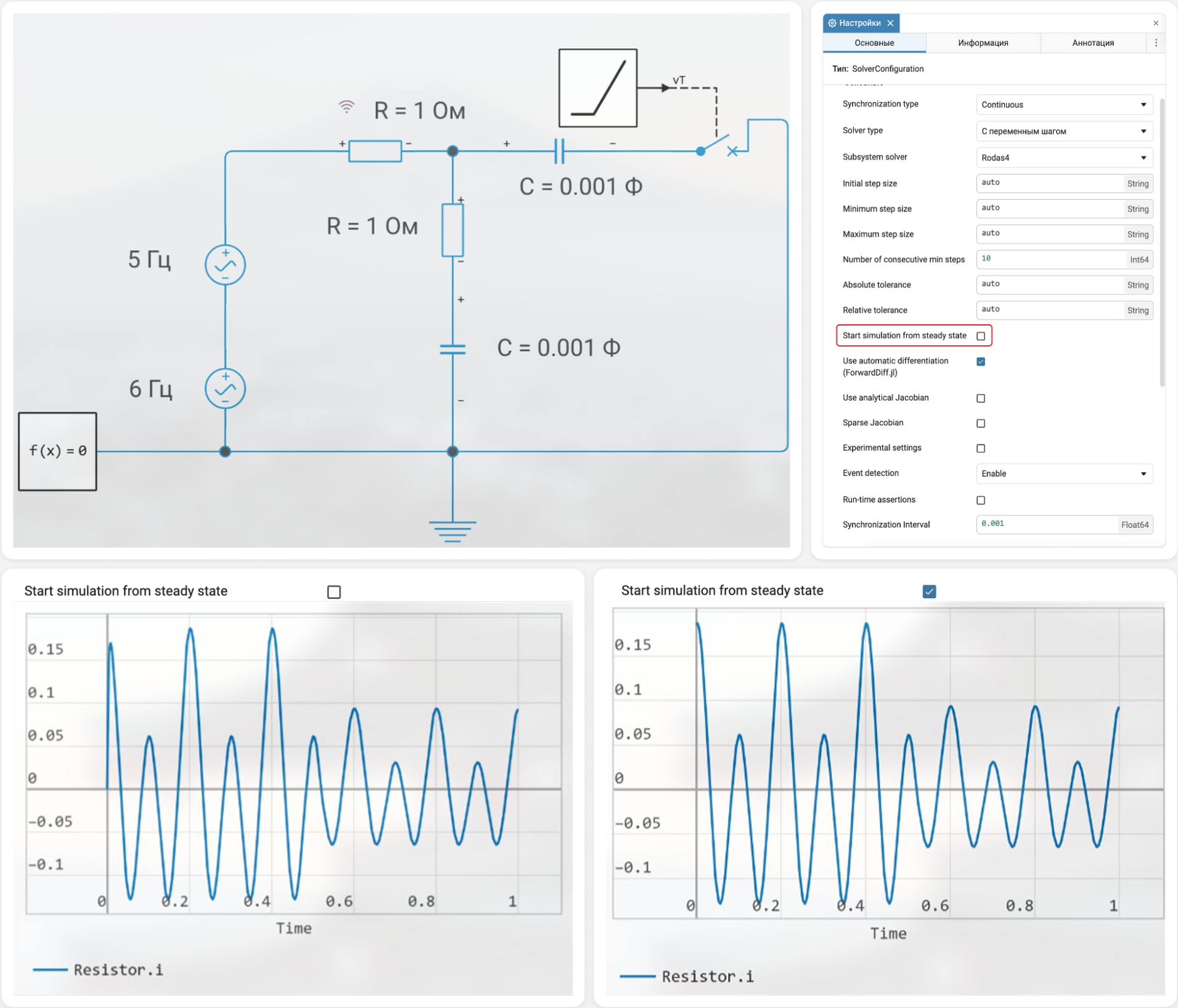
 Calculation of steady-state sinusoidal mode for linear physical networks
Calculation of steady-state sinusoidal mode for linear physical networks
Until now, only classical steady-state modes could be calculated in Engee, in which all derivatives of the state variables of the physical part of the model are zero. Now we support a special algorithm for linear physical networks that analyzes the harmonic components of a solution in a special way, which allows us to find a steady—state sinusoidal mode - that is, one in which the components of the solution either remain constant or are harmonic oscillations with constant amplitude and frequency.
Separately, we note that physical networks are supported with sources of harmonic oscillations at different frequencies simultaneously represented in the model. The most obvious application for the new functionality is electrical engineering and electric power engineering, but nothing prevents it from being used with mechanical, thermal, and various heterogeneous physical networks as long as they remain linear.
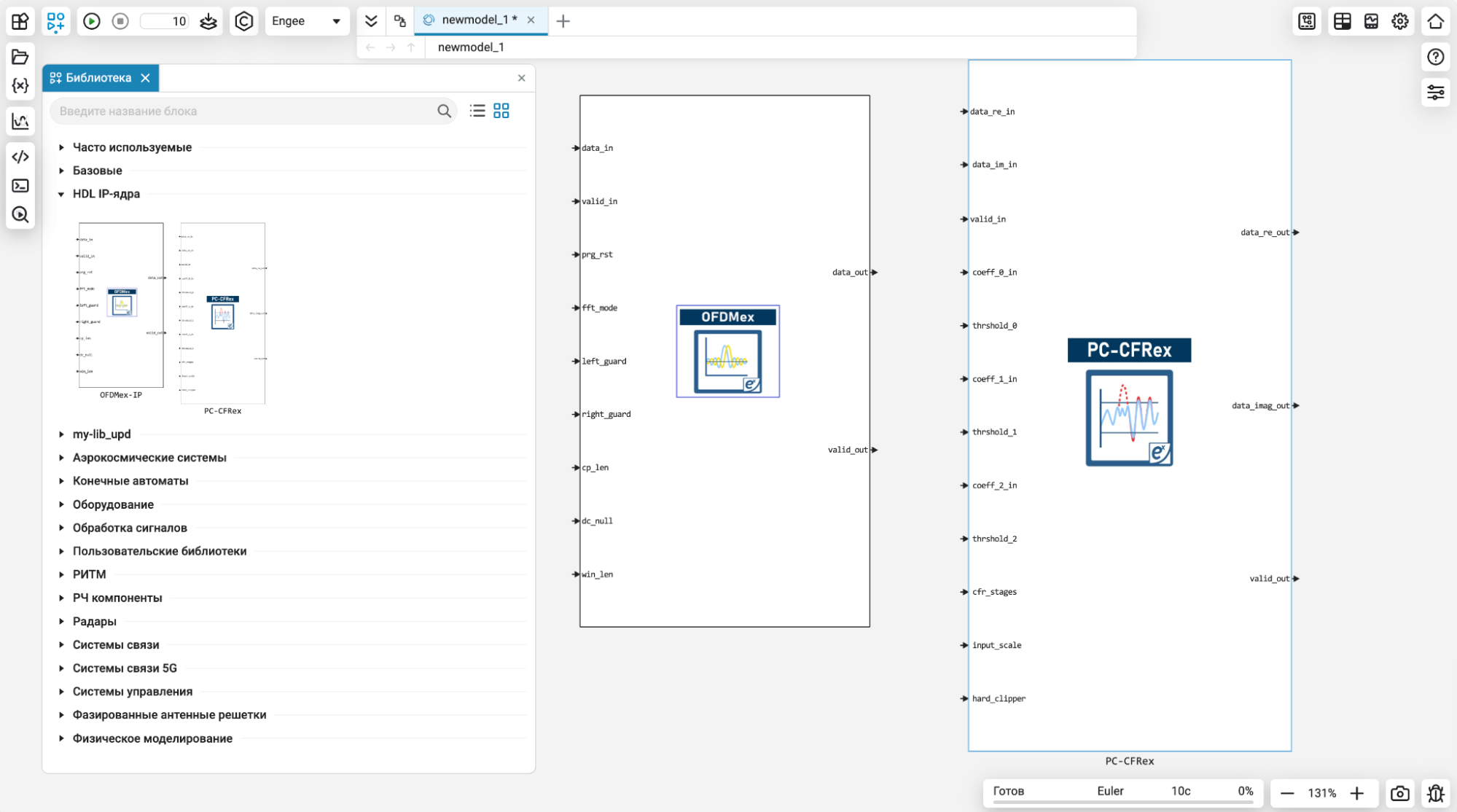
 Integration of Exponent’s IP cores into Engee
Integration of Exponent’s IP cores into Engee
CITM Exponenta works in the wireless technology industry and develops high-tech IP cores (blocks) for wireless systems providing reliable and efficient data transmission in various conditions.
To debug the IP cores in your Engee systems and algorithms, we integrate them as blocks for the Engee simulation environment. The corresponding category will now be available to you in the block library. The library will be gradually replenished, with the first available cores — OFDMex and PC-CFRex.
 Diagnostic messages when adding custom block libraries
Diagnostic messages when adding custom block libraries
Recall that user library  The Engee blocks can contain any blocks that are convenient for you — from standard libraries or custom blocks implemented using masks. Also recently, these libraries can be nested and multi-level. Sometimes there are various specific errors when adding them. Therefore, so that you do not miss such events, we have implemented and added to diagnostic window
The Engee blocks can contain any blocks that are convenient for you — from standard libraries or custom blocks implemented using masks. Also recently, these libraries can be nested and multi-level. Sometimes there are various specific errors when adding them. Therefore, so that you do not miss such events, we have implemented and added to diagnostic window  relevant information messages.
relevant information messages.
 New blocks and updates
New blocks and updates
Moist Air
Electrical
Fluid Network Interfaces
Isothermal Liquid
Gas
Phased Array System Toolbox
Signal Processing
Heat Exchangers
Aerospace
Mechanical
RF Blockset
HDL IP-cores
-
PC-CFRex
-
OFDMex-IP
Interfaces
rhythm
 Library updates and fixes
Library updates and fixes
Communication systems
#System Objects:
-
phased.ADPCACanceller
Functions:
-
range2tl
-
sonareqtl
-
sonareqsnr
-
sonareqsl
-
tl2range
Signal processing
*System Objects:
-
dsp.RLSFilter
-
dsp.LMSFilter
Functions:
-
peak2peak
-
peak2rms
-
rssq
-
dtw
-
medfilt1
-
dpss
-
diric
-
sinc
-
sawtooth
-
intfilt
-
allpass2wdf
-
gmonopuls
-
gauspuls
-
tukeywin
-
triang
-
taylorwin
-
rectwin
-
parzenwin
-
nuttallwin
-
kaiser
-
hann
-
firls
-
fircls1
-
fir2
-
scaleFilterSections
-
interp
-
pulstran
-
undershoot
-
enbw
-
statelevels
-
slewrate
-
settlingtime
-
pulsewidth
-
pulsesep
-
pulseperiod
-
overshoot
-
midcross
-
falltime
-
dutycycle
-
medfreq
-
meanfreq
-
edr
-
phasez
-
phasez
-
freqz
-
freqz
-
firpm
-
firpm
Maths
Functions:
-
fzero
-
angle
-
sin
-
cos
-
abs
-
interp1
-
conv2
-
coeffs
-
spline
-
var
-
min
-
median
-
mean
-
max
-
std
-
detrend
-
movmedian
-
movmad
-
rms
RF components
Functions:
-
capacitor
-
circuit
-
inductor
-
resistor
-
add
-
setterminals
-
clone
-
setports
 Hardware support, interfaces, and external integrations
Hardware support, interfaces, and external integrations
 Engee External API
Engee External API
The external API in Engee now supports executing long-running commands via the /external/command/eval method. This allows you to start executing a long-running command, get its ID, and periodically poll the execution status.
Additional information about the external API is available in the documentation.: External programming interface for accessing Engee.
 Code generation
Code generation
 Verilog code generation for atomic subsystems
Verilog code generation for atomic subsystems
Atomic subsystems are now supported for Verilog code generation. In the generated code, the atomic subsystem turns into an independent Verilog module in a separate file.:
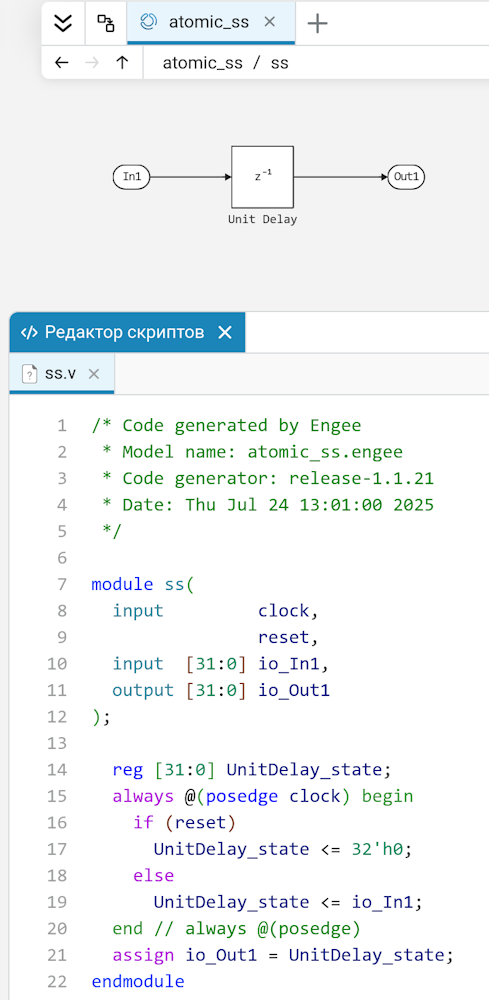
 The ability to simulate the generated Verilog code via Icarus
The ability to simulate the generated Verilog code via Icarus
The easiest way to verify the generated Verilog code is through automatic block generation. C Function as described in documentation. For advanced users, the Engee HDL simulator Icarus, which uses a different verification mechanism, is now available on the command line. Look for demonstrations of working with Icarus/iverilog in the community.
 Running models on rhythm
Running models on rhythm
 Synchronization of the support package version for RHYTHM and the Engee version
Synchronization of the support package version for RHYTHM and the Engee version
The support package for RHYTHM must be synchronized with the version of Engee being used. Now, in case of a version mismatch (for example, the support package is installed via engee.com , and the RHYTHM is used in a closed loop Engee other version) the model will not be able to run on the rhythm. Contact technical support to receive a support package for RHYTHM for offline installation.
 Documentation
Documentation

.svg)