Parameterization of a two-winding power transformer
Description of the model
This example shows how to parameterize two-winding трансформатор according to the passport data and the verification of the calculation of the parameters was carried out. The model's appearance:
Calculation of transformer parameters
As an example for calculation, let's take the turbofan engine-80000/110/10. Reference parameters [1]:
- Rated power - 80 MVA;
- Voltage VN - 115 kV;
- Voltage NN - 10.5 kV;
- Short-circuit voltage - 10.5 %;
- Short circuit loss (short circuit) - 310 kW;
- No-load loss - 70 kW;
- No-load current (XX) - 0.6%.
Rated power, VA:
Sn = 80e6;
Winding voltage VN, V:
Uvn = 115e3;
Winding voltage NN, V:
Unn = 10.5e3;
Short circuit voltage, %:
Uk = 10.5;
Short circuit losses, W:
Pkz = 310e3;
Losses XX, W:
Ph = 70e3;
Current XX, %:
Ih = 0.6;
Calculation of winding parameters in named units
Active resistance of the windings:
import Printf.@printf
Rvn = Pkz * Uvn^2 / (2 * Sn^2)
Rnn = Pkz * Unn^2 / (2 * Sn^2)
@printf "Active resistance of the high-voltage winding: %.3f ohms" Rvn
@printf "Active winding resistance NN: %.5f ohms" Rnn
Total resistance Z:
Zvn = Uk / 100 * Uvn^2 / (2 * Sn)
Znn = Uk / 100 * Unn^2 / (2 * Sn)
@printf "Total resistance of the high-voltage winding: %.3f ohms" Zvn
@printf "Total winding resistance of NN: %.5f ohms" Znn
Inductive resistance X:
Xvn = sqrt(Zvn^2 - Rvn^2)
Xnn = sqrt(Znn^2 - Rnn^2)
@printf "Inductive resistance of the high-voltage winding: %.3f ohms" Xvn
@printf "Inductive resistance of the NN winding: %.5f ohms" Xnn
Inductance L:
Lvn = Xvn / (2 * pi * 50)
Lnn = Xnn / (2 * pi * 50)
@printf "Winding inductance HH: %.3f Hh" Lvn
@printf "Winding inductance NN: %.5f Gn" Lnn
Total losses in XX mode:
Sh = Ih / 100 * Sn
@printf "Total losses XX: %d VA" Sh
Magnetizing power of the Qh transformer:
Qh = sqrt(Sh^2 - Ph^2)
@printf "Magnetizing power of the transformer: %d var" Qh
Active resistance of the magnetization circuit Rm:
Rm = Uvn^2 / Ph
@printf "Active resistance of the magnetization circuit: %d ohms" Rm
Inductive resistance of the magnetization circuit Xm:
Xm = Uvn^2 / Qh
@printf "Inductive resistance of the magnetization circuit: %d ohms" Xm
Inductance of the magnetization circuit:
Lm = Xm / (2 * pi * 50)
@printf "Magnetization circuit inductance: %.3f Gn" Lm
Calculation of winding parameters in relative units
Active resistance R:
R_pu = Pkz / (2 * Sn)
@printf "Active resistance of the high-voltage and low-voltage windings: %.5f O.E." R_pu
Total resistance Z:
Z_pu = Uk / (2 * 100)
@printf "The total resistance of the high-voltage and low-voltage windings: %.5f O.E." Z_pu
Inductance L:
L_pu = sqrt(Z_pu^2 - R_pu^2)
@printf "Inductance of the high-voltage and low-voltage windings: %.5f O.E." L_pu
Total losses in XX mode:
Sh_pu = Ih / 100
@printf "Total losses in XX mode: %.3f O.E." Sh_pu
Magnetizing power of the transformer:
Qh_pu = sqrt(Sh_pu^2 - (Ph / Sn)^2)
@printf "Magnetizing power of transformer: %.3f O.E." Qh_pu
Active resistance of the magnetization circuit:
Rm_pu = Sn / Ph
@printf "Active resistance of the magnetization circuit: %.3f O.E." Rm_pu
Inductance of the magnetization circuit:
Lm_pu = 1 / Qh_pu
@printf "Magnetization circuit inductance: %.3f O.E." Lm_pu
Calculation results
Let's put the data in a table:
using Pkg
"PrettyTables" in [p.name for p in values(Pkg.dependencies())] ? using PrettyTables : Pkg.add("PrettyTables")
colomn1 = ["R", "X", "L", "Rm", "Xm", "Lm"]
colomn2 = [Rvn, Xvn, Lvn, Rm, Xm, Lm]
colomn3 = [Rnn, Xnn, Lnn, Rm, Xm, Lm]
colomn4 = [R_pu, L_pu, Lm_pu, Rm_pu, Lm_pu, Lm_pu]
data = hcat(colomn1, colomn2, colomn3, colomn4);
header = (["Parameter", "Named Primary", "Named Secondary", "Relative"])
pretty_table(
data,
header = header,
alignment = :l,
formatters = ft_printf("%5.5f")
)
Transfer of parameters to the transformer unit
Transfer of calculated parameters to transformer blocks T1 and T2:
model_name = "two_winding_transformer"
model_name in [m.name for m in engee.get_all_models()] ? engee.open(model_name) : engee.load( "$(@__DIR__)/$(model_name).engee");
for i in 1:2
engee.set_param!(model_name * "/T" * string(i),
"R_1_pu" => R_pu,
"R_2_pu" => R_pu,
"X_1_pu" => L_pu,
"X_2_pu" => L_pu,
"R_m_pu" => Rm_pu,
"X_m_pu" => Lm_pu,
"include_leakage_reactance" => true,
"include_magnetizing_resistance" => true,
"include_magnetizing_reactance" => true
);
end
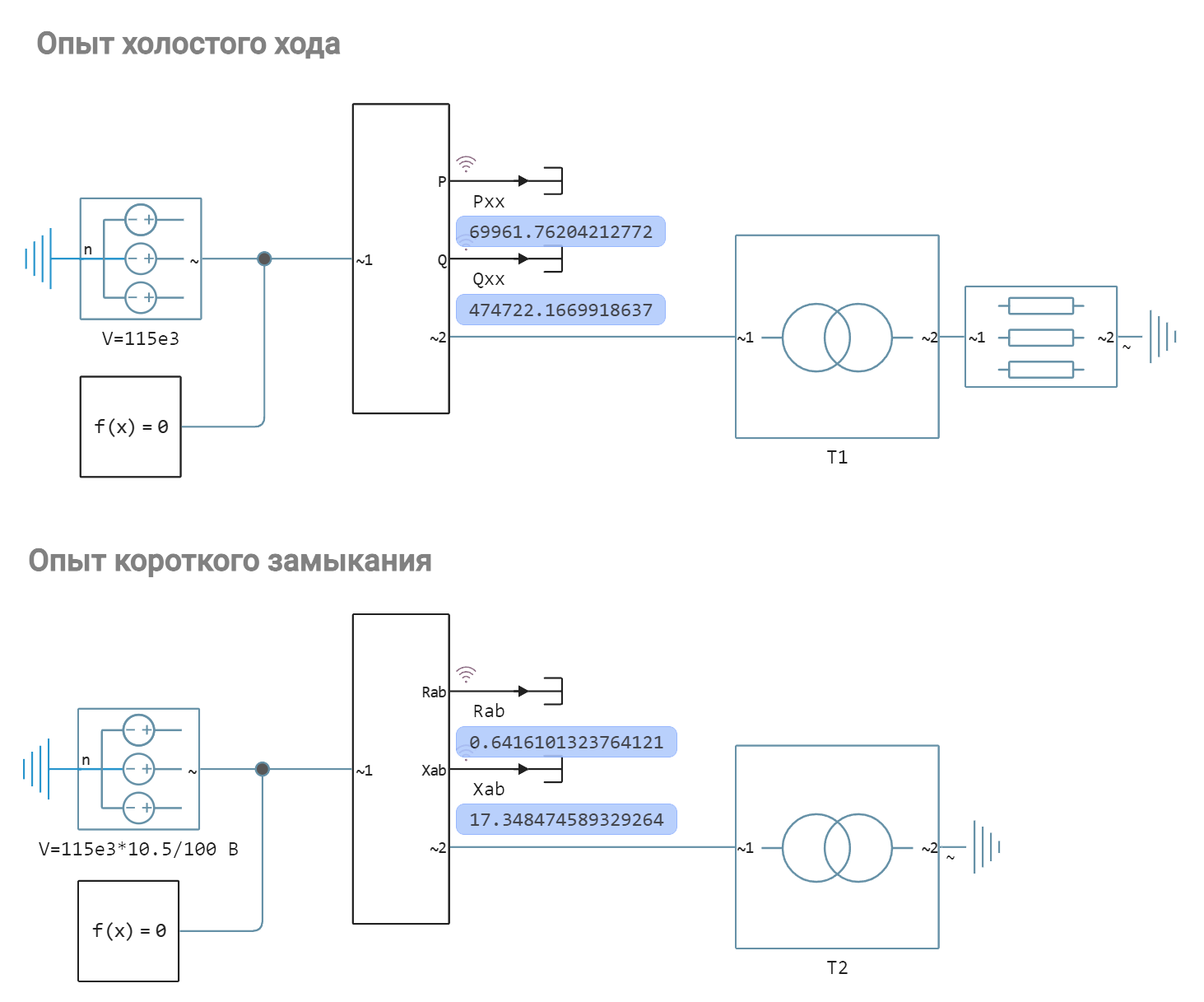
Verification of parameter calculation
results = engee.run(model_name);
Pxx = results["Rhx"].value[end];
Qxx = results["Qxx"].value[end];
Rab = results["Rab"].value[end];
Xab = results["Xab"].value[end];
@printf "Relative error of Rh losses: %.3f%%\n" abs(Pxx - Ph) / Ph * 100
@printf "Relative error of loss Qx: %.3f%%\n" abs(Qxx - Qh) / Qh * 100
@printf "Relative error of the active resistance of the windings: %.3f%%" abs(Rab - 2 * Rvn) / (2 * Rvn) * 100
@printf "Relative error of the inductive resistance of the windings: %.3f%%" abs(Xab - 2 * Xvn) / (2 * Xvn) * 100
Links
- Handbook on the design of electrical networks /
edited by D. L. Faybisovich. – 4th ed., revised and add. – M. : ENAS, 2012. – 376 p. : ill.