Calculation of the steady-state mode of the IEEE 9 Bus model
Description
A demo example has already been presented in the Community "Calculation of electrical network modes" using a separate Engee application. He introduces the classic tabular approach to calculating steady-state regimes (a la RastrWin). With the introduction of the block Load Flow Source in the library and options Start from steady state the calculation of modes in dynamic models of electric power systems is now available in the solver. This demo project shows how to calculate the steady-state for a power system consisting of 9 buses, formulated at the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
Model
Using the source data from Mathworks demo example, we parameterize the blocks of loads, power lines, transformers and generating units.
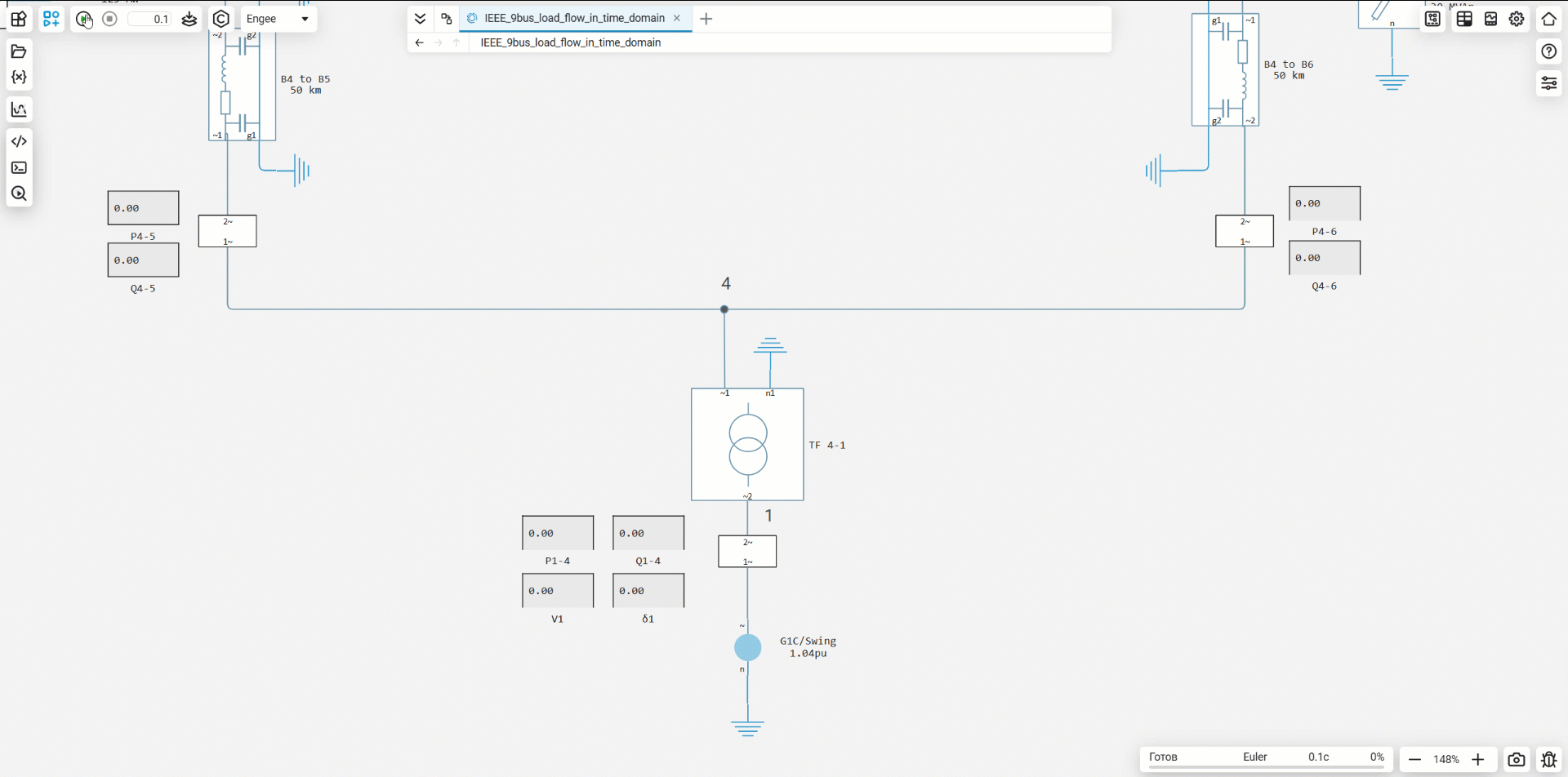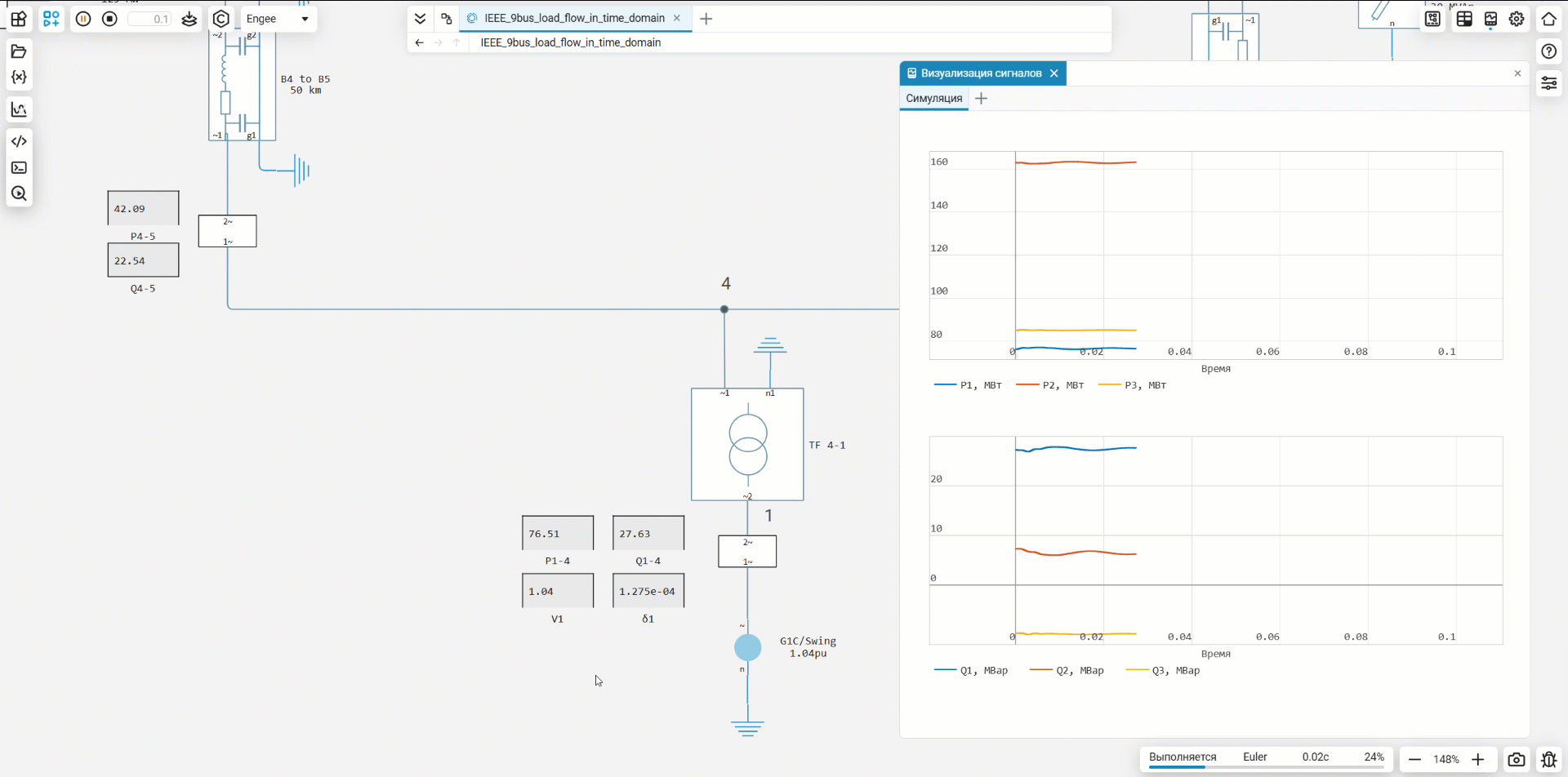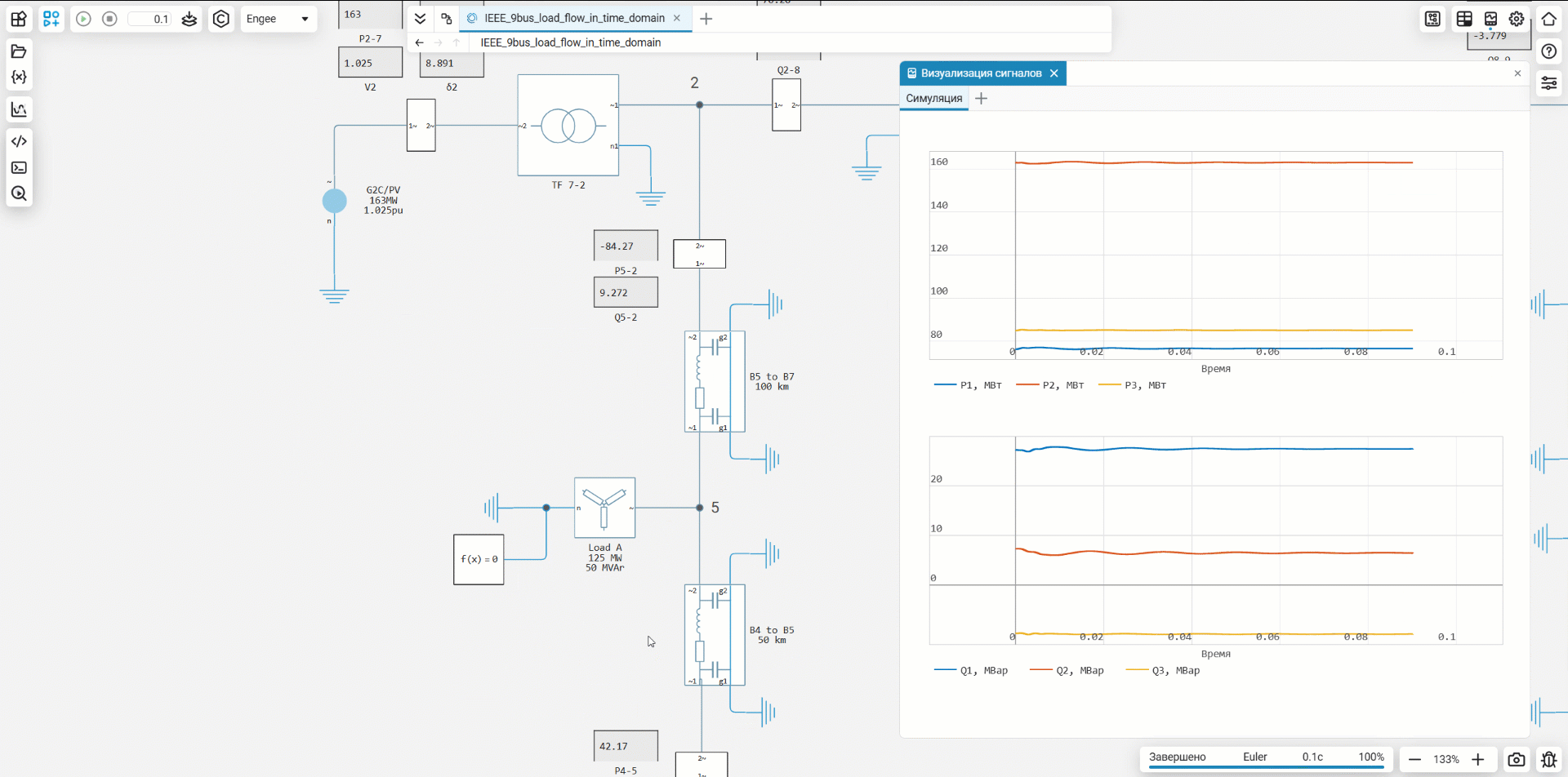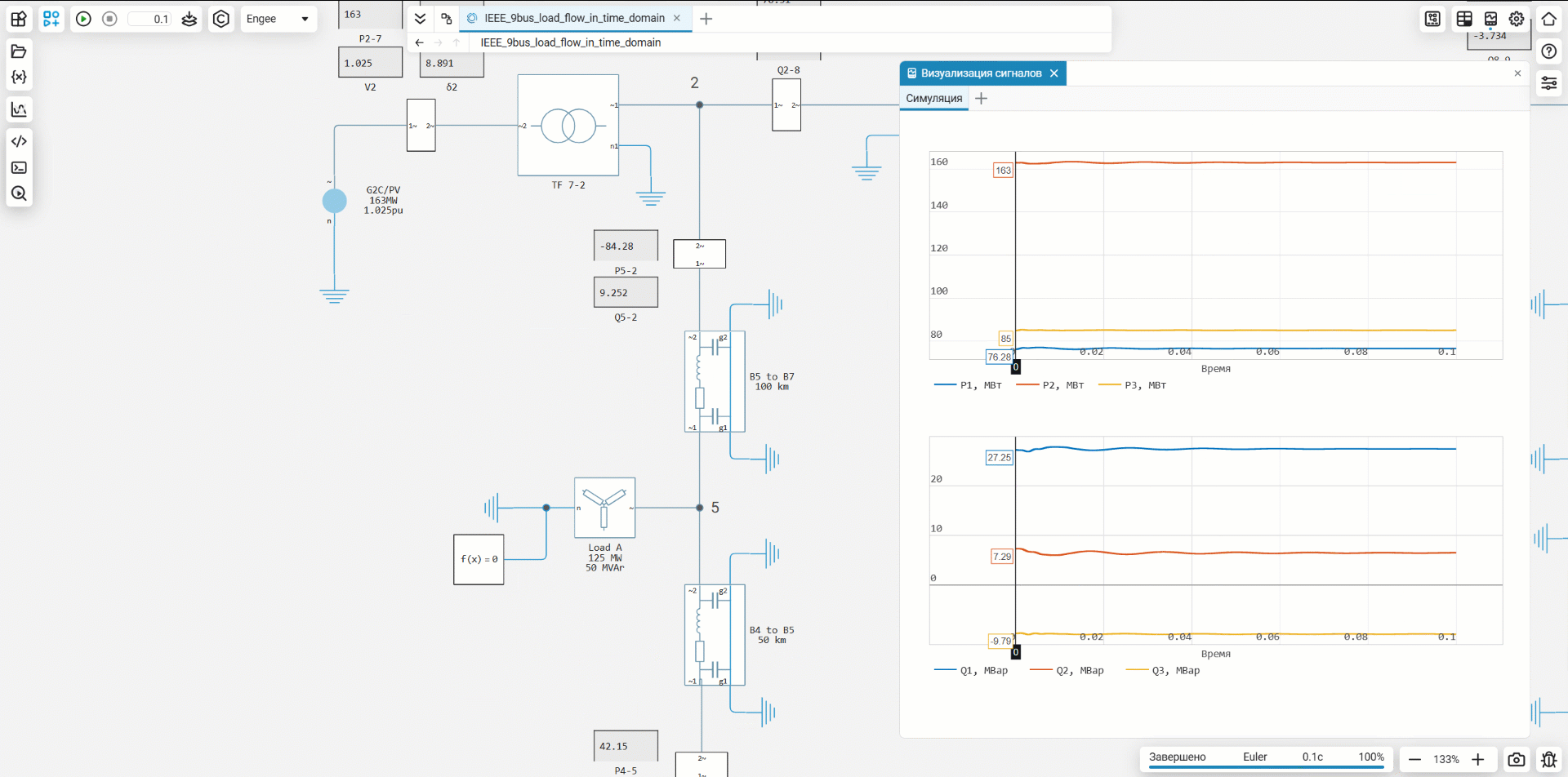
For convenience, displays have been added to the nodes that transmit power, voltage, and angle values from subsystems with meters.
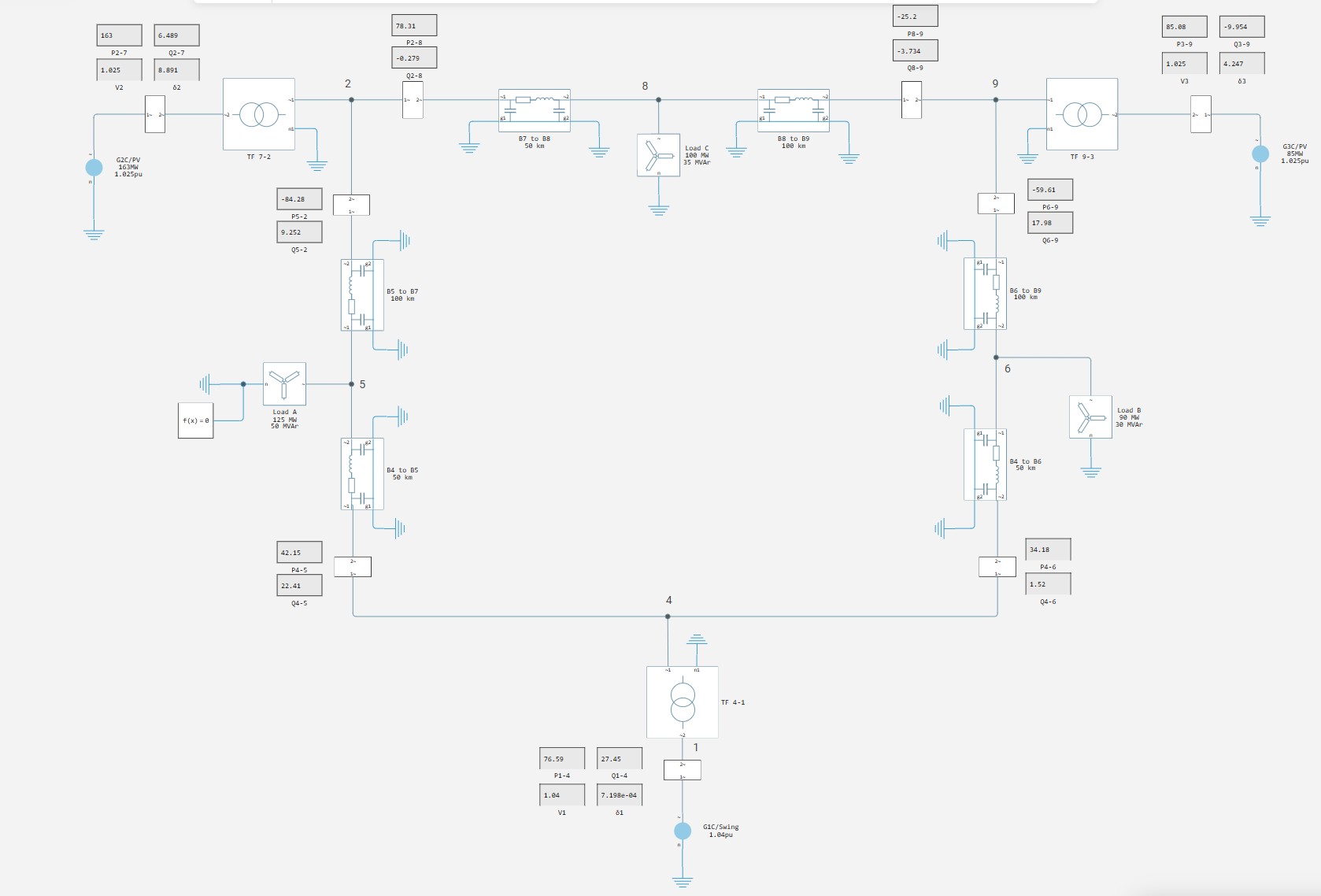
Configuring the solver to find the steady state
To start the model from steady state, enable the [Start simulation from steady] option in the solver. state](https://engee.com/helpcenter/stable/ru/fmod-utility/solver-configuration.html#Parameter:StartFromSteadyState). You can also change the type of solver Subsystem solver. We will focus on the robust implicit Euler ImplicitEuler (Robust).
In addition, it is important to note the setting of the initialization accuracy Tolerance=1e-4, which can be reduced to increase the accuracy of finding the steady state.
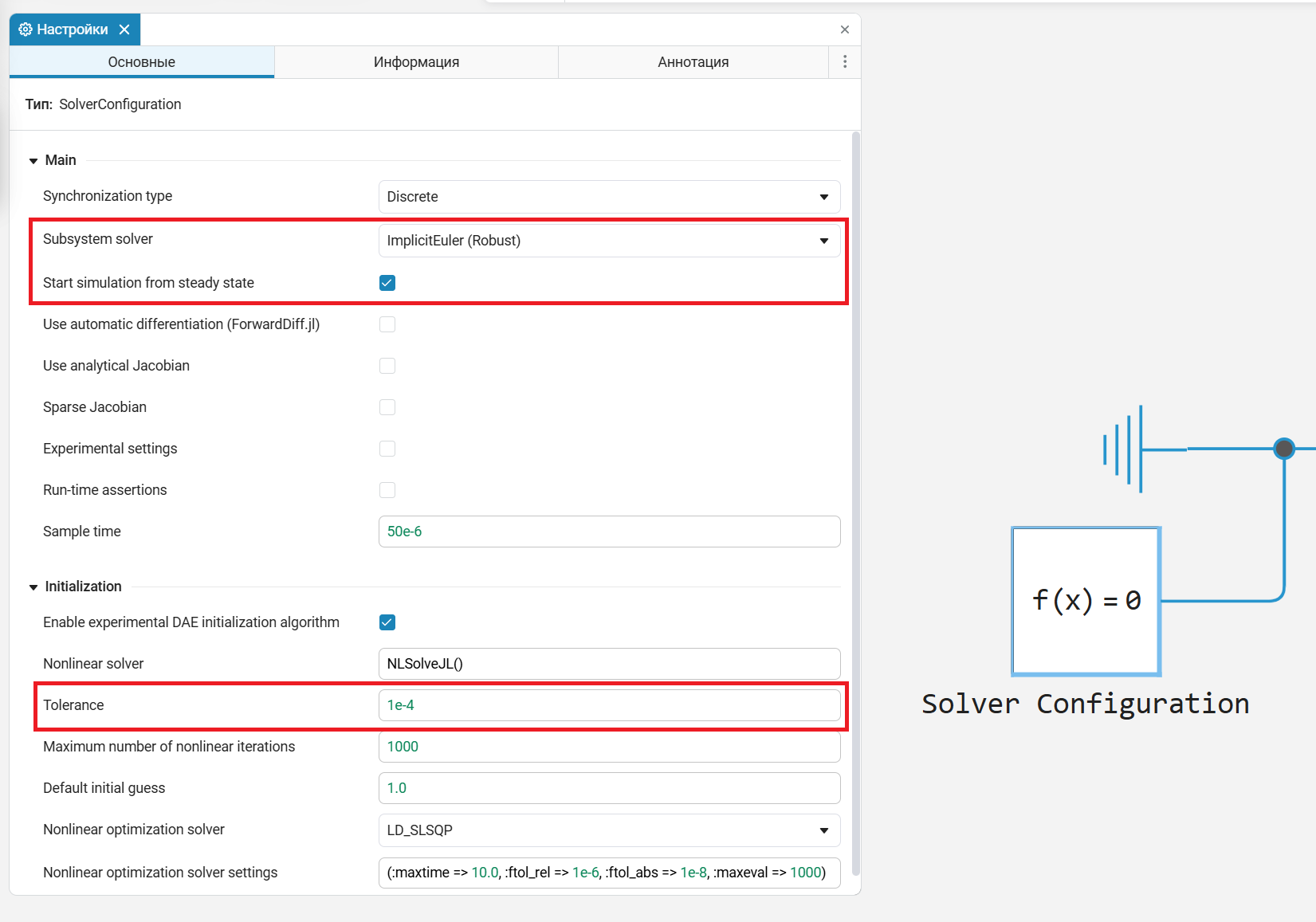
However, if the accuracy value is too low (for example, try 1e-8), the solver will not be able to find the steady state.
Thus, setting up the solver is a search for balance: the accuracy value should be small enough to ensure the necessary engineering accuracy, but not so rigid as to make the solution impossible. It is recommended to start with the default value and change it if necessary, monitoring convergence.
Running the model and visualizing the results
After starting the model, the calculated mode parameters (voltage, power, angles) can be observed on the built-in displays or on graphs. This allows you to instantly evaluate the correctness of the calculation and obtain the initial data for subsequent dynamic modeling.
Comparison with other software
In [the original article in Figure 2.19](https://www.amazon.de/Power-System-Control-Stability-Engineering/dp/0471238627 The following diagram is provided, which serves as a reference test example for software verification in the field of modeling electric power systems.
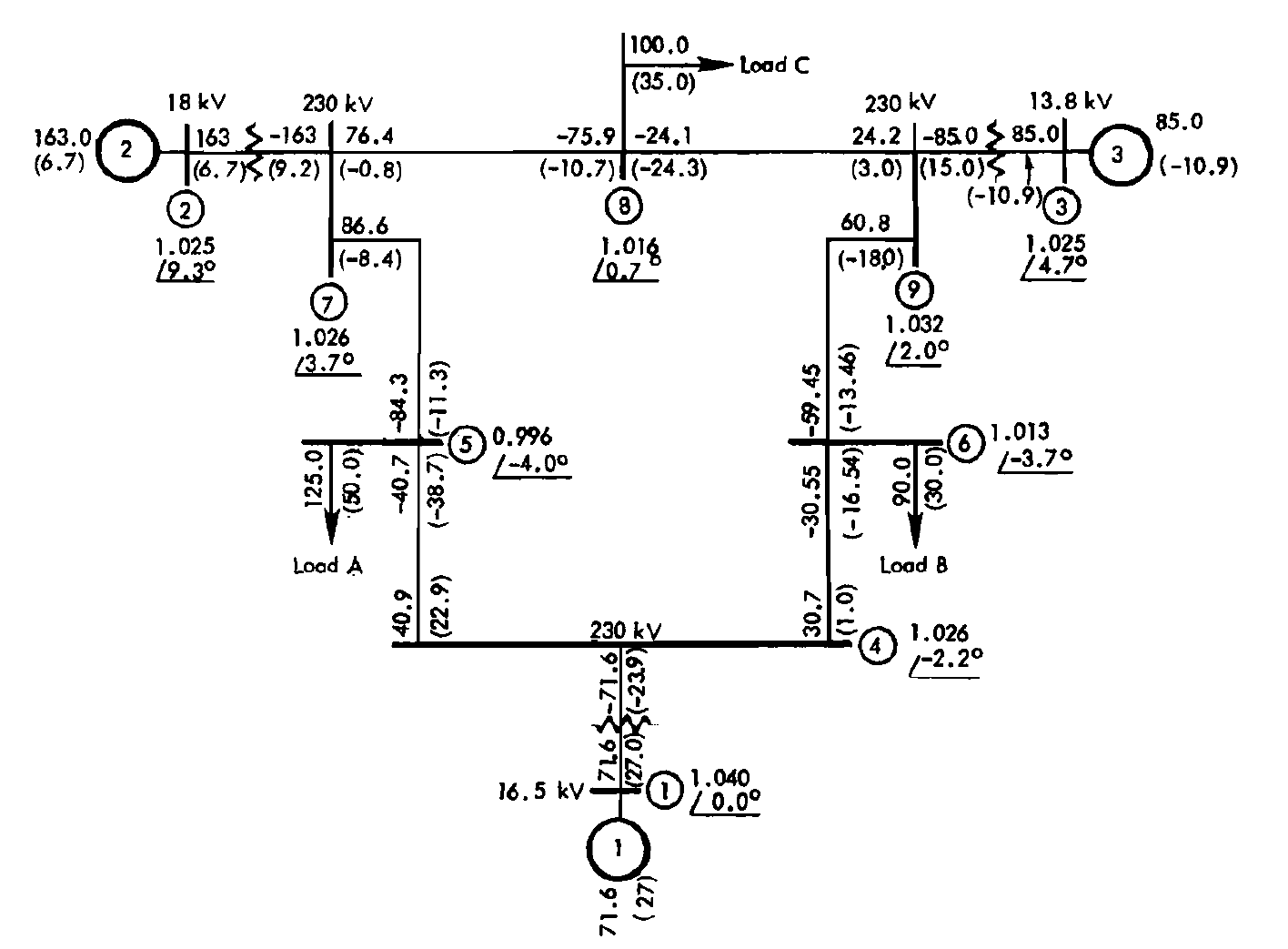
The results of these calculations are periodically compared with various software, for example, well-known commercial packages [PSCAD and PSS/E from Simemens] (https://www.pscad.com/uploads/knowledge_base/ieee_9_bus_technical_note.pdf ).
Below is a summary table with the results of calculating the power on buses 1, 2 and 3, obtained using various software tools. This table clearly demonstrates the degree to which they correspond to the original data of the article.
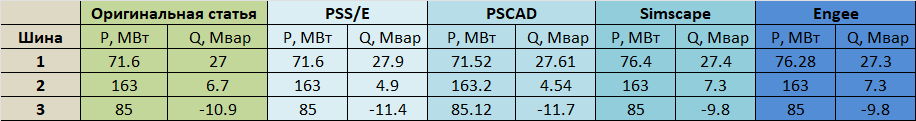
Strictly speaking, we are interested in comparing with Simscape, because the source data was filled using the source data from [Mathworks demo example] (https://www.mathworks.com/help/sps/ug/ieee-9-bus-loadflow.html ). The Simscape simulation results, although they have slight discrepancies with the original, have explanations for "differences due to power transmission line models and configurations of the transformers used." In this particular example, the goal was not to achieve complete convergence with the values from the original article, so we proceed to the conclusions.
Conclusions
The Engee results, verified on Simscape, demonstrate high engineering accuracy. The observed minimal residual discrepancies are expected and do not affect the correctness of the model. At the moment, the calculation of steady-state modes of dynamic models in Engee is performed in the time domain. Despite the computational complexity, thanks to the integration of the Load Flow Source block and solver settings, all the functionality is stable and ready for practical use.