Masks and strings in the Engee Function
In Engee, you can add a simple user interface to a block. This is called block masking. Masks can be used to hide the internal structure of the unit from the user. This is a great technique, and let's add a mask to the Engee Function block from last post.
The EF_pdist2 function that we used has an optional parameter, the calculation mode (metric). During the project, we will give the user the opportunity to control it through a mask.
include("PDIST2.jl");
Let's remember what the module code looks like.:
;cat PDIST2.jl
How do I pass a string from a mask to an Engee Function?
Before masking the Engee Function, it is necessary to consider a functional limitation - the Engee Function cannot work with type parameters. String. But the calculation method is set by a string. Therefore, we need to encode the selected method with a certain number, pass this number as a parameter to the Engee Function, and then decode it. In other words, the mask will need not one parameter, but two. Then you can implement such a scheme:
We will decode the calculation mode using a dictionary, since the Dict data type implements a collection of key-value pairs. In this case, the key can be any base type. Therefore, it is possible to make even such a dictionary.:
mode_dict_t = Dict(1=>"euclidean",2=>"squaredeuclidean",3=>"manhattan",4=>"cosine")
It can be seen that the key here is an integer, and the value is a string. This allows us to do the following:
EF_mode = PDIST2.mode_dict_t[1]
Now let's take a look at the code of the Engee Function block methods.:
include("/user/start/examples/base_simulation/advanced_block_masking/PDIST2.jl")
mutable struct Block <: AbstractCausalComponent
cache::Matrix{Float64};
modeC::Int64
function Block()
c = zeros(Float64,INPUT_SIGNAL_ATTRIBUTES[1].dimensions);
info("Allocated $(Base.summarysize(c)) bytes for pdist2")
info("Selected $(PDIST2.mode_dict_t[mode])")
new(c,mode)
end
end
function (c::Block)(t::Real, in1, in2)
try
c.cache = PDIST2.EF_pdist2(in1,in2;metric=PDIST2.mode_dict_t[c.modeC]);
catch
error("Matrix Dimensions should be equal!")
stop_simulation()
end
return c.cache
end
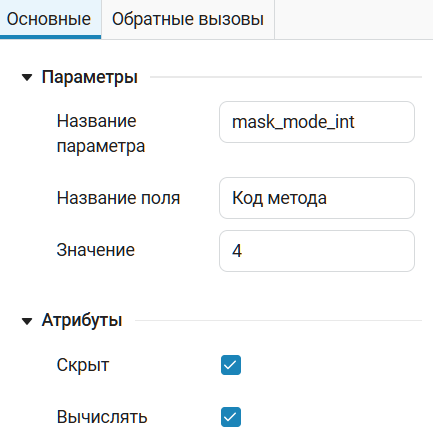
modeC is a parameter that takes the value of a numeric variable from a mask (see ). Thus, we can pass the calculation method to our PDIST2 function as
PDIST2.mode_dict_t[c.modeC]
And we will get the number by calling back the "real" parameter from the drop-down list.:
if mask.parameters.mask_mode.value == "euclidean"
mask.parameters.mask_mode_int.value = 1;
elseif mask.parameters.mask_mode.value == "squaredeuclidean"
mask.parameters.mask_mode_int.value = 2;
elseif mask.parameters.mask_mode.value == "manhattan"
mask.parameters.mask_mode_int.value = 3;
elseif mask.parameters.mask_mode.value == "cosine"
mask.parameters.mask_mode_int.value = 4;
end
So the mask will look like this:
.png)
Note that the mask_mode_int parameter must be computable. And it's hidden because we don't want to let the user break anything.
.png)
Finally, we will open and run the final model in all modes.:
demoroot = @__DIR__
mdl = engee.open(joinpath(demoroot,"EF_DF.engee"))
for k in keys(PDIST2.mode_dict_t)
println("Running the model with the $ mode(PDIST2.mode_dict_t[k])")
engee.set_param!("EF_DF/PDIST2", "mask_mode"=>PDIST2.mode_dict_t[k])
engee.run(mdl;verbose=true);
end
Conclusions
During the project, we learned how to drop string parameters into the Engee Function, and also used dictionaries in a standard, albeit unobvious way.